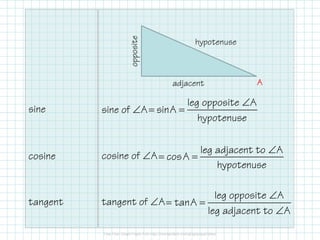
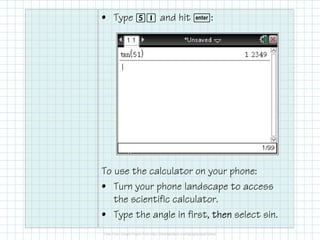
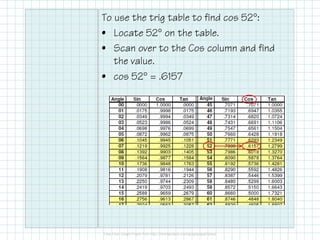
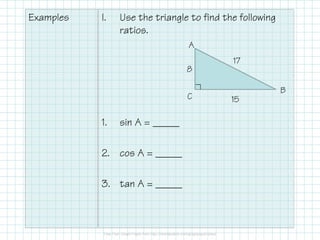
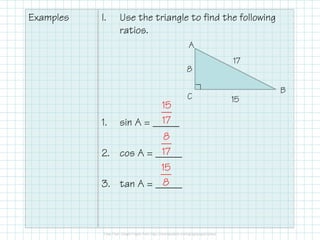
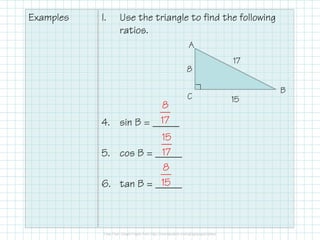
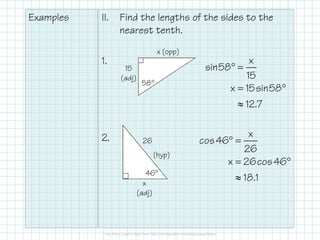
The document covers foundational concepts in trigonometry, focusing on the definitions and application of sine, cosine, and tangent ratios as well as their inverses. It explains how to solve for missing sides or angles in right triangles using either calculators or trig tables, emphasizing the importance of memorizing these ratios along with mnemonic aids. Additionally, it provides examples to demonstrate how to calculate these ratios and solve related problems.