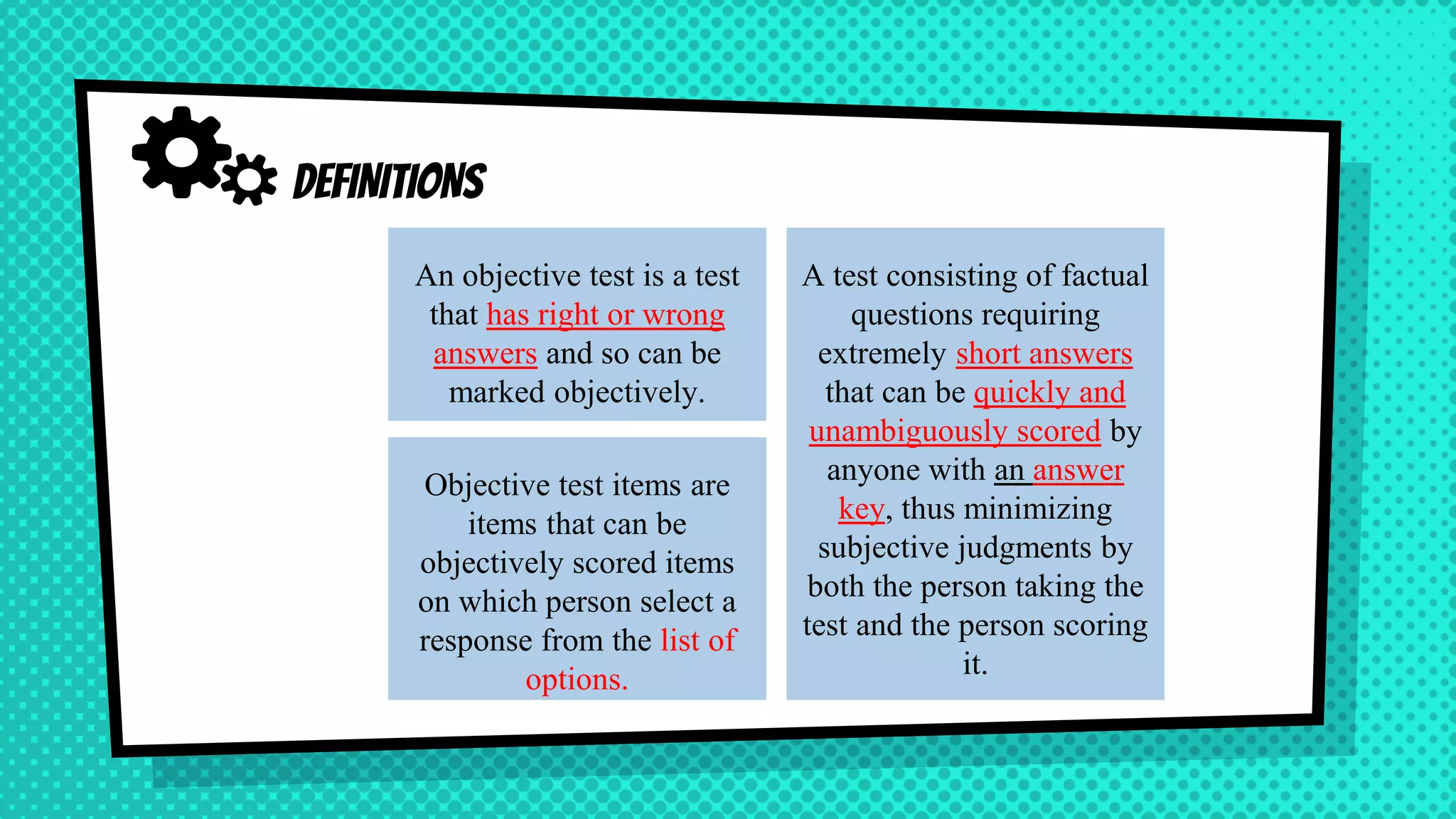
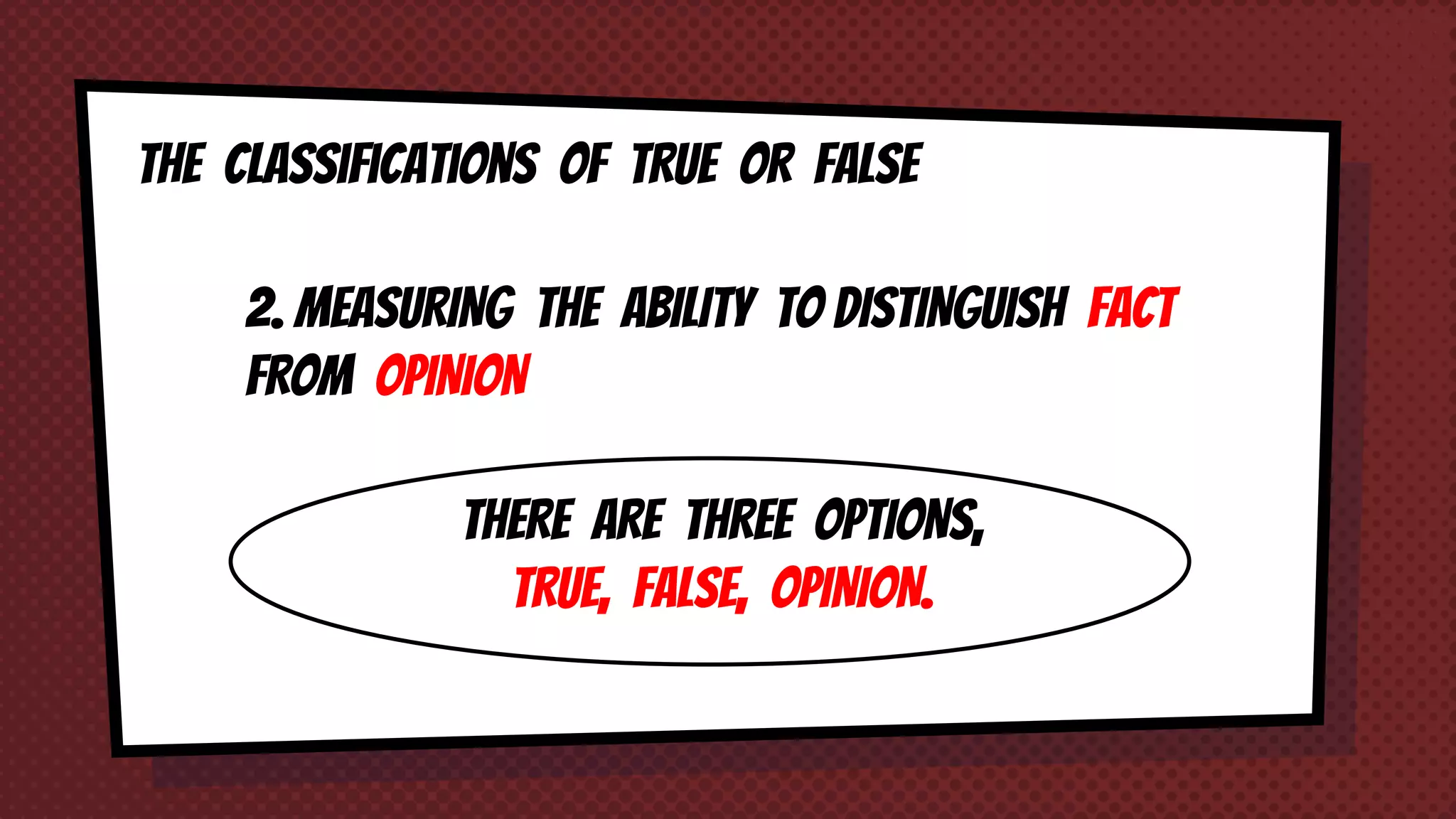
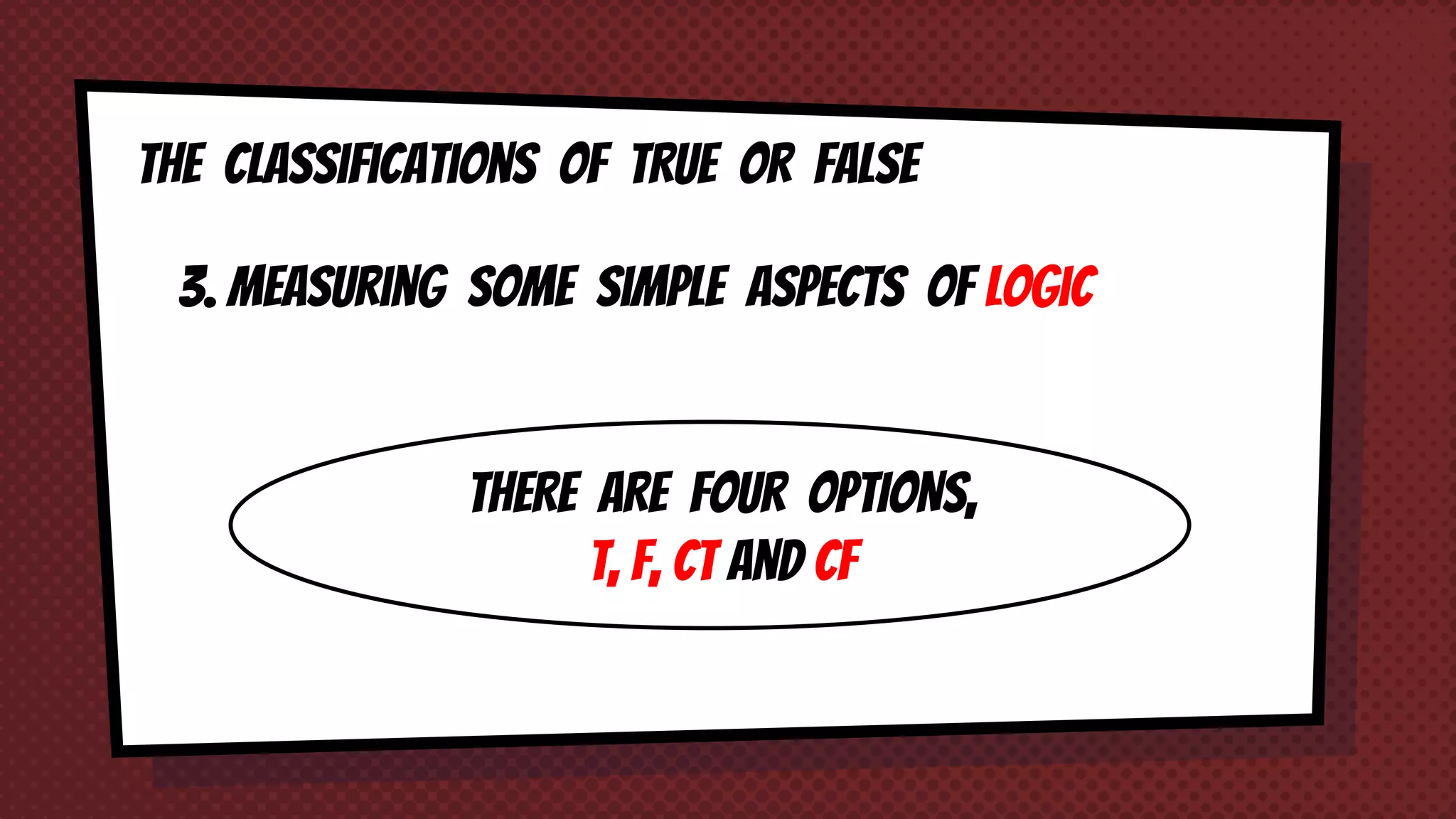
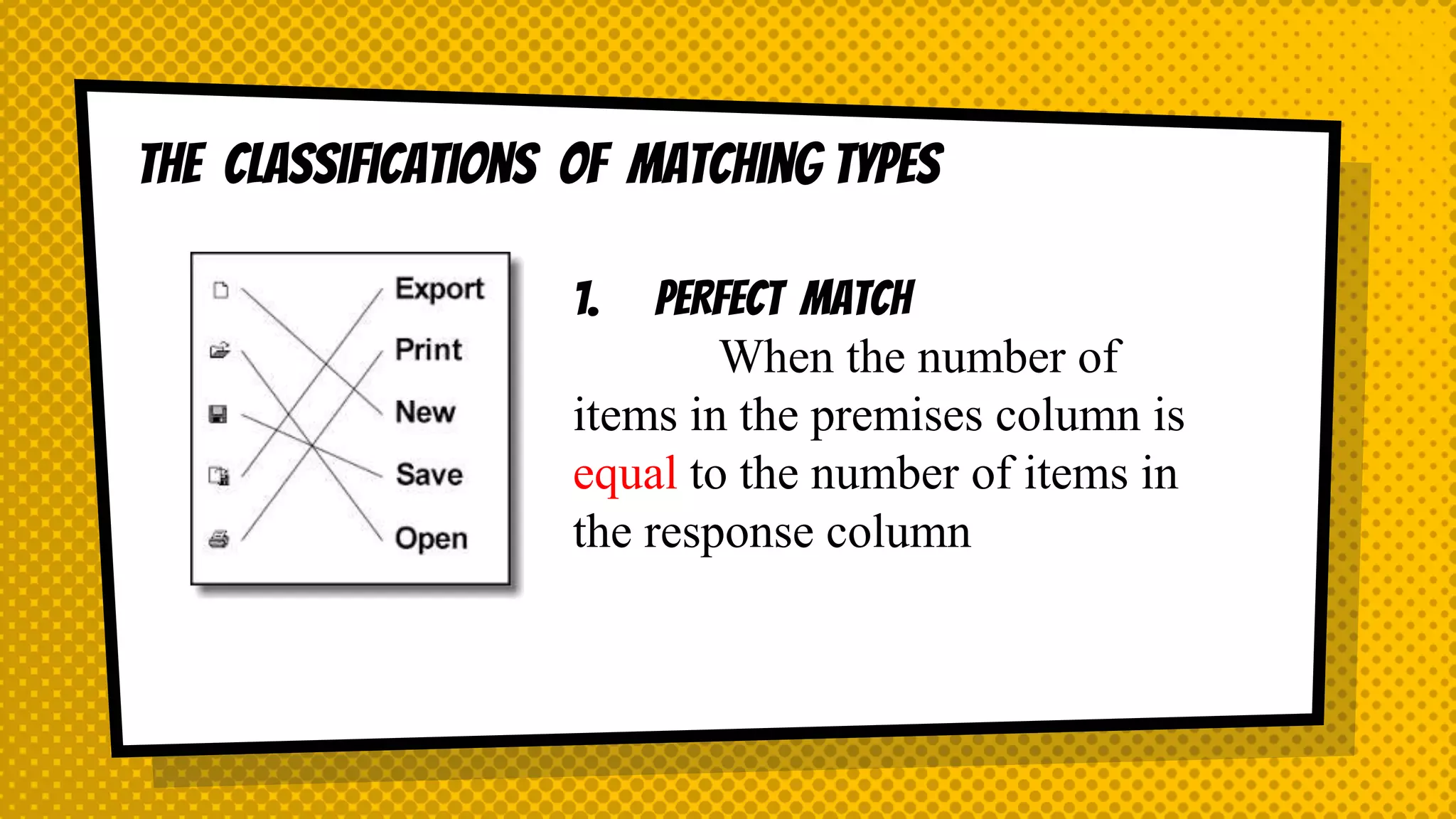
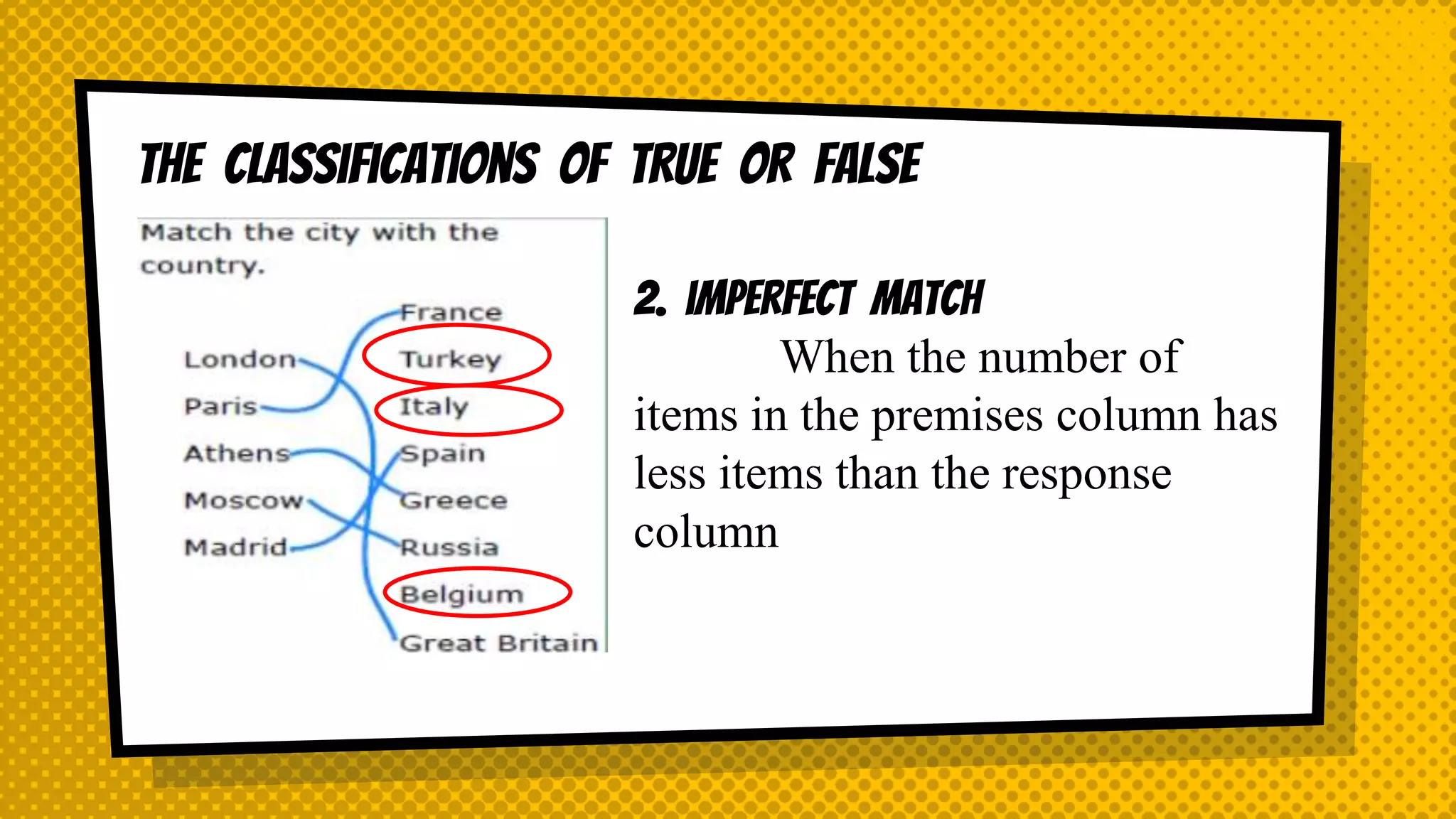
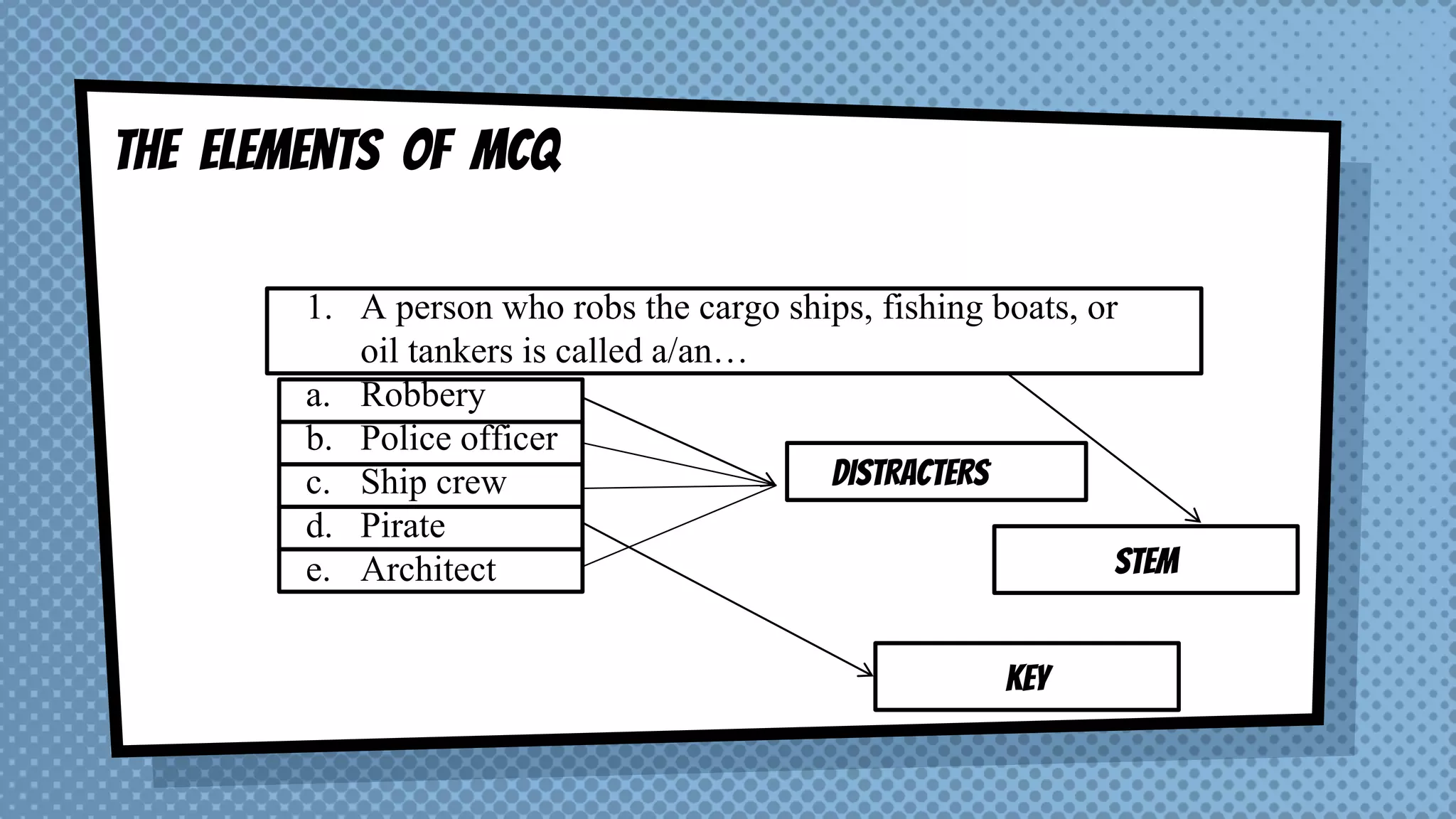
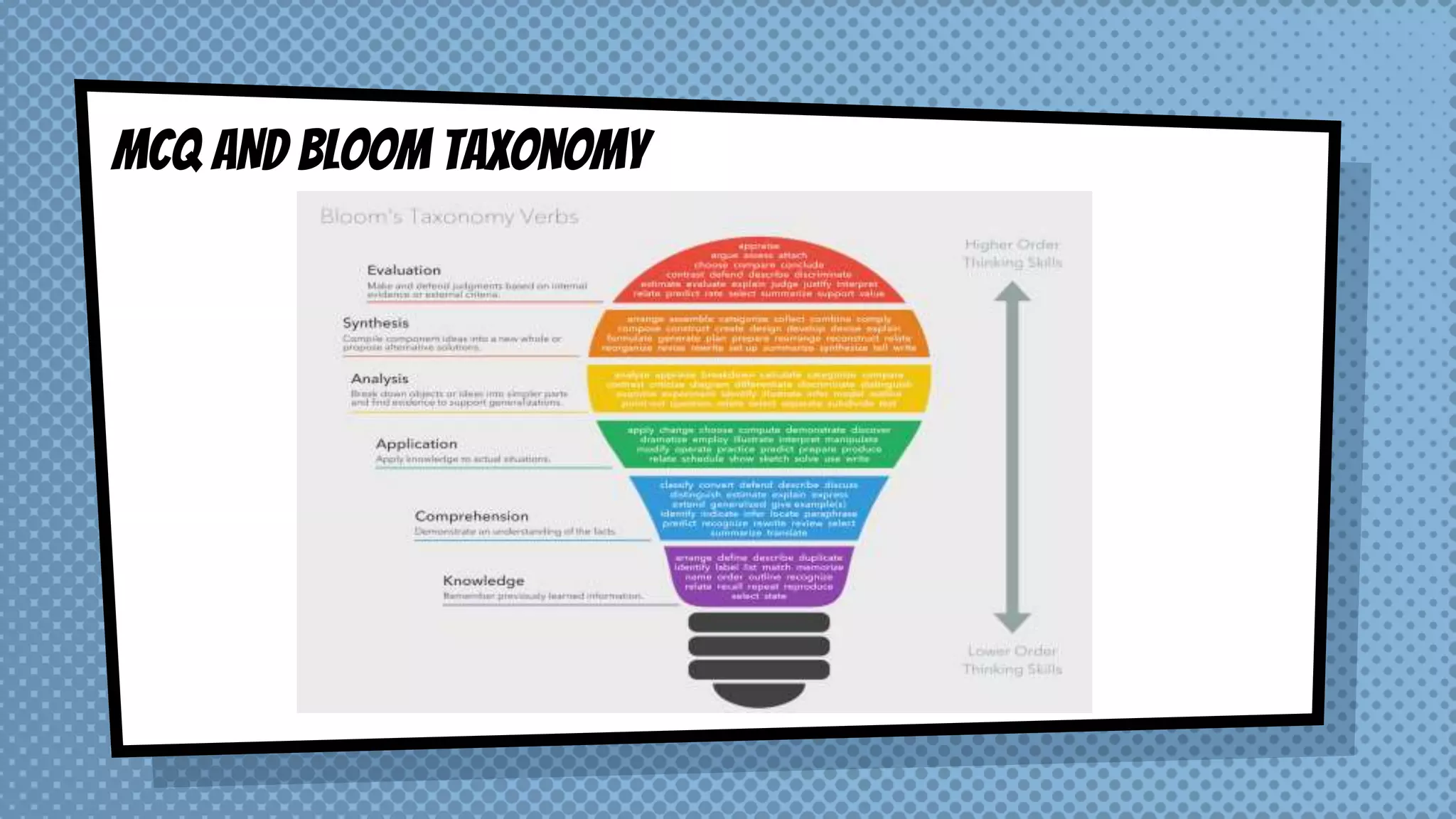
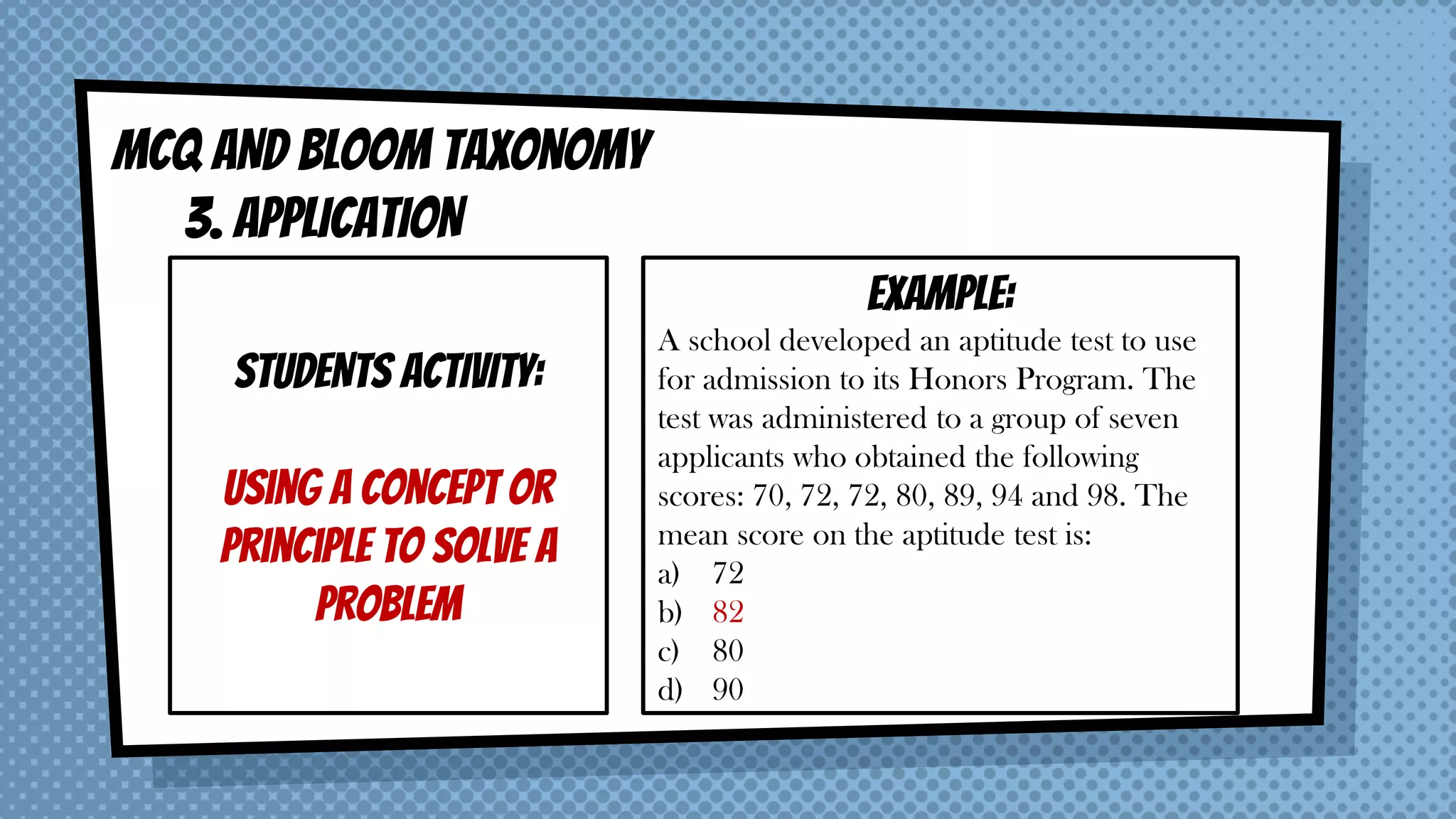
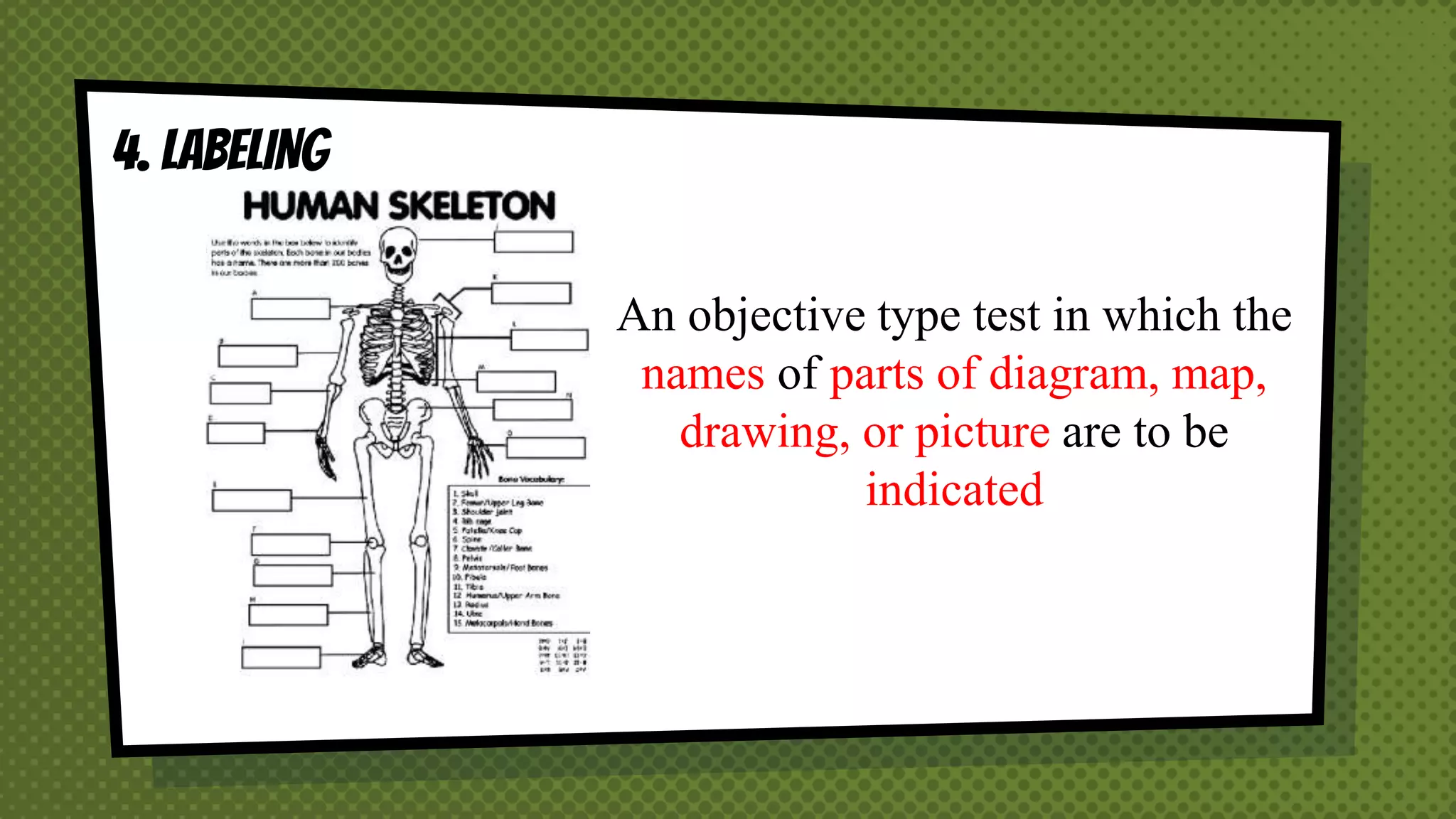
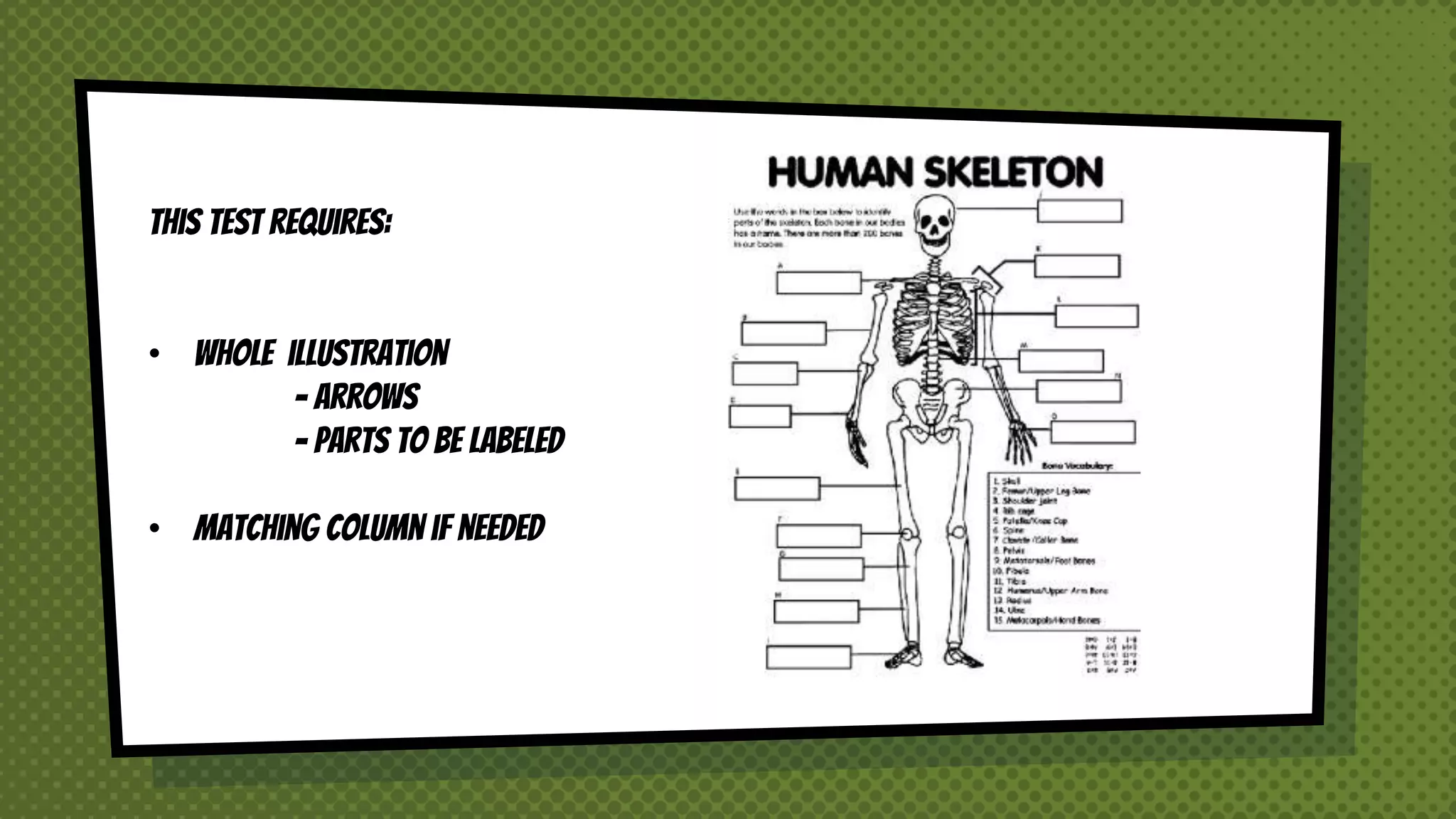
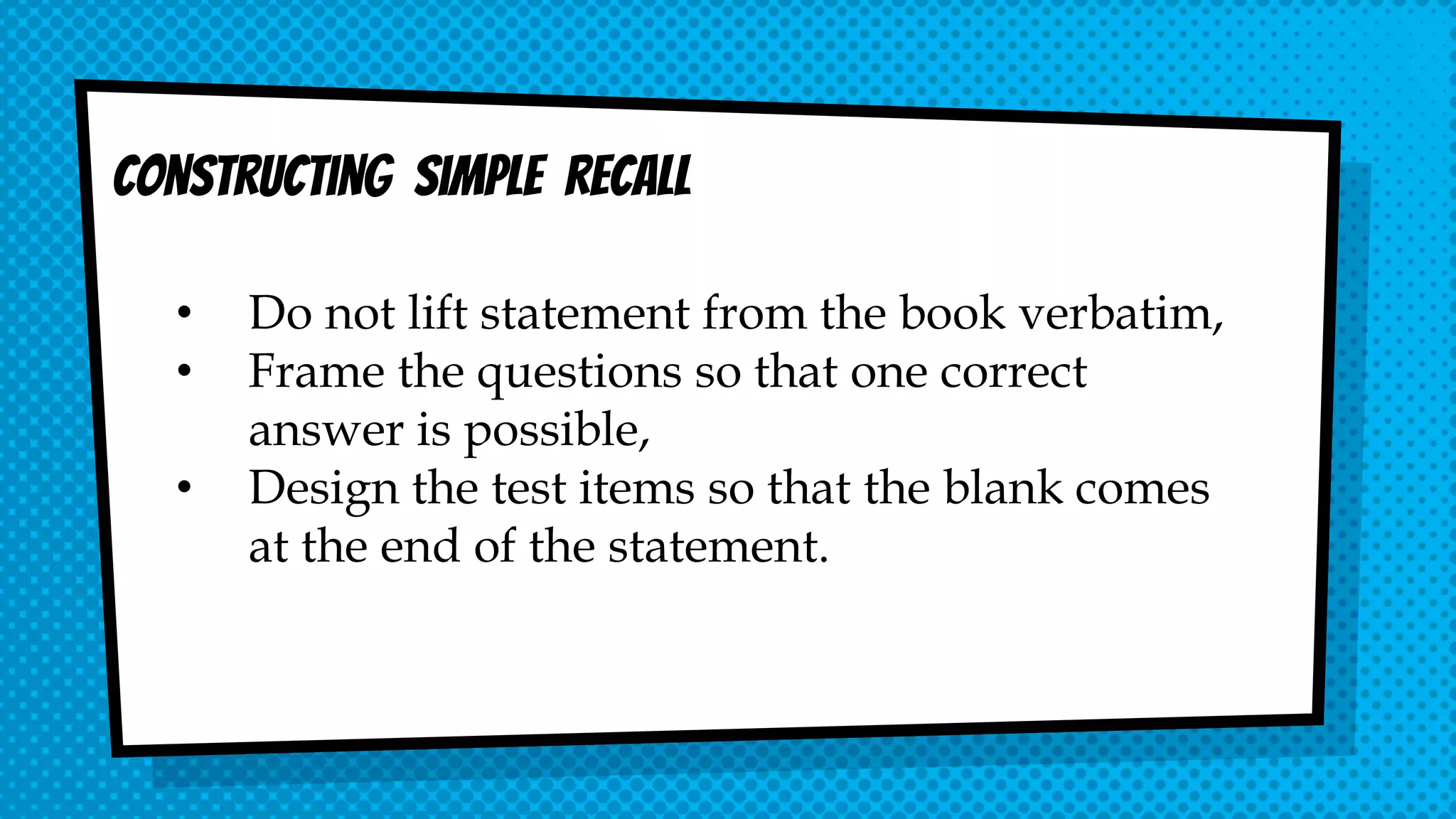
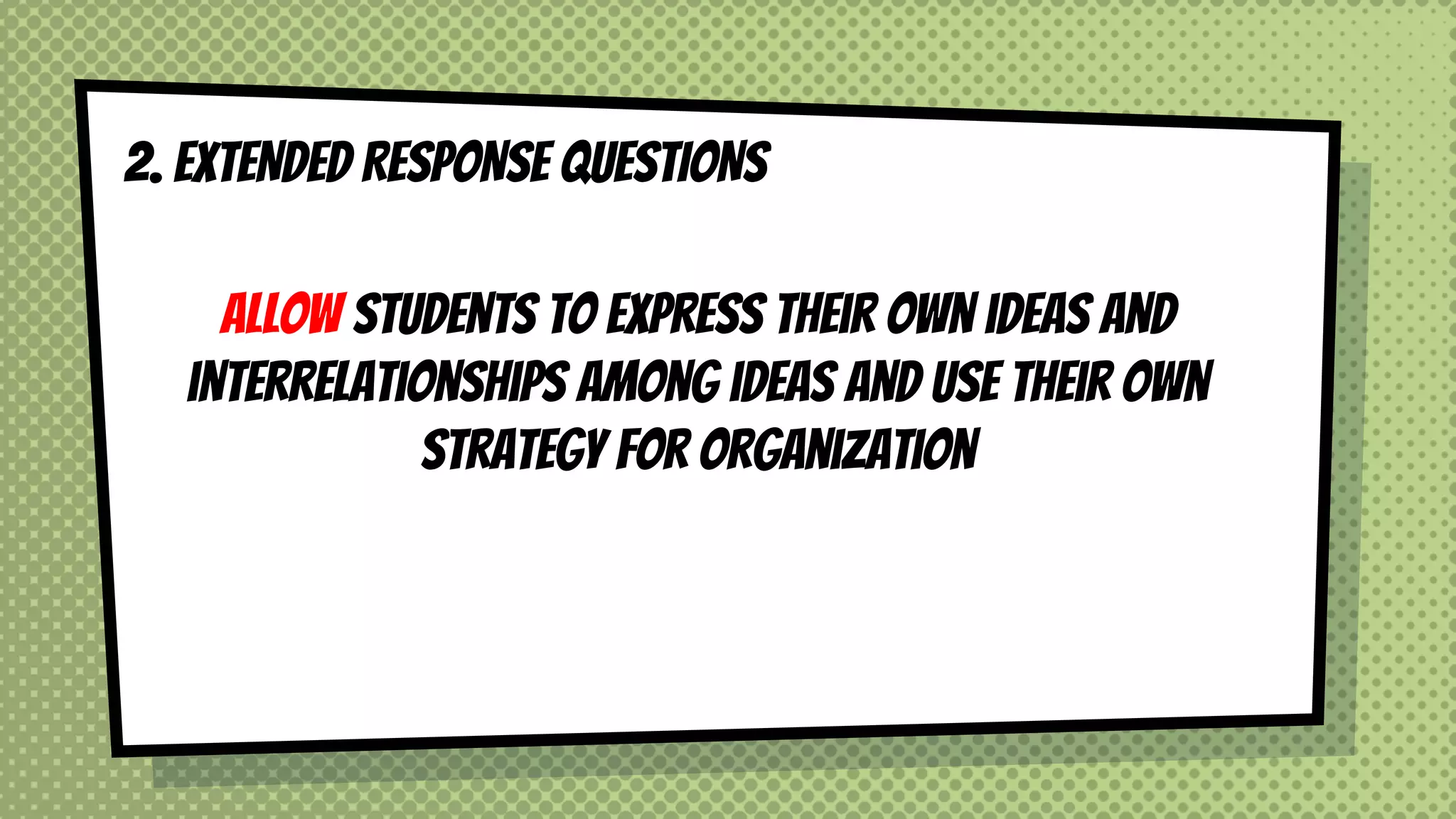
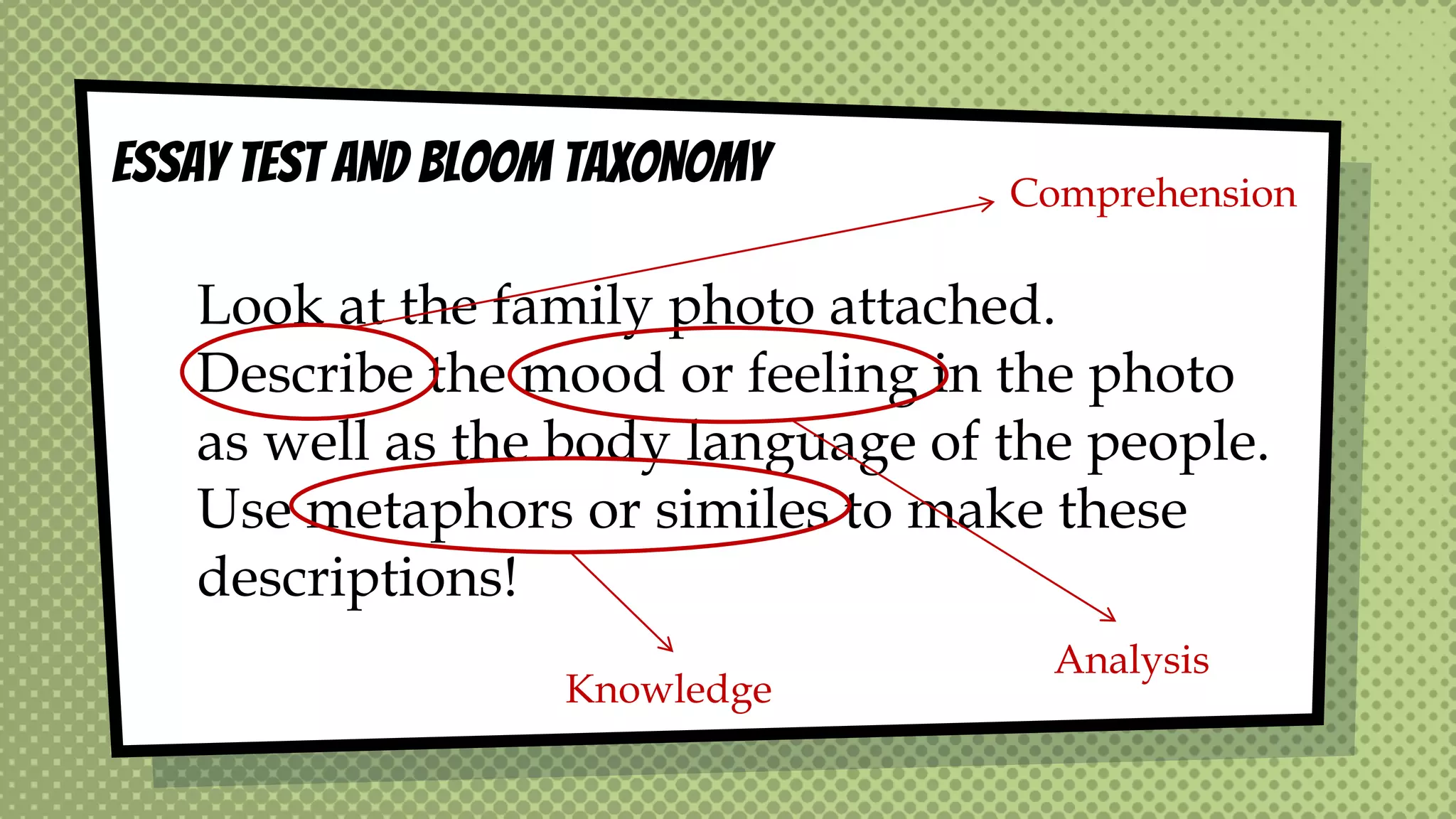
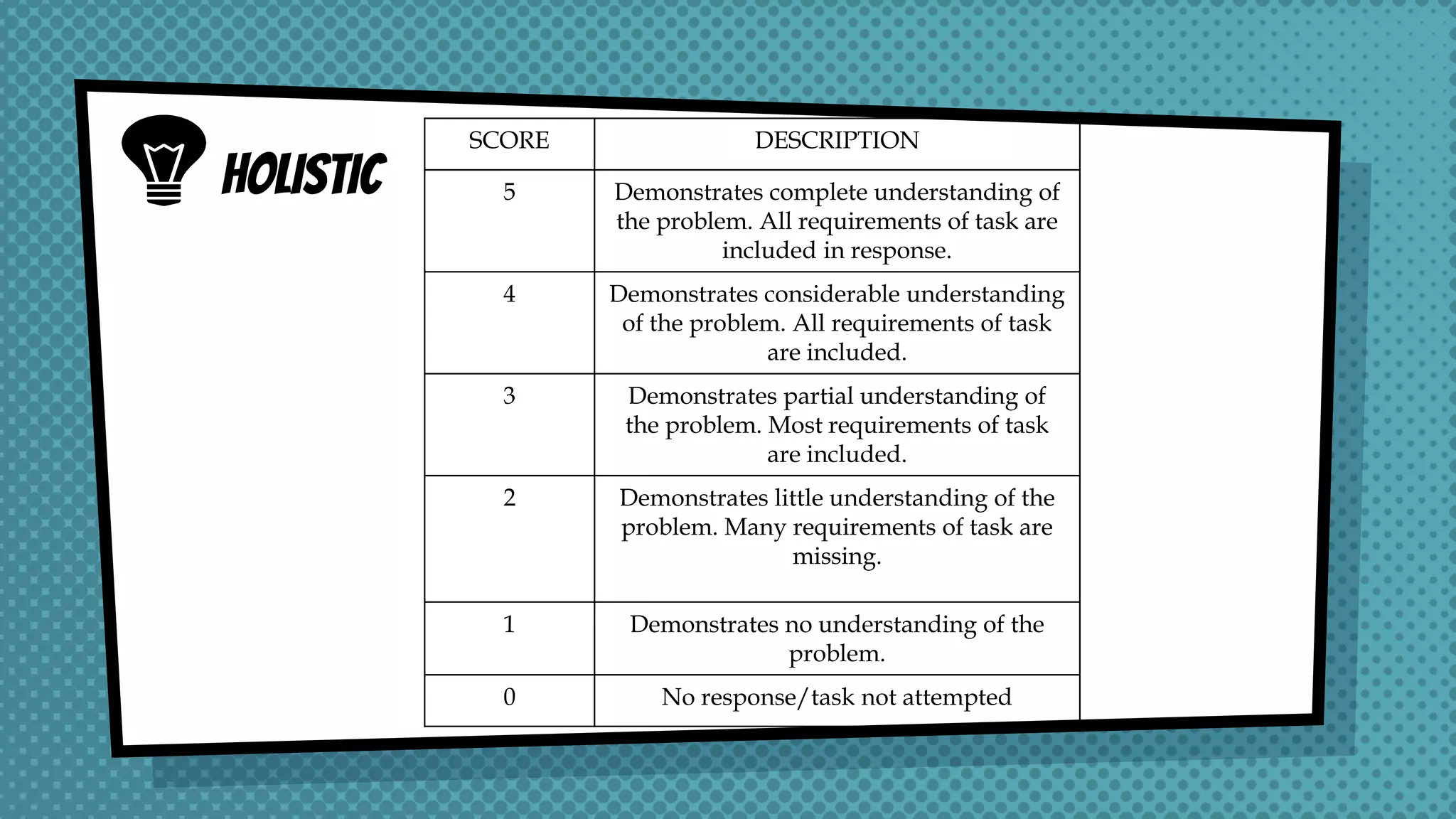
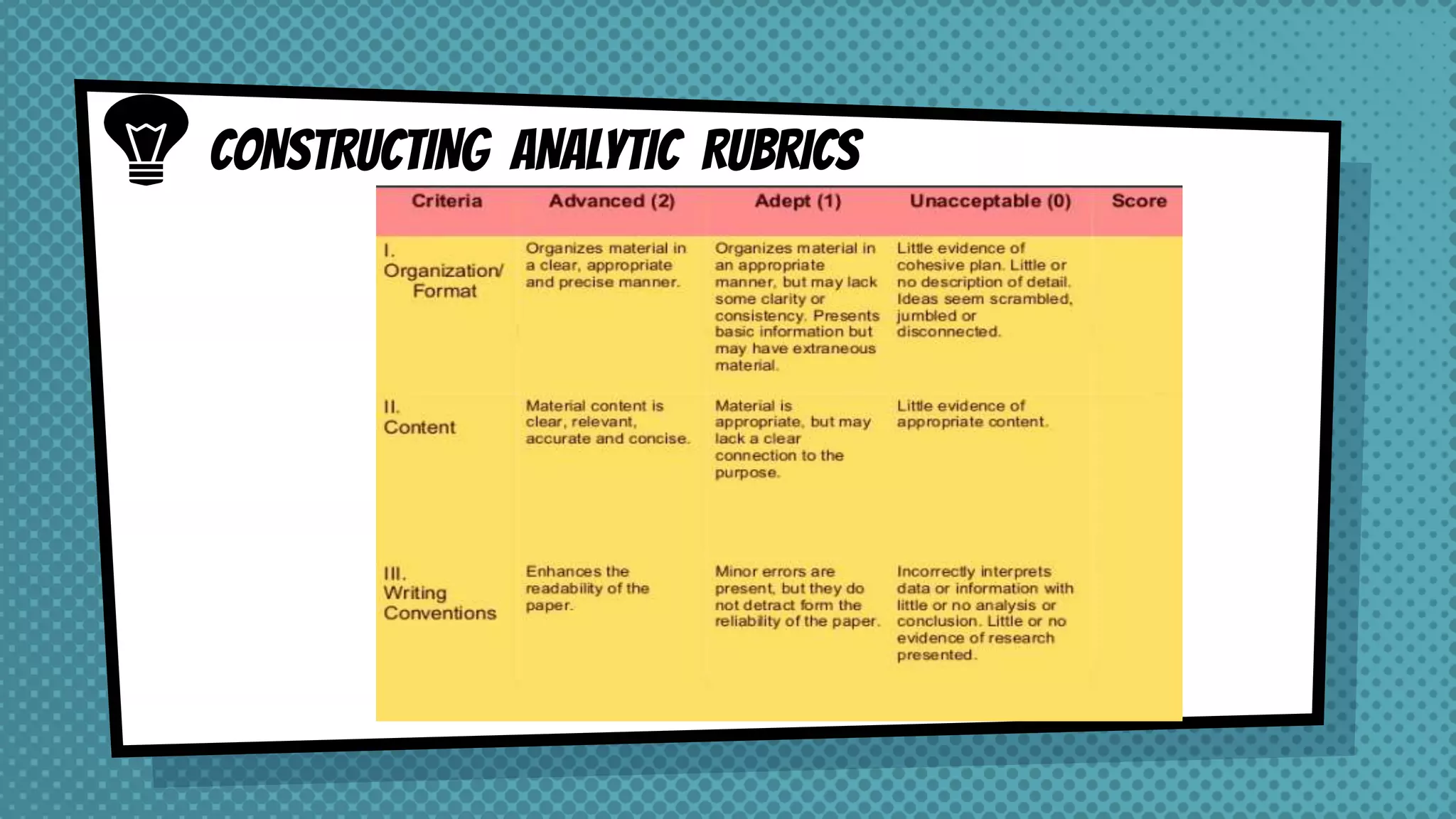
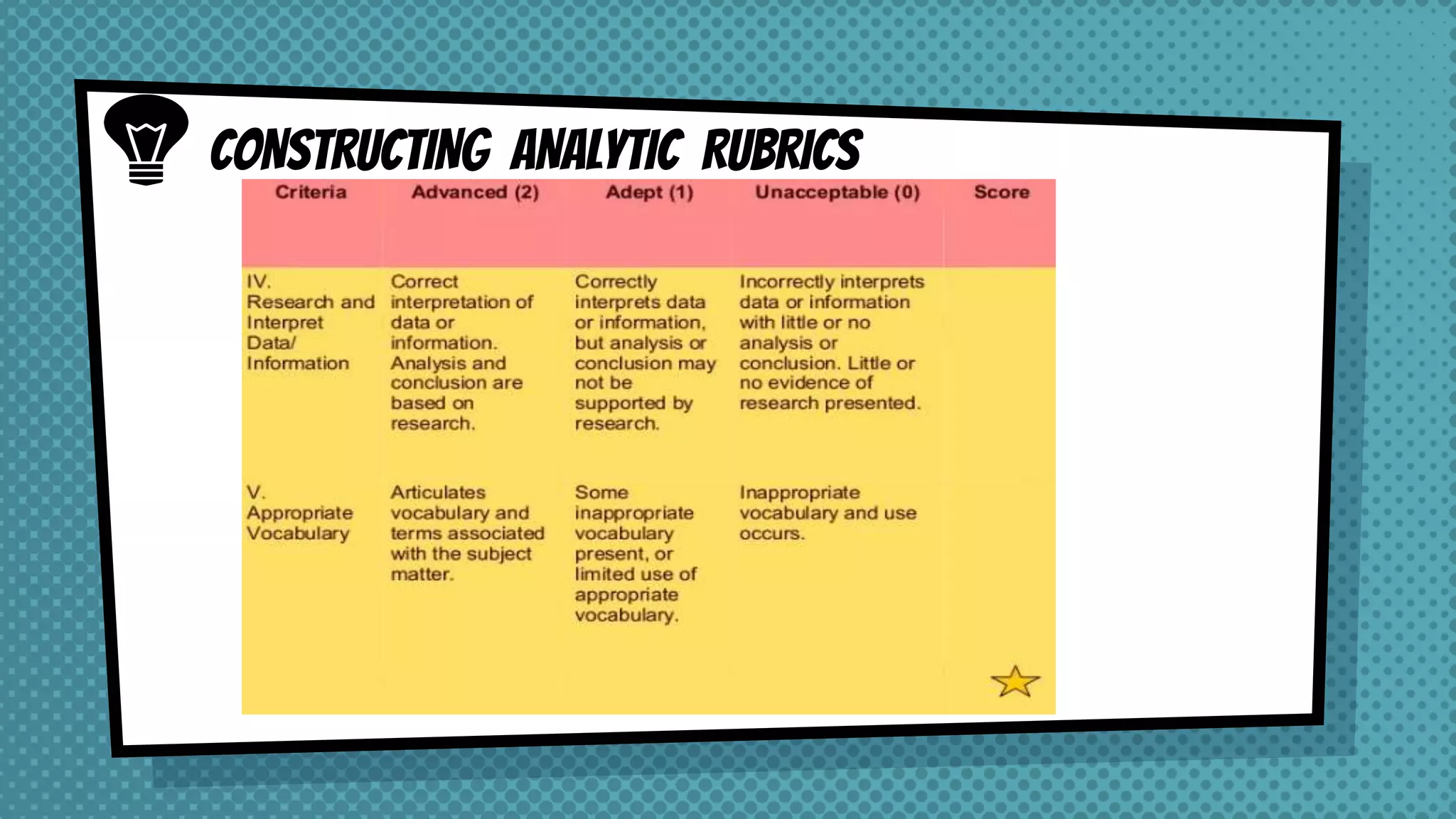
The document discusses objective and essay tests, outlining their definitions, types, strengths, and weaknesses. Objective tests can be scored instantly and include formats like true/false, multiple choice, and completion questions, while essay tests allow for elaborative answers but are more challenging to grade. The document highlights the importance of each testing method in assessing student knowledge and higher-order thinking skills.