Embed presentation
Downloaded 1,670 times




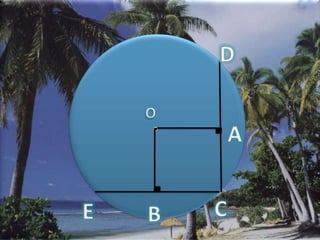



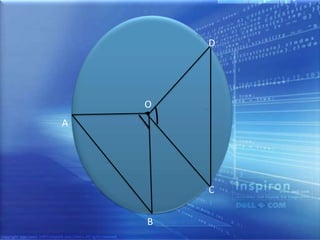




A circle is defined as all points in a plane that are equidistant from a fixed center point. The center point is called the center of the circle, and the fixed distance from the center is called the radius. The longest chord that can be drawn through the center is the diameter. If two chords of a circle are equal in length, then their distances from the center are also equal, as proven using the Side-Side-Side congruence rule for triangles.











