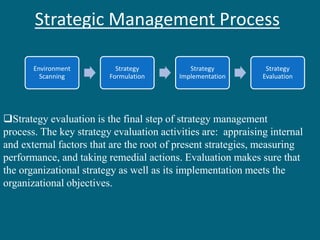
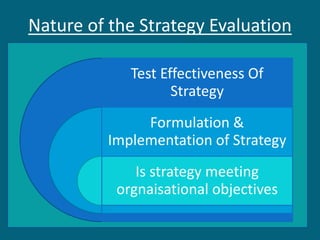
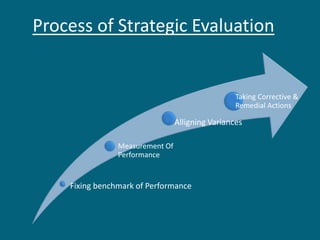
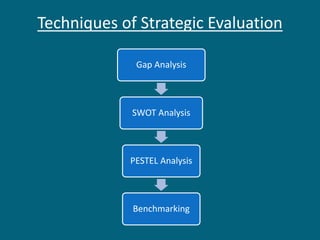
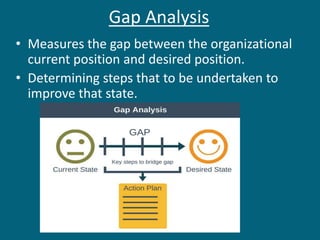
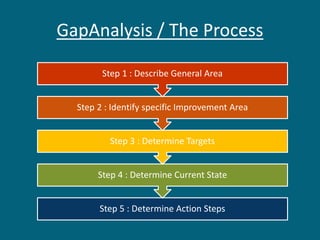
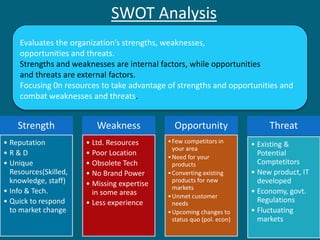
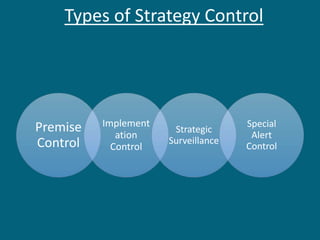
The document discusses strategic evaluation and control as a process to assess the effectiveness of strategies in achieving organizational objectives and outlines key activities including performance measurement and corrective actions. It highlights the importance of strategy evaluation for aligning decisions with goals, providing insights for strategists, and ensuring strategic choices remain valid. Various techniques for strategic evaluation, such as gap analysis, SWOT analysis, and PESTEL analysis, are also detailed, alongside types of strategic controls that monitor and adjust strategies in response to changing conditions.