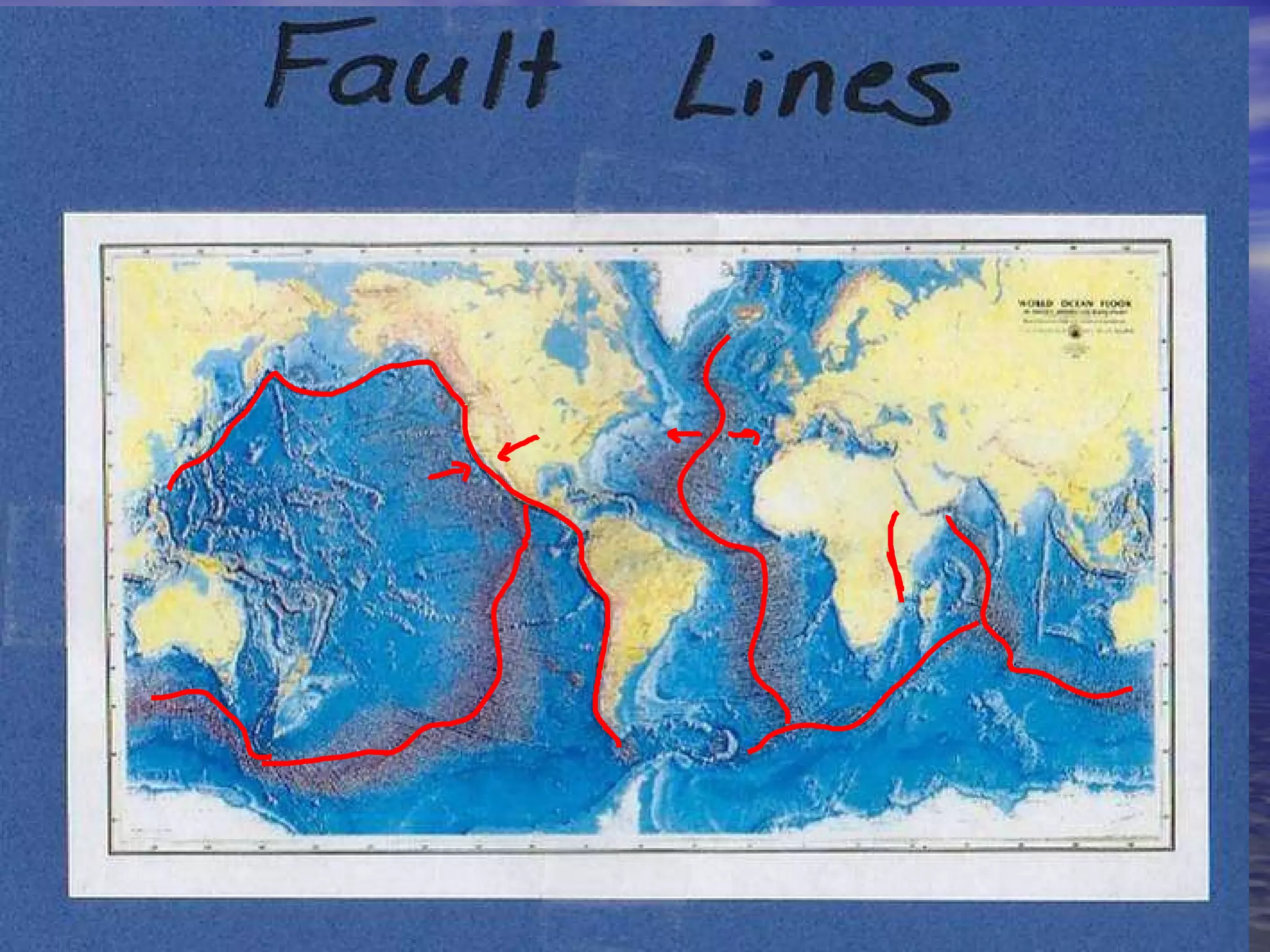
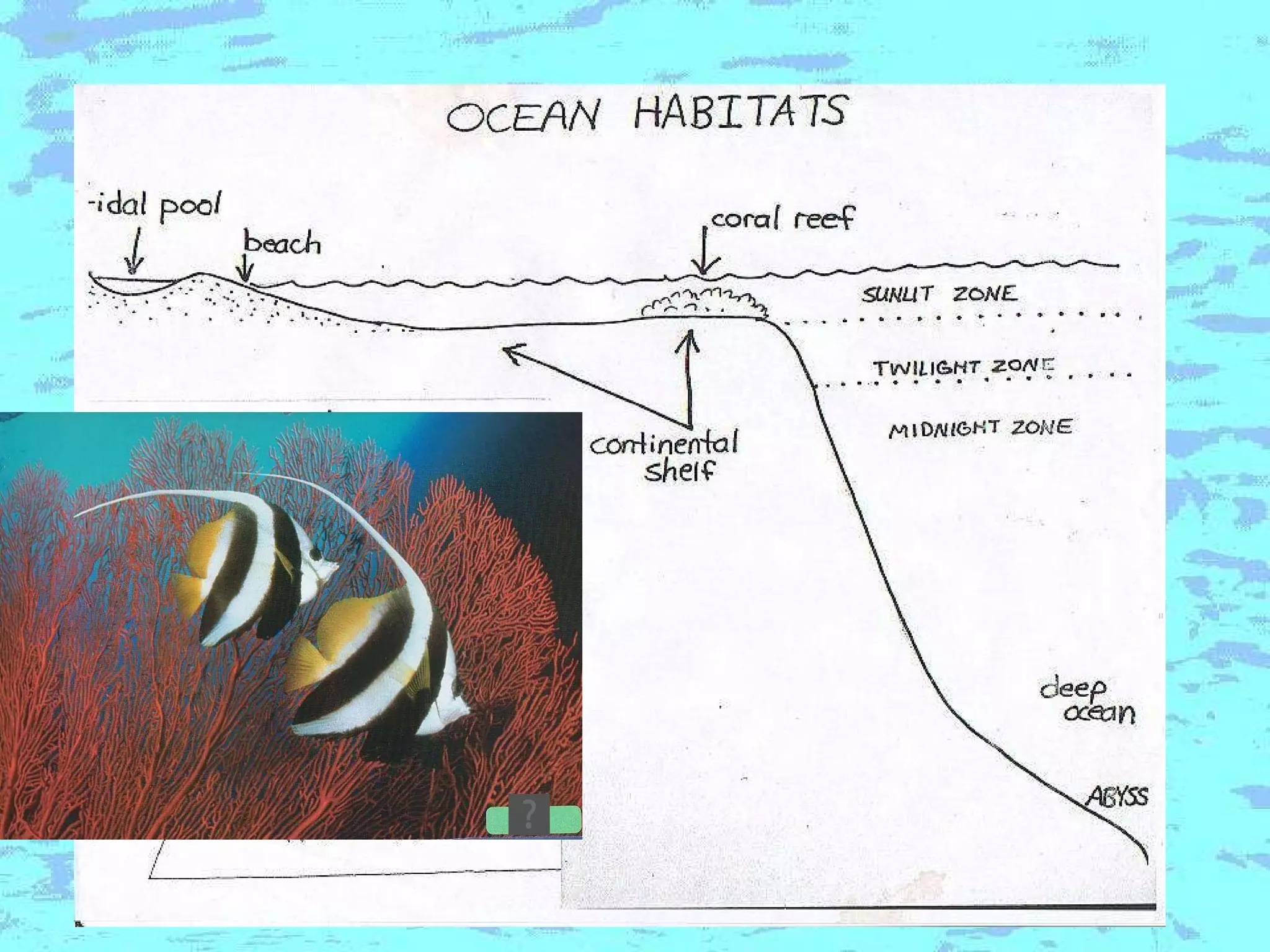
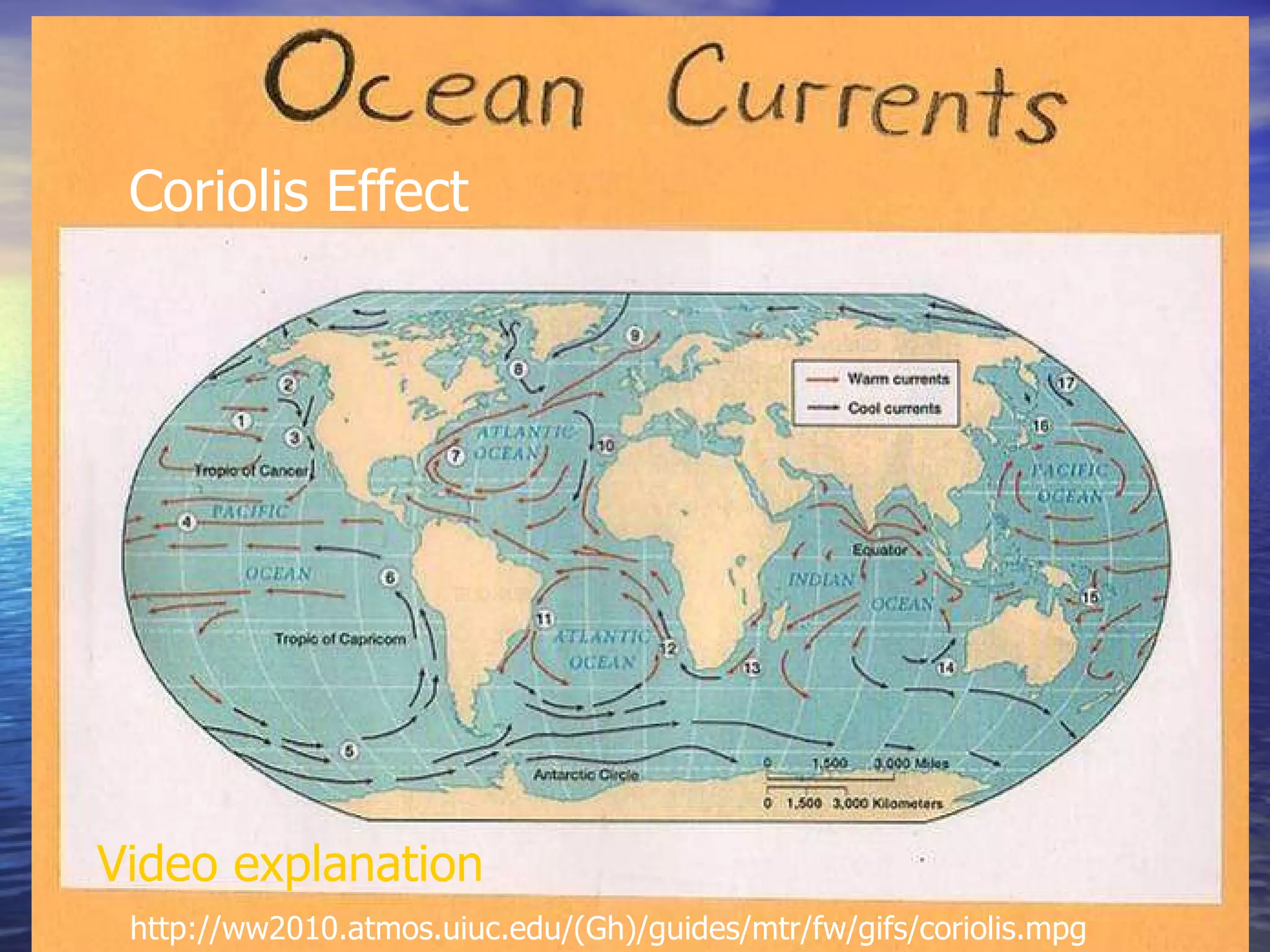
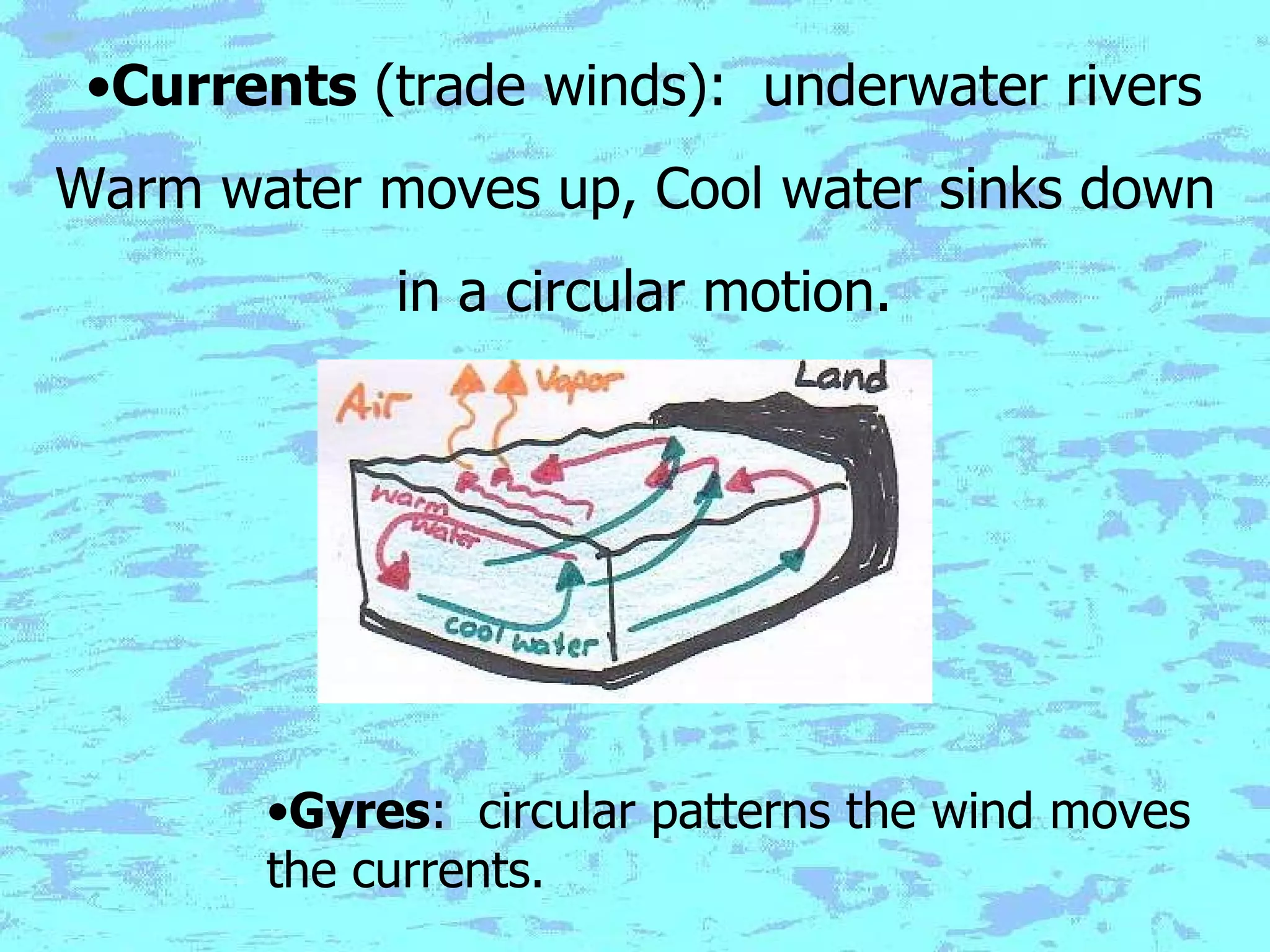
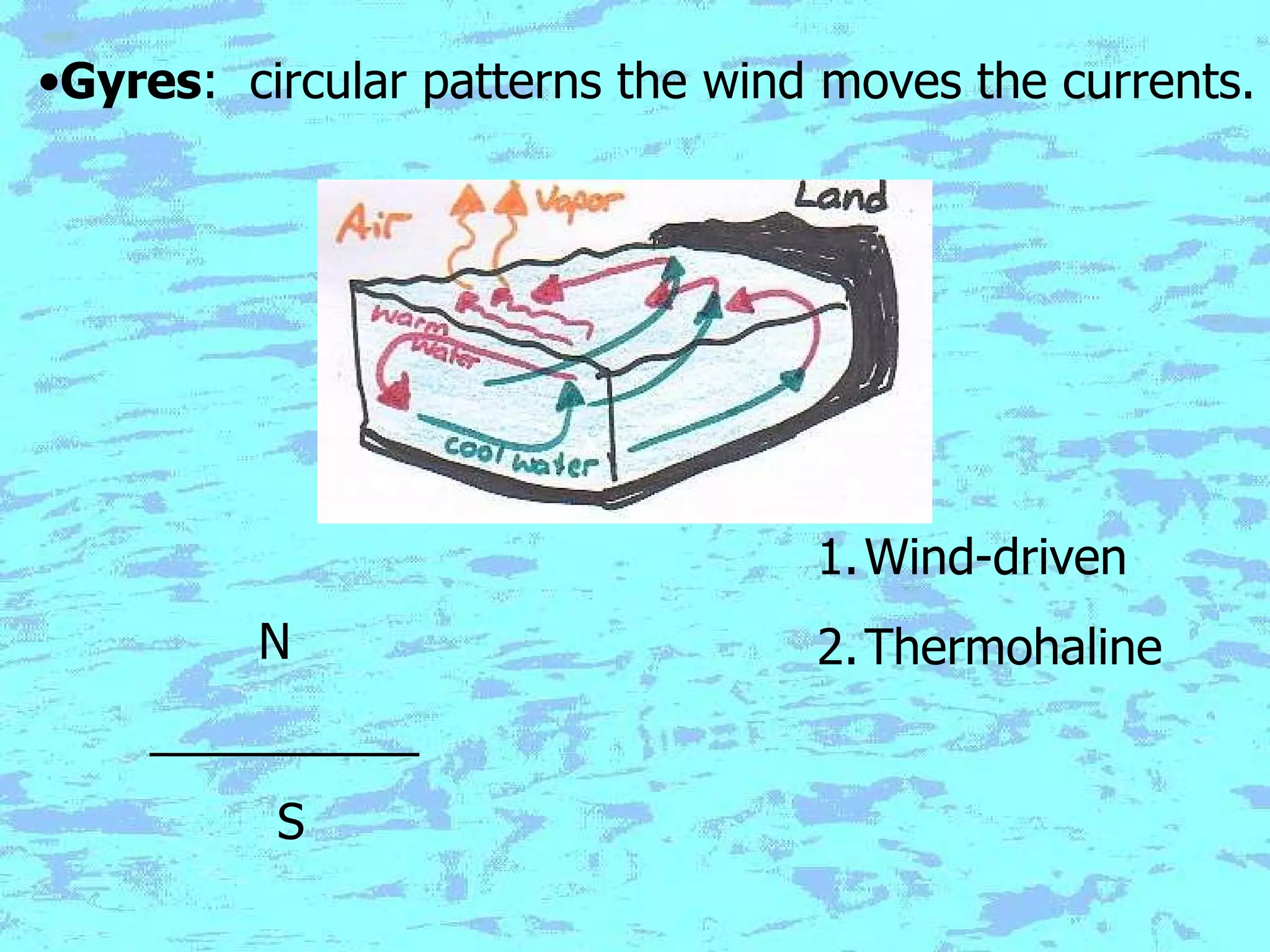
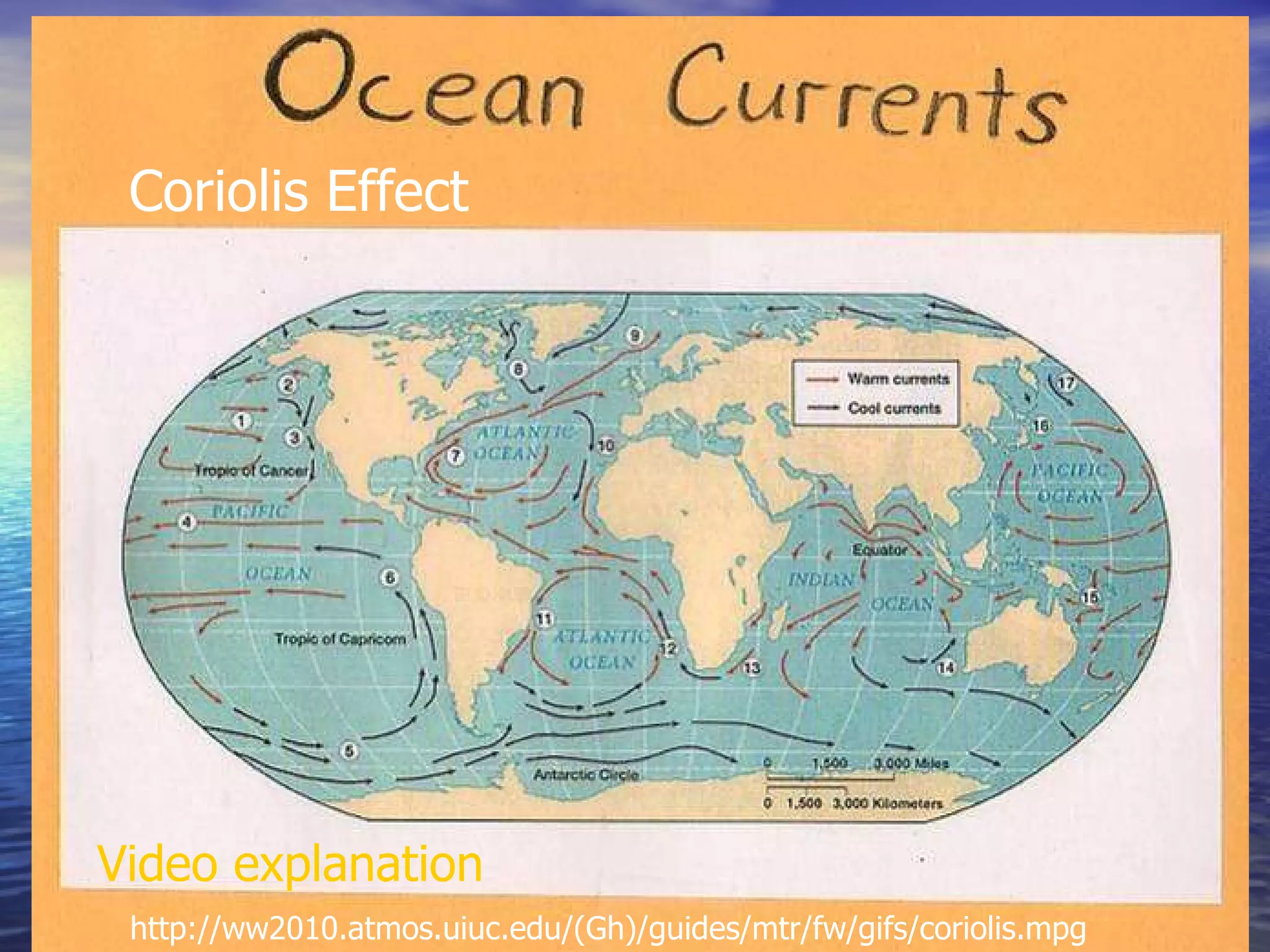
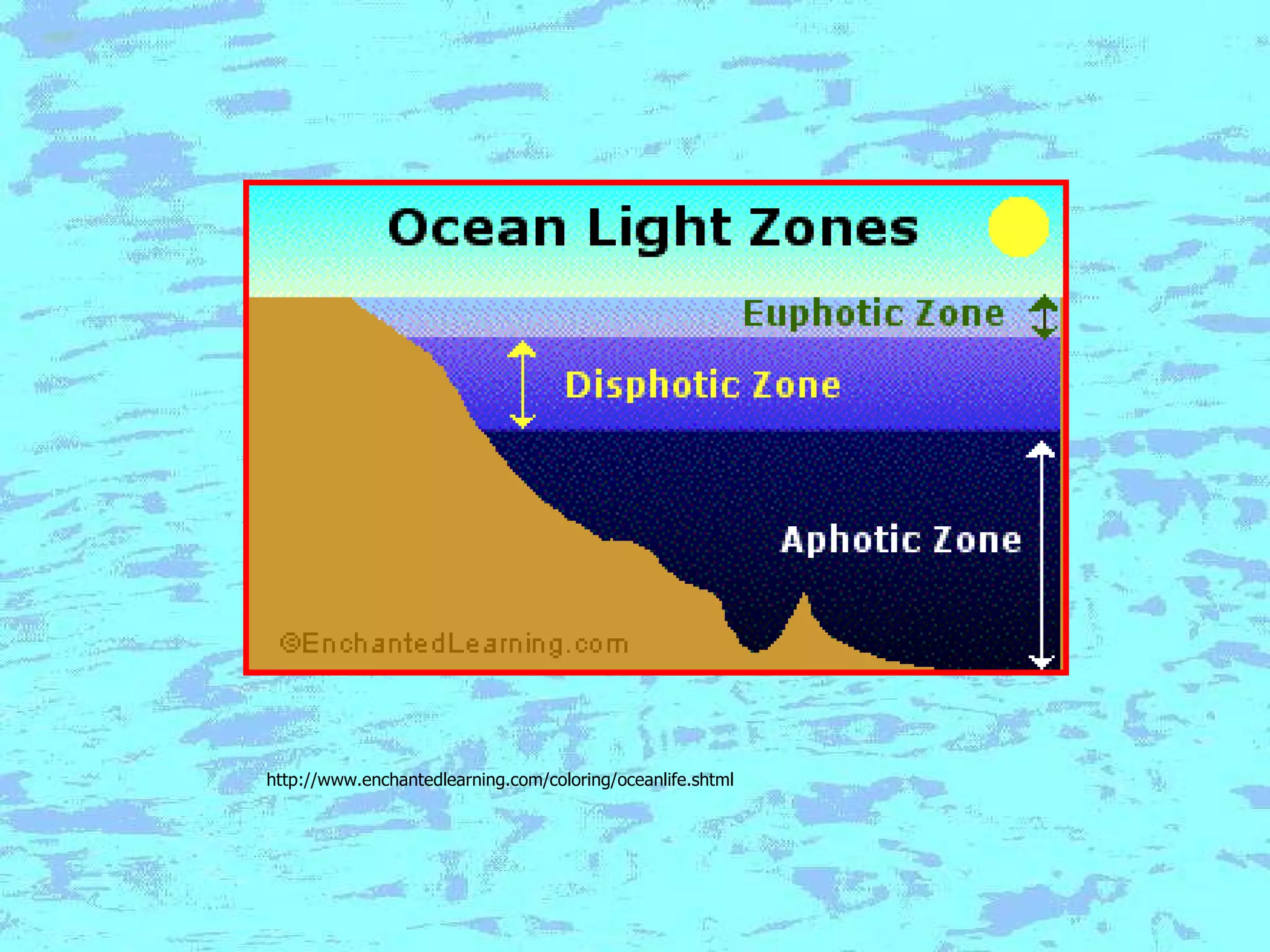
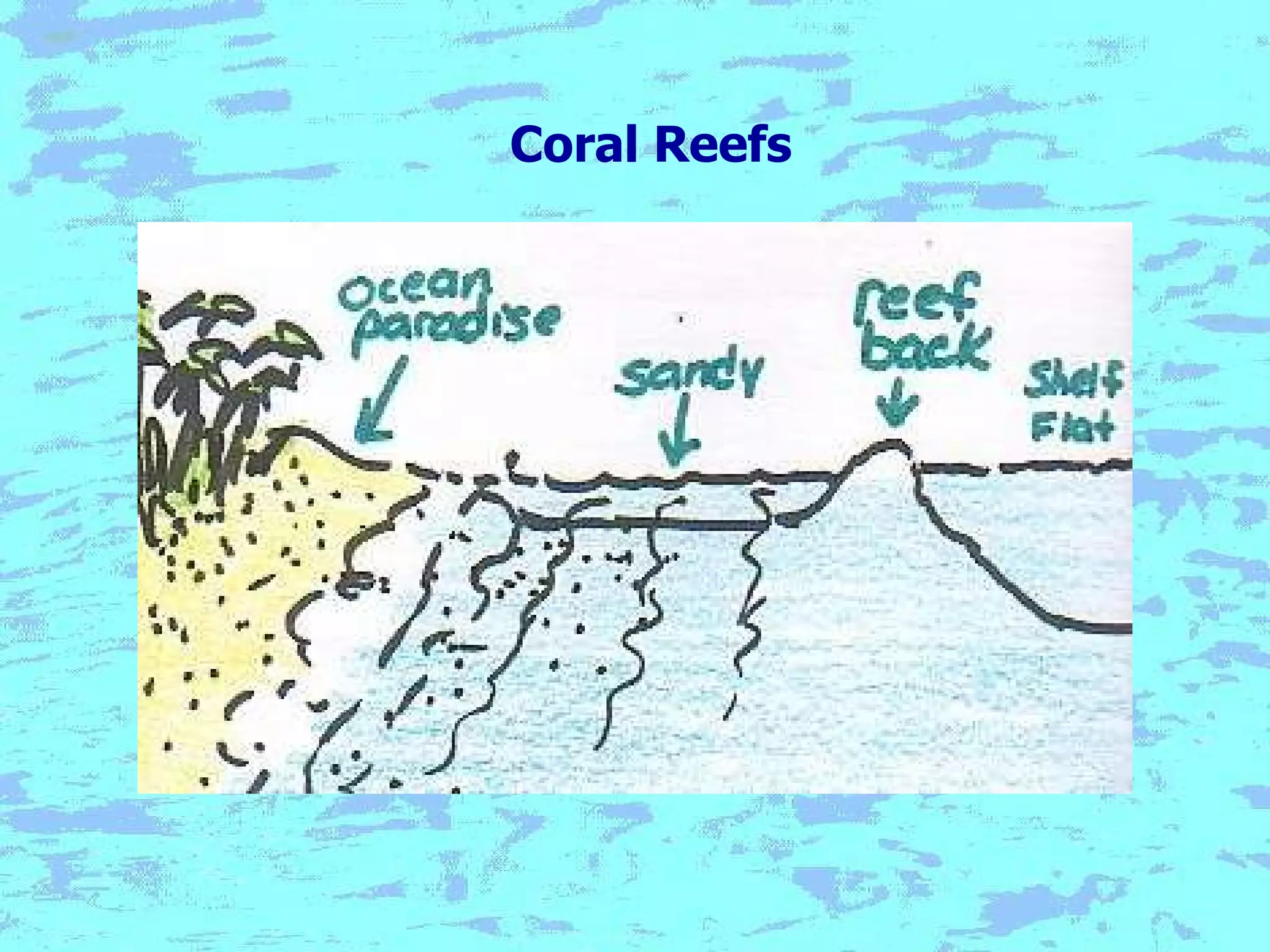
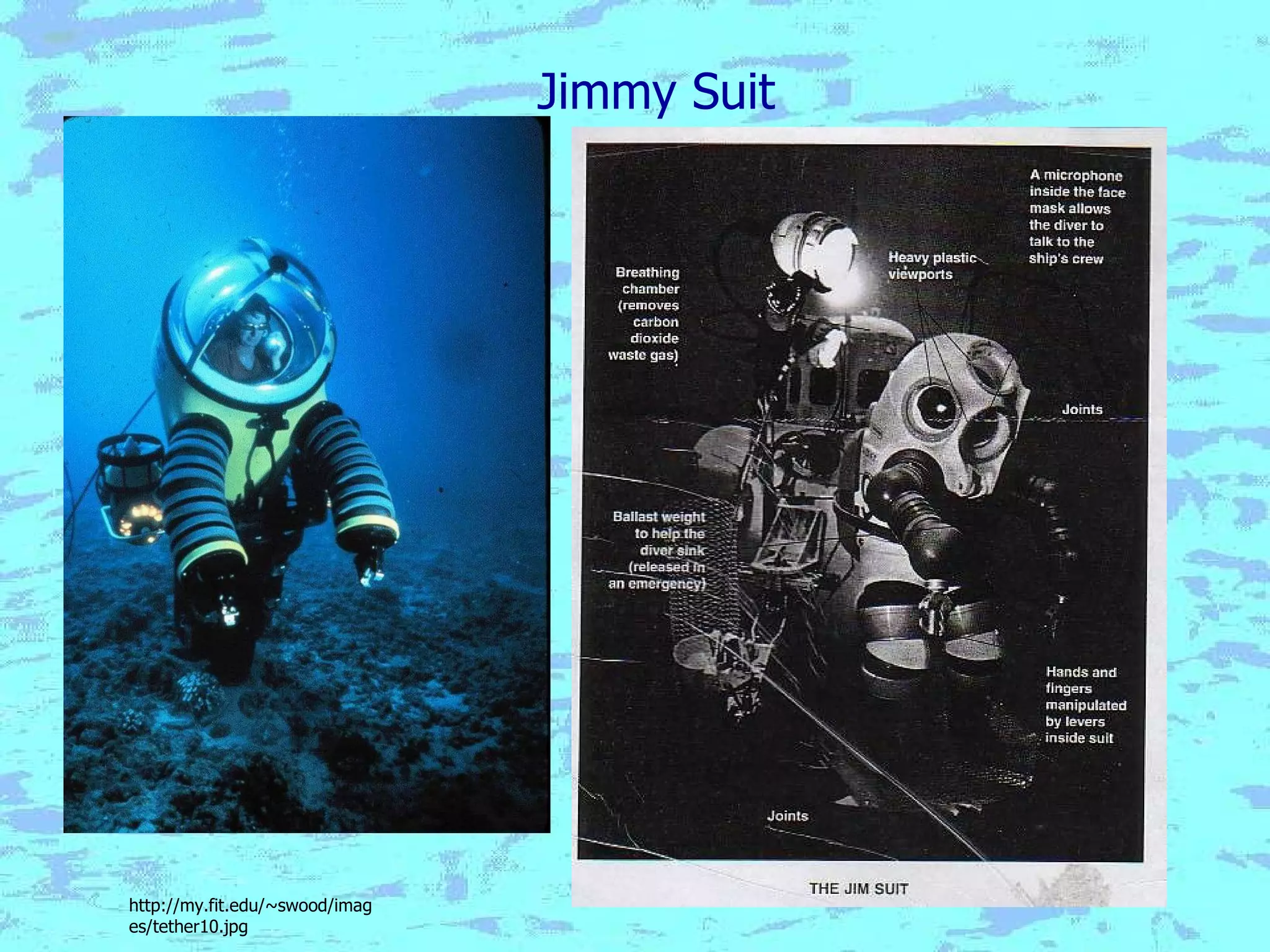
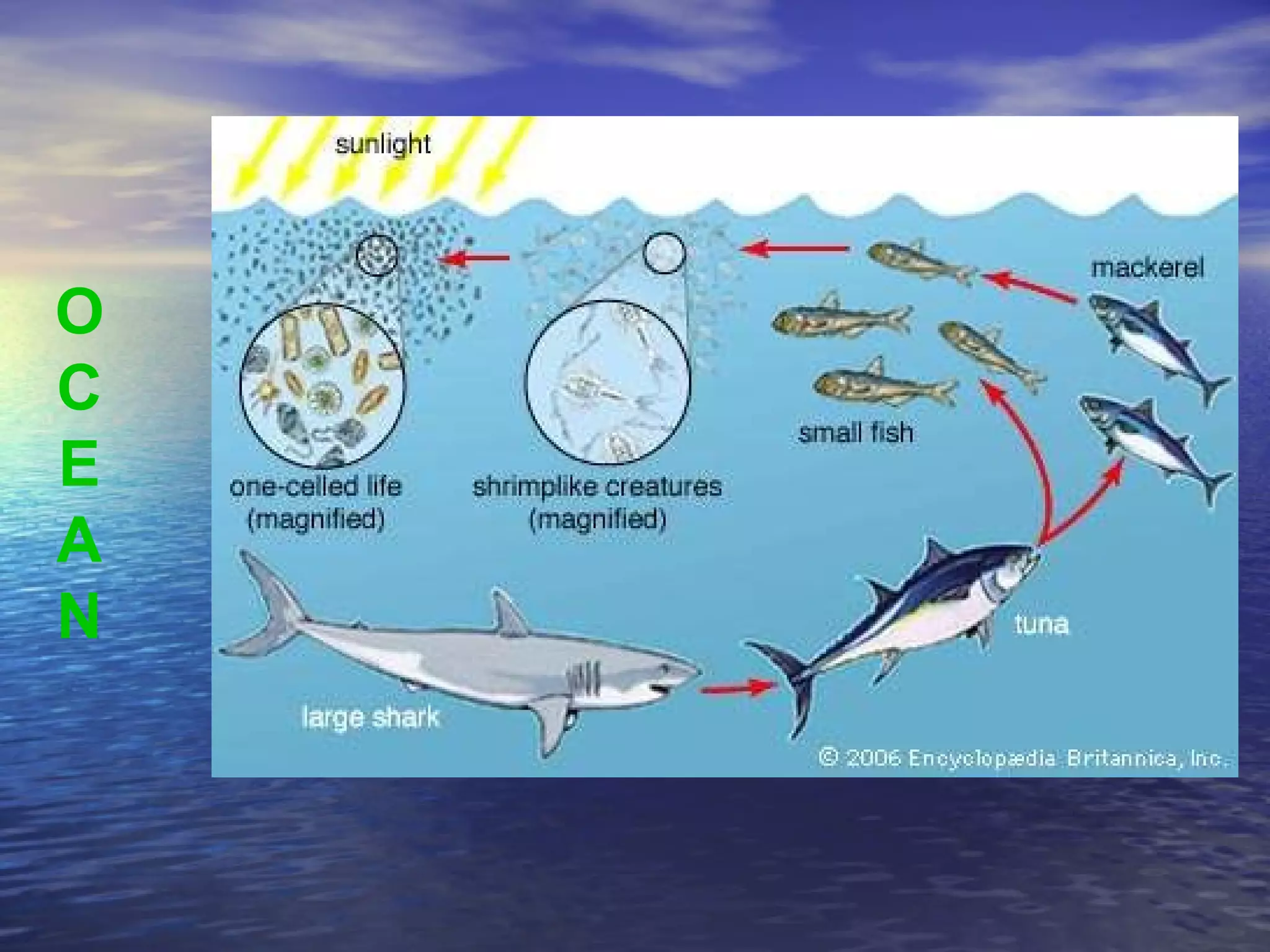
The document presents an overview of oceans, detailing their composition, exploration methods, and significant aspects like ocean currents, zones, and biodiversity. It discusses the ecological roles of reefs and currents in influencing climate and highlights various ocean zones, including the intertidal, twilight, and midnight zones. Additionally, it touches upon the impact of human activities and global warming on marine environments and resources.