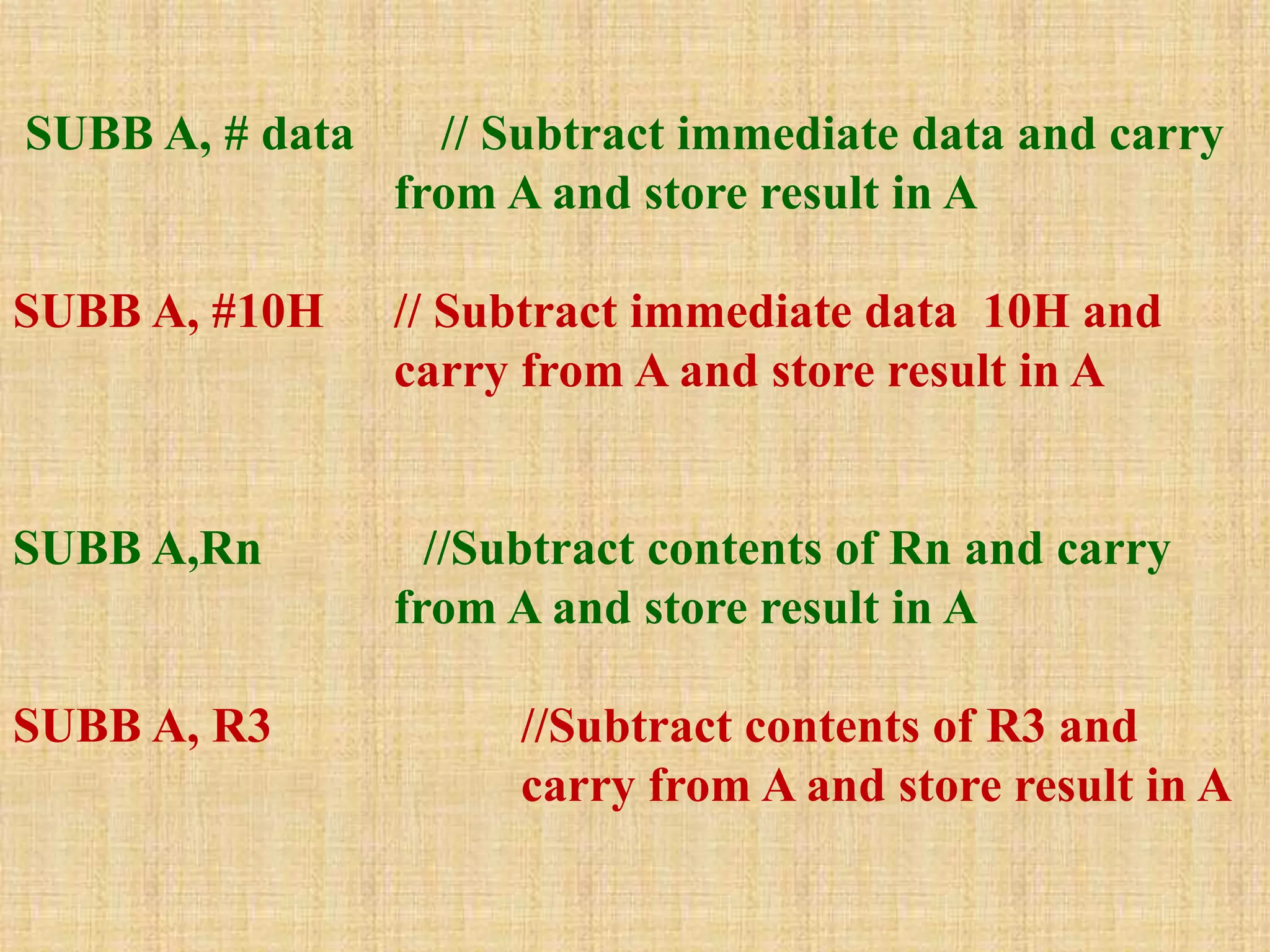
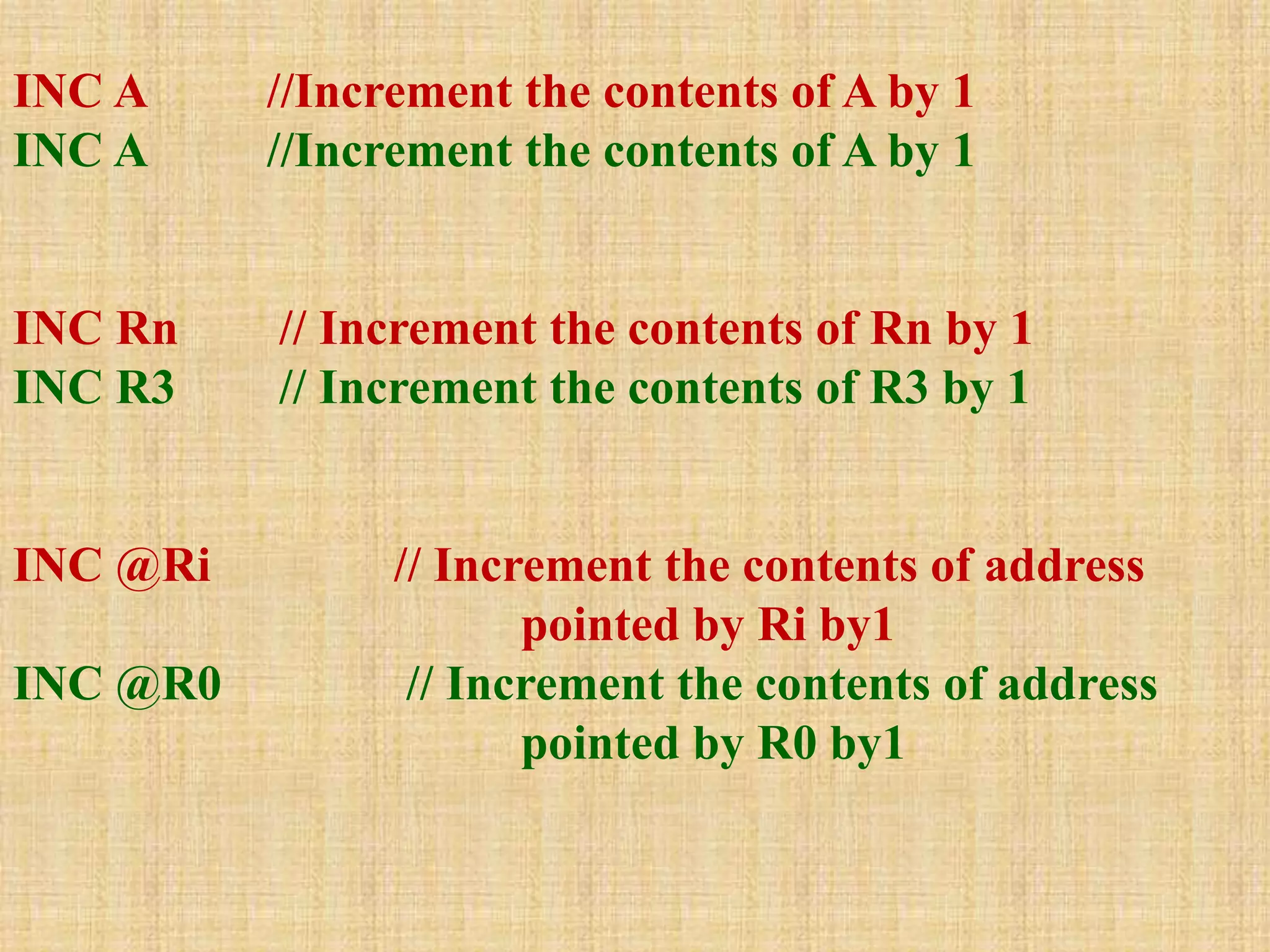
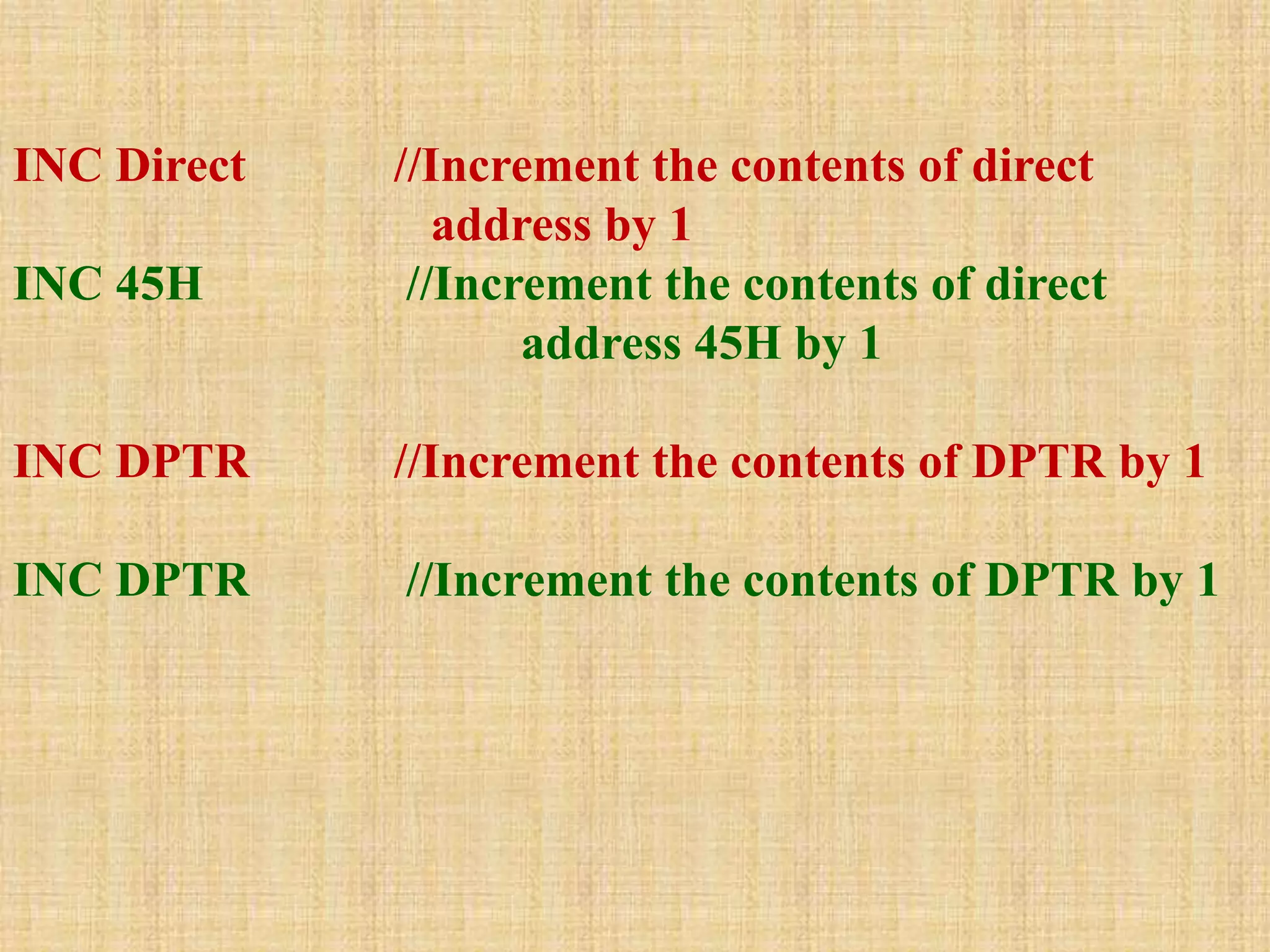
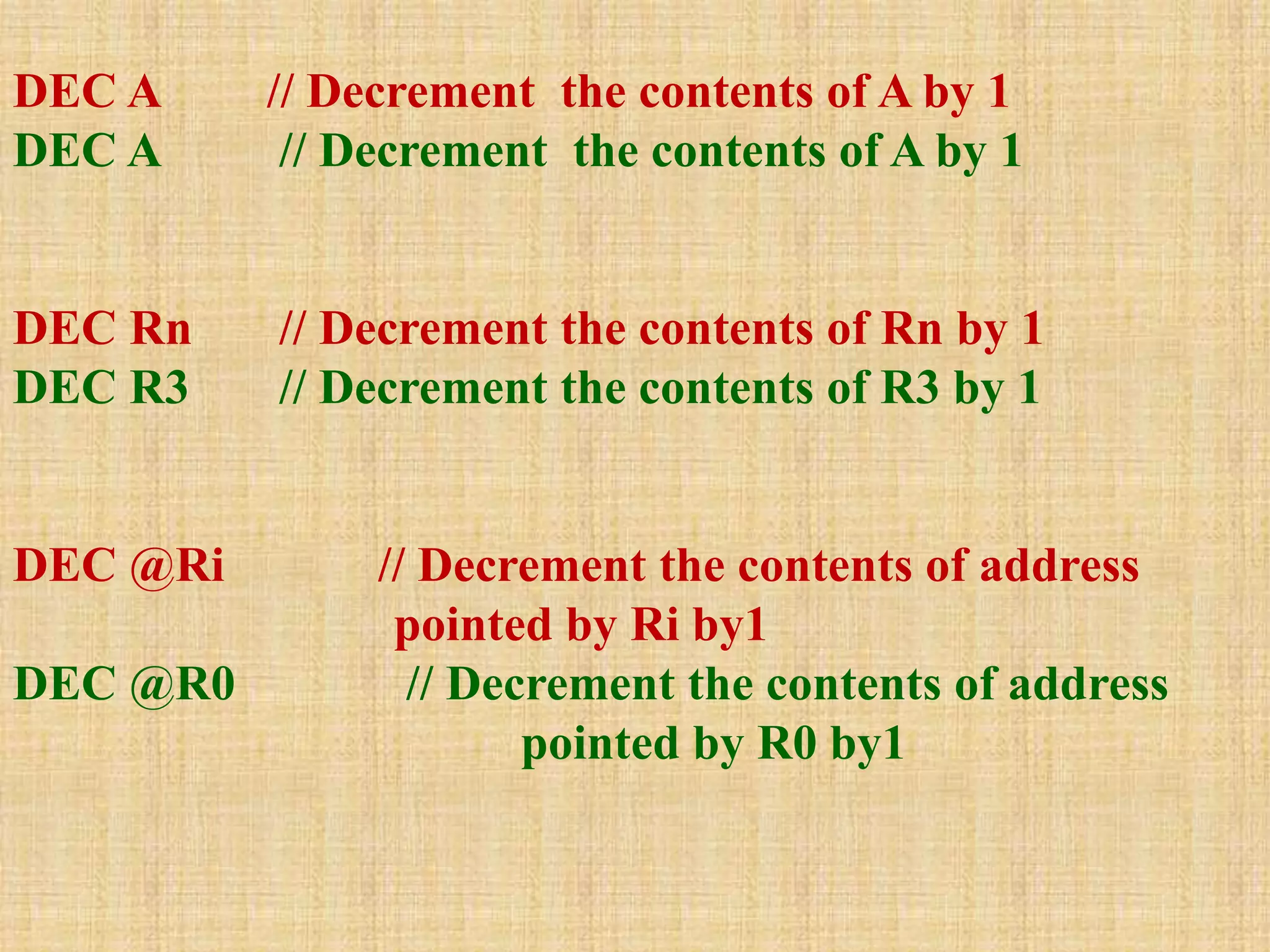
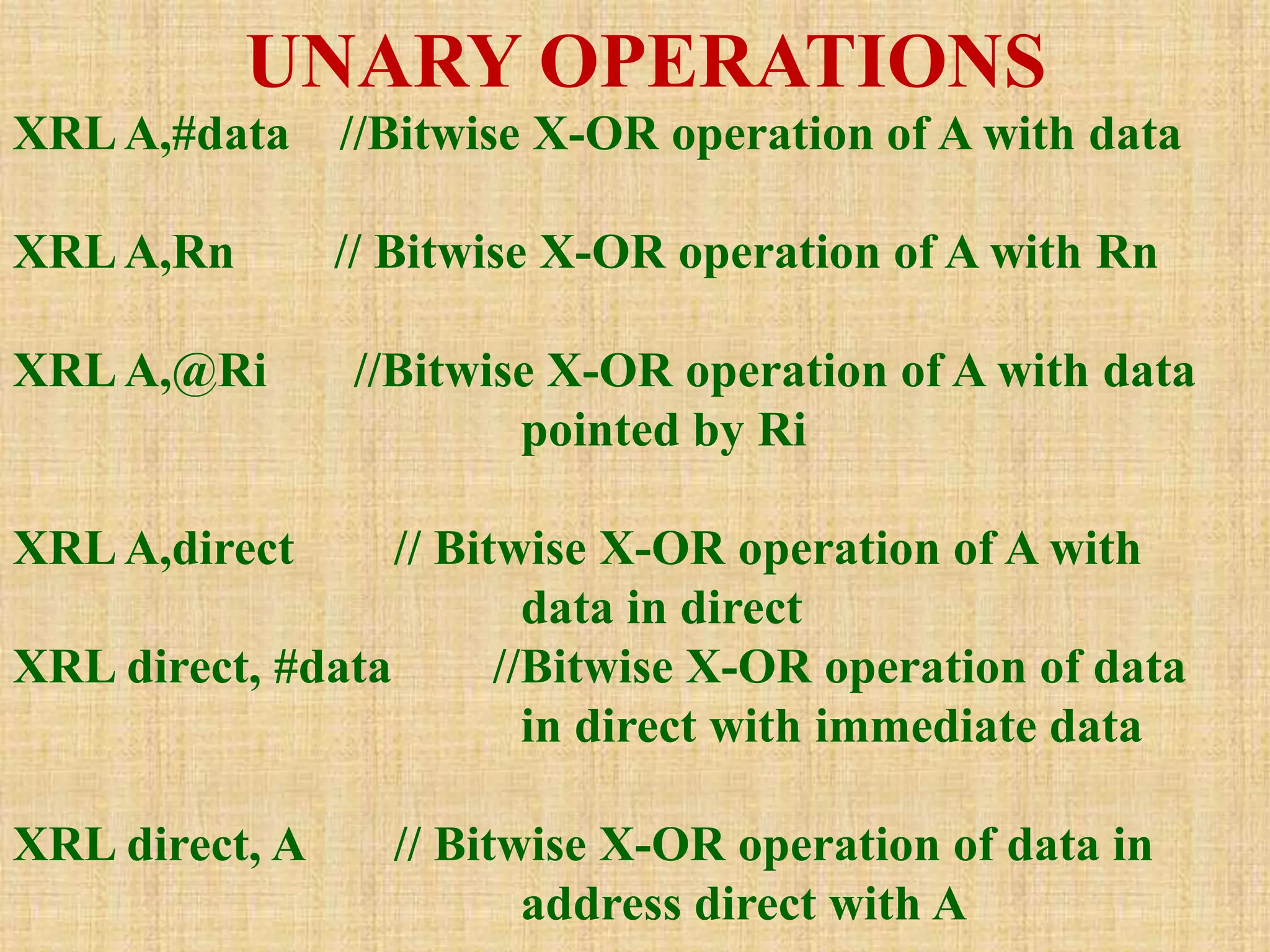
This document summarizes arithmetic and logical instructions for the 8051 microcontroller. It describes addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division instructions that perform operations on registers and memory. It also covers increment, decrement, and logical instructions like AND, OR, and XOR that operate on registers and memory locations using bitwise operations. Flags are updated based on arithmetic results.