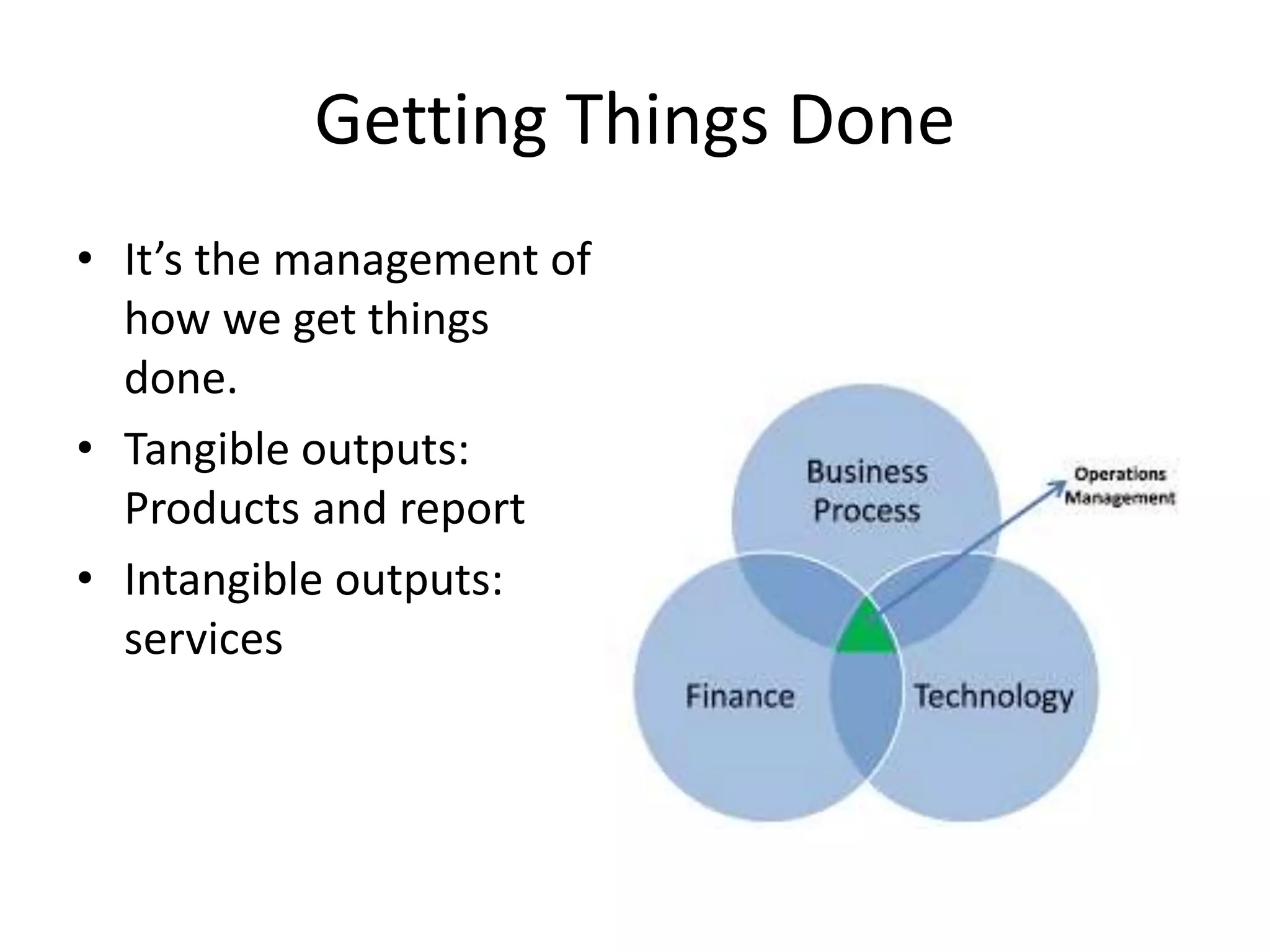
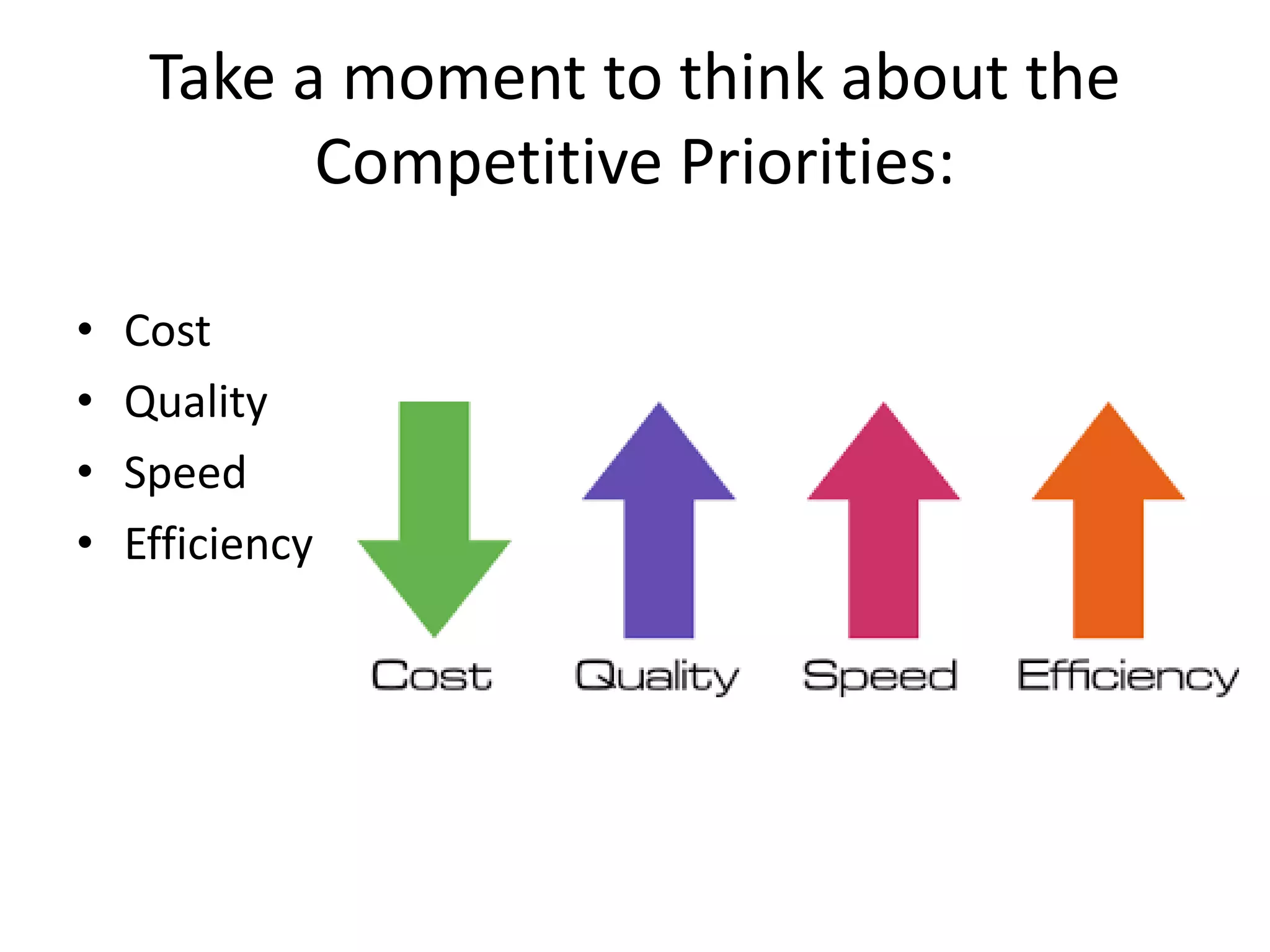
Operations management involves overseeing business processes to produce goods and services effectively and efficiently, focusing on maximizing productivity while ensuring quality. Companies compete on four dimensions: cost, quality, speed, and flexibility, which define their market position and customer expectations. Success requires balancing value and productivity, and understanding operations is essential in a competitive business environment.