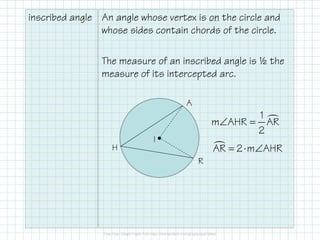
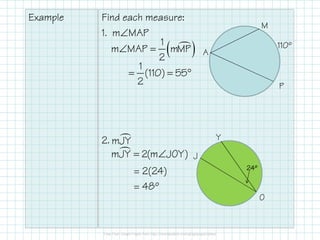
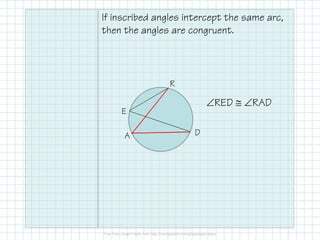
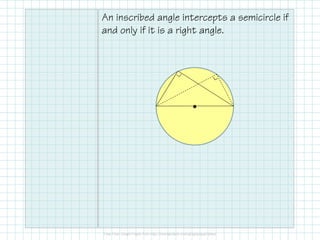
- An inscribed angle is half the measure of its intercepted arc. If inscribed angles intercept the same arc, they are congruent. An angle is a right angle if it intercepts a semicircle.
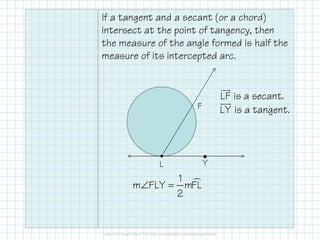
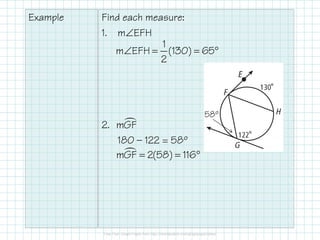
- For angles formed by intersecting secants or tangents at the point of tangency, the angle measure is half the intercepted arc.
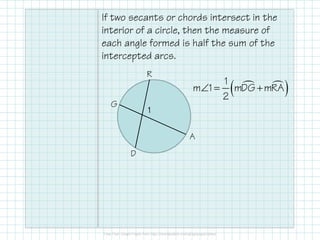
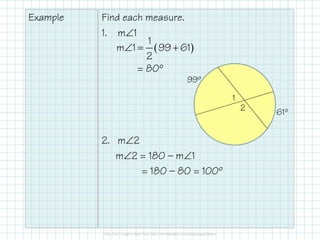
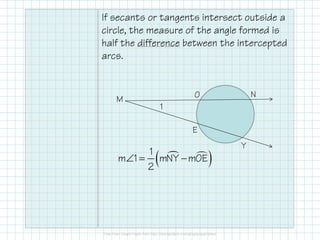
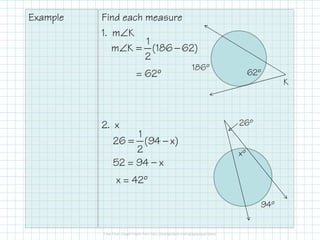
- When two secants or chords intersect in the interior of a circle, the angle measure is half the sum of the intercepted arcs. When they intersect outside the circle, the angle measure is half the difference of the intercepted arcs.
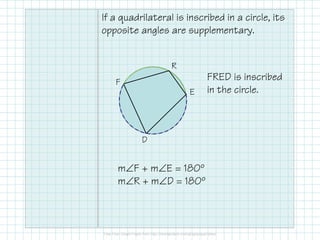
- Opposite angles of an inscribed quadrilateral are supplementary.