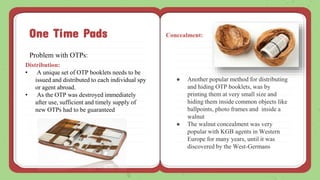
1) The one-time pad (OTP), also known as the Vernam cipher, is a encryption technique that was first described in 1882 and patented in the early 20th century.
2) It works by combining a randomly generated key that is at least as long as the plaintext with the plaintext using an XOR operation. This ensures the ciphertext is random and contains no information about the original message.
3) The key must be truly random, used only once, and both the sender and receiver must destroy their copy after use to maintain the security of the OTP. During the Cold War, spies used small booklets of random numbers as the one-time pads.