The document discusses key concepts in operations management, including:
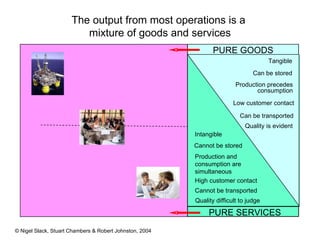
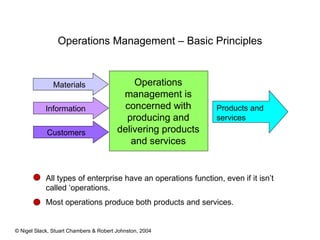
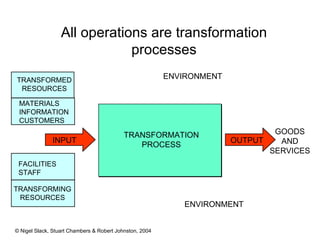
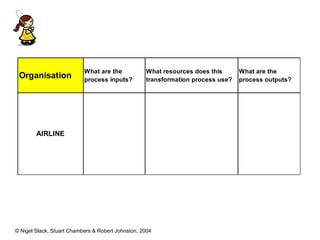
1) Most operations produce both goods and services, and transform inputs like materials, products, services, and information into outputs for customers.
2) Operations management is concerned with efficiently producing and delivering products and services.
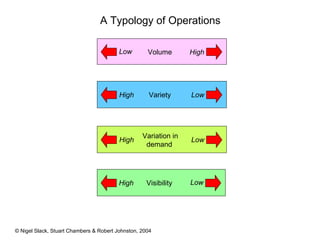
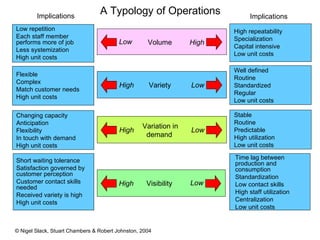
3) There is variation in operations depending on factors like demand, visibility, variety, and volume. This impacts considerations like capacity, flexibility, and costs.
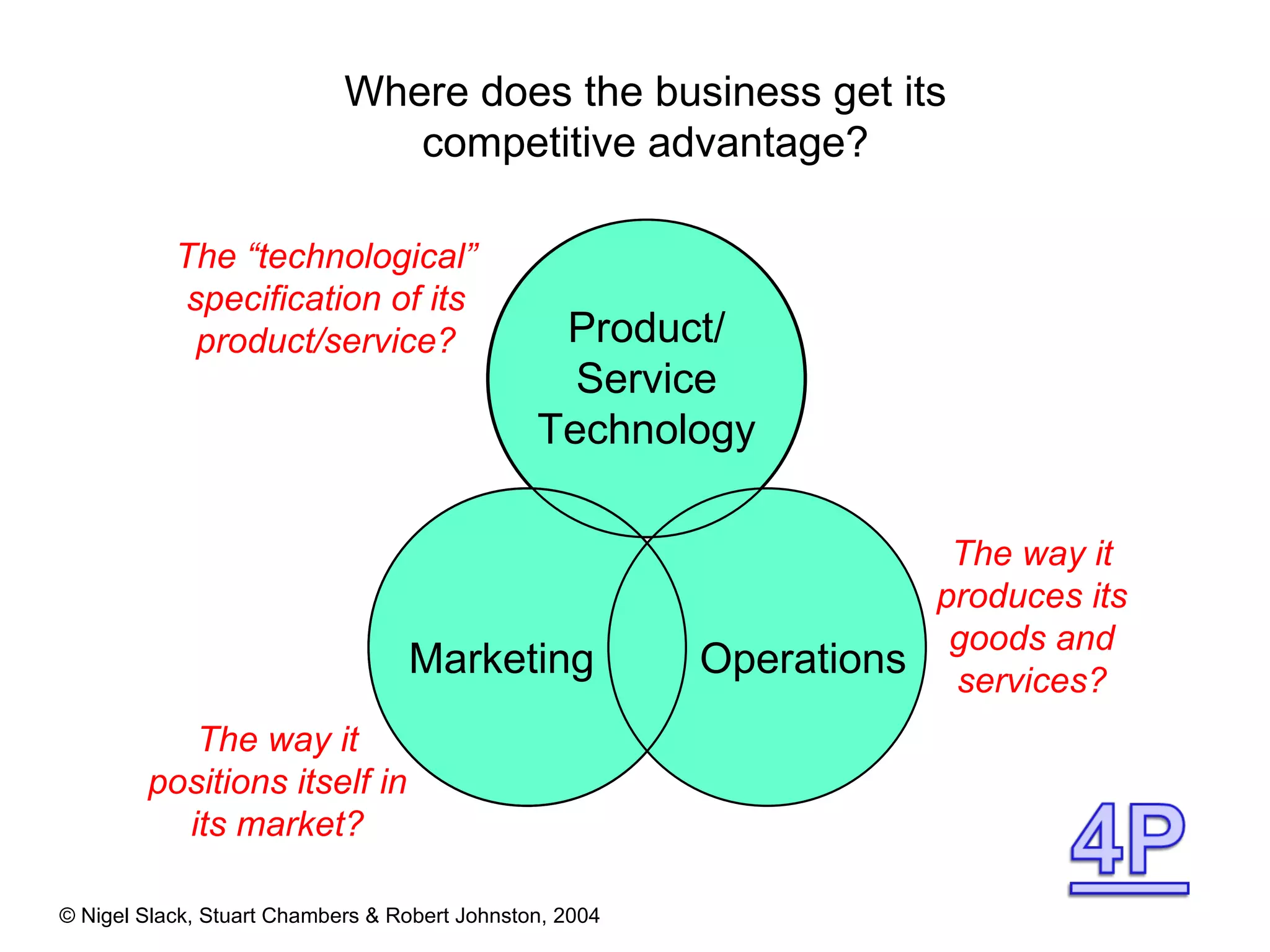
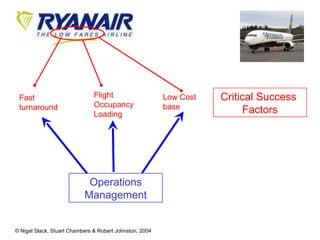
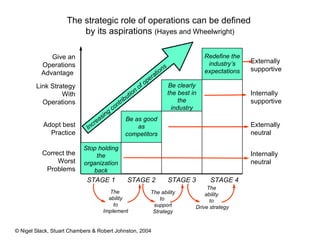
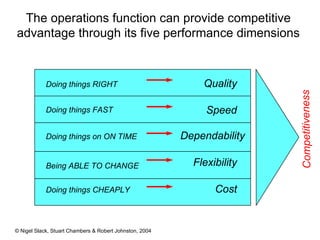
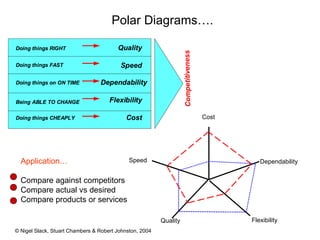
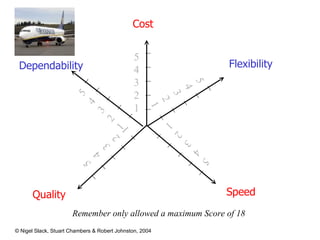
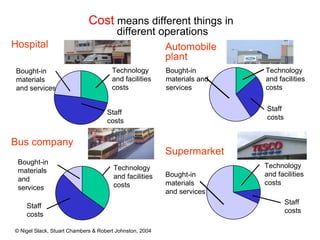
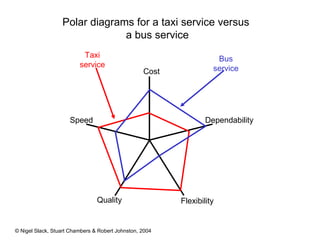
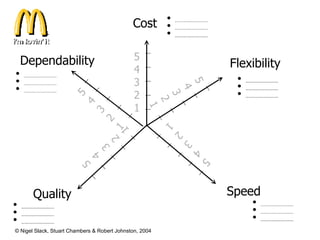
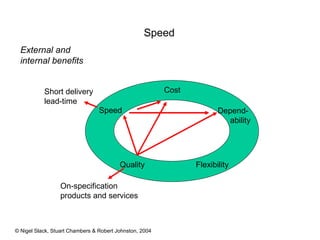
4) Competitive advantage can come from an operation's speed, flexibility, costs, dependability, and quality. Different operations may prioritize these dimensions differently based on their industry.