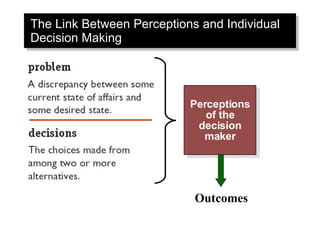
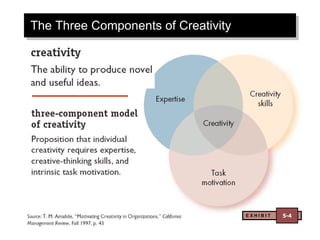
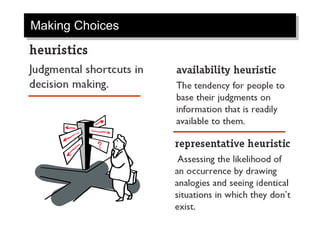
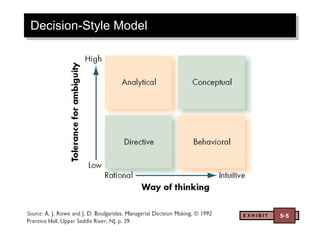
The document discusses decision making and creativity. It outlines the rational decision making model and its assumptions. It also discusses the three components of creativity. Additionally, it examines how decisions are actually made in organizations, considering factors like problem identification, alternative development, and organizational constraints. Cultural differences in decision making and ethics are also briefly covered.