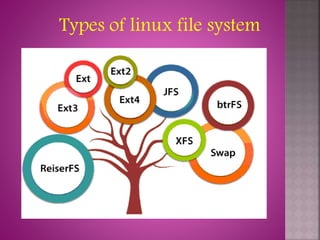
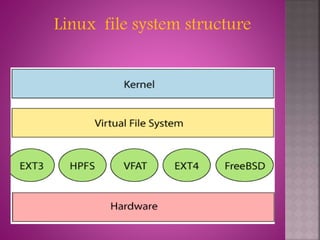
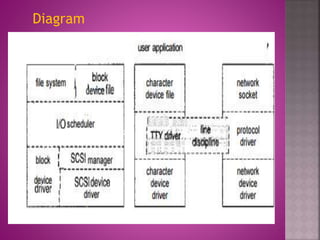
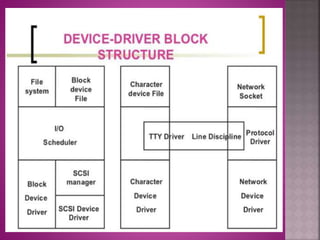
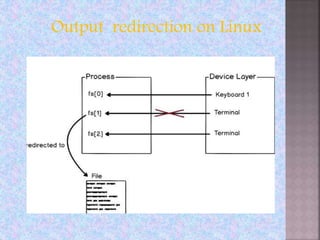
The document provides an overview of the Linux file system, describing its role in data management and storage organization within the Linux operating system. It discusses various types of Linux file systems such as ext, JFS, ReiserFS, XFS, Btrfs, and swap file systems, highlighting their features and uses. Additionally, the document covers the input and output mechanisms in Linux, including device classification and caching methods.