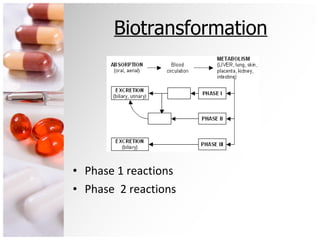
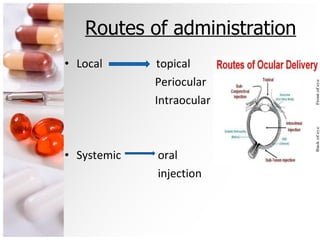
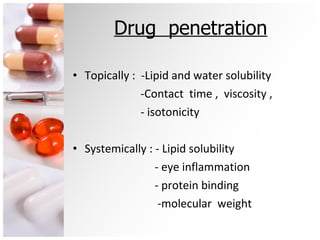
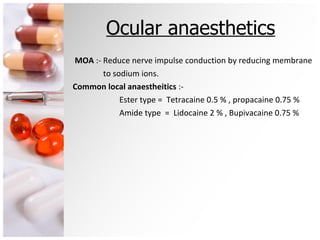
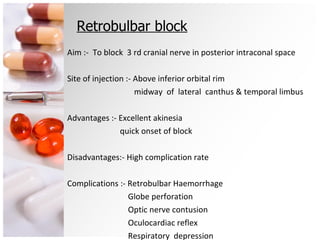
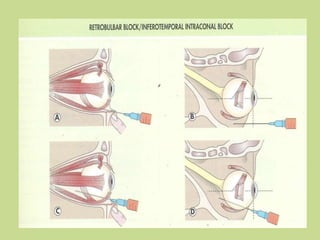
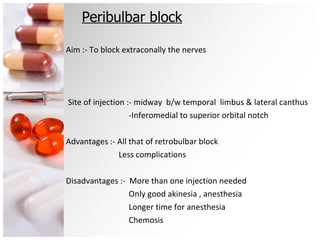
The document is a comprehensive overview of ocular therapeutics, detailing pharmacodynamics, pharmacokinetics, mechanisms of drug action, and various drug classifications including ocular anaesthetics, anti-glaucoma medications, antibiotics, antifungals, antivirals, and diagnostic agents. It also discusses routes of administration, therapeutic indices, adverse effects, and complications related to ocular procedures. A significant focus is on drug formulations, their mechanisms, indications, and side effects associated with treatment for various ocular conditions.




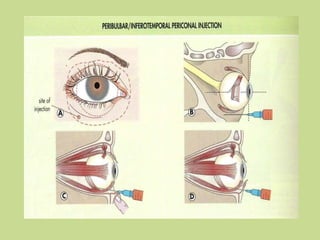
![Sub tenon’s block At 1 or 2 ‘0’ clock positions from corneal limbus [7-8 mm away] Using a 30 mm radius flexible cannula after perforating conjunctiva Passed beyond equator b/w tenon’s capsule & sclera Most frequent site is inferotemporal .](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oculartherapeutics-120131061654-phpapp02/85/Ocular-therapeutics-18-320.jpg)



![Adrenergic agonists Epinephrine MOA - On alpha , beta receptors – reduce aqueous formation increases aqueous outflow Side effects : Burning , stinging , Conjunctival blanching , CME , Endothelial toxicity follicular conjunctivitis [0.5 -2 %] tachycardia , hypertension Contradicted in aphakic & Closed angle glaucoma Apraclonidine MOA- On alpha 1,2 receptors –reduce aqueous formation Side eff : Itching ,dryness in mouth, follicular conjunctivitis, mydriasis Use : to reduce IOT after laser trabeculoplasty [0.25 – 1 %] Brimonidine – alpha 2 selective Side eff :- dryness in mouth ,fall in Bp,](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oculartherapeutics-120131061654-phpapp02/85/Ocular-therapeutics-23-320.jpg)

![Hypertonic agents MOA - Raises the osmotic pressure to reduce intra ocular pressure Glycerol [ 10 % infusion / 1 gm /kg oral ] Side effects : nauseating sweet taste ,diarrhoea,headache Mannitol [ 20 % infusion ] Side effects : Hypervolemia , pulmunory edema](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oculartherapeutics-120131061654-phpapp02/85/Ocular-therapeutics-25-320.jpg)

![Antibacterials PENICILLINS MOA :- Bactericidal Destroys cell wall [gram + , gram – cocci,spirochetes] - penicillin G [1 lakh U/ml topical] [0.5 M U/ ml sub conj inj ] [5 M U / 4 hrs IV] - Cloxacillin [penicillinase resistant] [50-100 mg/kg] 6 hrly oral [staphylococci] - Amoxycillin [25-50 mg/kg] 6 hrly oral [ gram +,- bacteria] Adverse eff :- Hypersensitivity reactions , rash ,..](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oculartherapeutics-120131061654-phpapp02/85/Ocular-therapeutics-27-320.jpg)
![QUINOLONES MOA :- [ Bacterial ] Anti DNA gyrase – inhibits division & supercoiling [gram -- bacteria , gram + bacteria ,chlamydia, mycoplasma] - Ciprofloxacin :- 0.3 % topical , 500 mg BD oral , 5-10 mg/kg IV 200 mg /ml intravitreal Uses :- Keratoconjunctivitis, ulcers,blepharitis, dacryocystitis , infectious endoophthalmitis S/E :- Arthropathy in children ,GIT irritation, Photosensitivity ,rash, liver damage - Gatifloxacin :-](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oculartherapeutics-120131061654-phpapp02/85/Ocular-therapeutics-28-320.jpg)
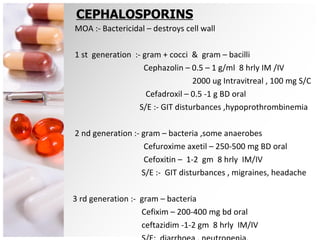
![Chloramphenicol MOA :- Bacteriostatic , Inhibits Protein synthesis by binding to 50 S ribosomal subunit [gram +,- aerobes , chlamydia,ricketssia,mycoplasma] 0.5 % ointment, 50 mg /kg 4 times oral 2 mg/ml intravitreal Uses :- Intraocular infections Conjunctivitis Side eff :- Bone marrow depression Aplastic anemia , agranulocytosis](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oculartherapeutics-120131061654-phpapp02/85/Ocular-therapeutics-31-320.jpg)


![SULPHONAMIDES MOA :- Bacteriostatic - Inhibits folate synthesis [PABA folic acid ] [gram - ,+ bacteria] Sulfacetamide , Sulfamethoxazole , sulfadiazine Topically 10% ,20 % ,30 % drops Oral 2-4 gm/day TDS COTRIMOXAZOLE MOA :- Inhibits Dihydro folate reductase in conversion of DHF THF Sulfamethoxazole [400 mg ] + trimethoprim [80 mg]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oculartherapeutics-120131061654-phpapp02/85/Ocular-therapeutics-34-320.jpg)
![Antifungals Polyene antibiotics :- MOA - Selective action on ergosterol of fungal cell membrane forming micropores – increase permeability Amphotericin B – Against yeast ,filamental fungi [0.25 % topical ] [ 0.25 mg/kg oral] Nystatin - against candida [ 1 lakh u/gm oint] Natamycin – against candida , aspergillus ,fusarium [ 5 % suspension] Uses in keratomycosis and endophthalmitis[5-10 ug intravitreal] Common side effects : allergic hypersensitivity reactions](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oculartherapeutics-120131061654-phpapp02/85/Ocular-therapeutics-36-320.jpg)
![Imidazoles :- MOA - Block fungal cytochrome P-450 enzyme in ergosterol [increase permeability tru membrane] Clotrimazole :- [1 % topical] Miconazole :- [ 1 % drops,2 % oint, 5-10 mg sub conj ] Ketoconazole :- [200-800 mg oral daily , 0.5 mg intravitreal] Uses :- candida,fungal , endoophthalmitis Side effect:- liver toxicity Triazoles :- Fluconazole - [100-200 mg oral] [0.2% topical] [0.1 mg intravitreal] Uses :- Candida,cryptococcus](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oculartherapeutics-120131061654-phpapp02/85/Ocular-therapeutics-37-320.jpg)


![Ocular antiallergics MOA – Competitive antagonist of H1 receptors Uses - vernal keratoconjunctivitis , Giant papillary conjunctivitis Allergic conjunctivitis CPM – 4 times /day topical Azelastine - 2 times/day Loratadine/ cetrizine – at bed time Mast cell stabilizers MOA – Stabilizes mast cells and prevent release of histmaine Cromolyn sodium [2-4 % ] 6 hrly Olapatadine [0.1 % ] 12 hrly](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oculartherapeutics-120131061654-phpapp02/85/Ocular-therapeutics-40-320.jpg)

![Anti VEGF MOA : Inhibits vascular EGF in retinal ischaemia Uses : Diabetic retinopathy , macular edema , ROP ARMD - Intravitreal inj - Pegaptanib [macugen ] Ranibizumab [ lucentis ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oculartherapeutics-120131061654-phpapp02/85/Ocular-therapeutics-45-320.jpg)

![Viscoelastics Properties - optical - cohesive [ space maintaining tissue manipulation in surgery] - dispersive [ Coating ocular surface protecting corneal endothelium lower surface tension] - Elasticity Sodium hyaluronate 1 % Sodium hyaluronate 3 % & chondroitin sulphate 4 % Hydroxy propyl methyl cellulose 3 % Uses :- - In gonioscopy - in intra ocular surgeries](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oculartherapeutics-120131061654-phpapp02/85/Ocular-therapeutics-47-320.jpg)
![IRRIGATING SOLUTIONS Characteristics of an ideal solution : -- Maintain moisture of & cleanse ocular tissues -- Isotonicity electrolyte and p H same as aqueous -- Maintain pressure of globe -- Protect delicate ocular structures -- Endothelial nourishment Available preparations :- Balanced salt solution[BSS] BSS plus Dextran containing soln Glucose fortified BSS plus USES :- Intraocular – in cataract surgery Extraocular – FB removal,tonometry,gonioscopy](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oculartherapeutics-120131061654-phpapp02/85/Ocular-therapeutics-48-320.jpg)
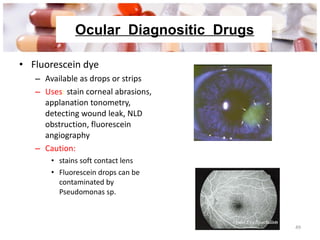
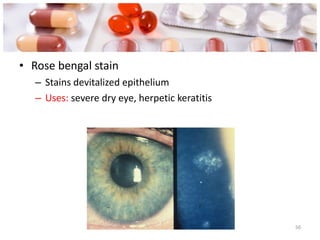
![Ocular toxicology : Amiodarone :- Vortex keratopathy Digitalis :- Chromatopsia [seeing yellow colour ] Chloroquine :- Bull’s eye maculopathy Ethambutol :- Optic neuropathy , colour vision disturbed Corticosteroids :- Posterior sub capsular cataracts Thioridazine :- Pigmentary retinopathy Copper, Gold :- Lenticular opacities Rifabutin :- Anterior uveitis](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oculartherapeutics-120131061654-phpapp02/85/Ocular-therapeutics-51-320.jpg)
