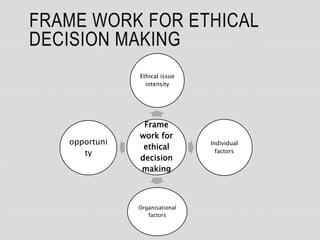
This document outlines an ethical decision-making process presented by Anandu K P. It begins by defining ethics as dealing with ideas about good and bad behavior or what is morally right and wrong. When faced with an ethical dilemma, this process helps determine the right course of action. The framework considers ethical issue intensity, individual factors like age and experience, and organizational factors like culture. The 7-step process involves identifying the problem, collecting information, evaluating alternatives, making a decision, acting, and reviewing the action and consequences.