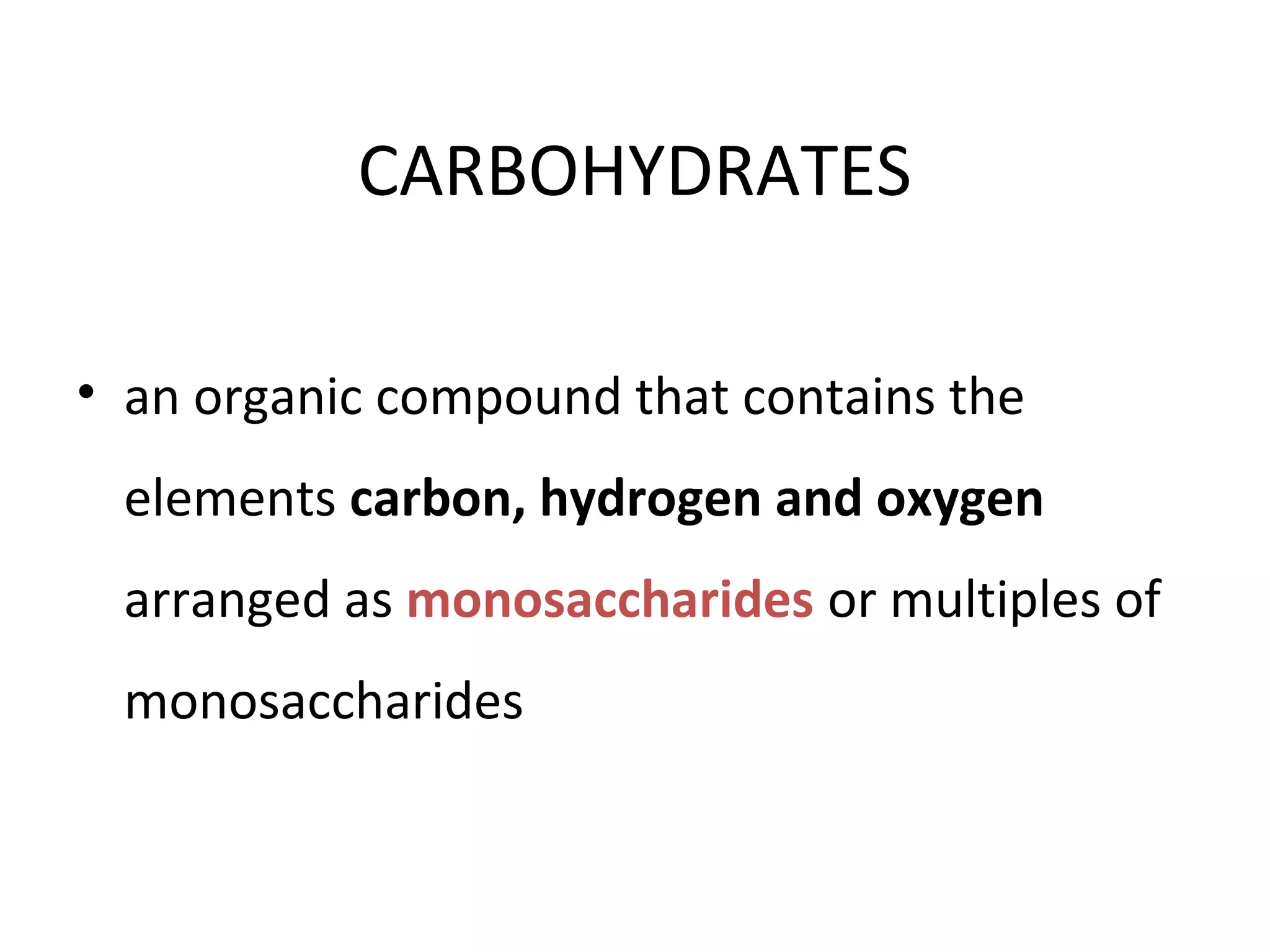
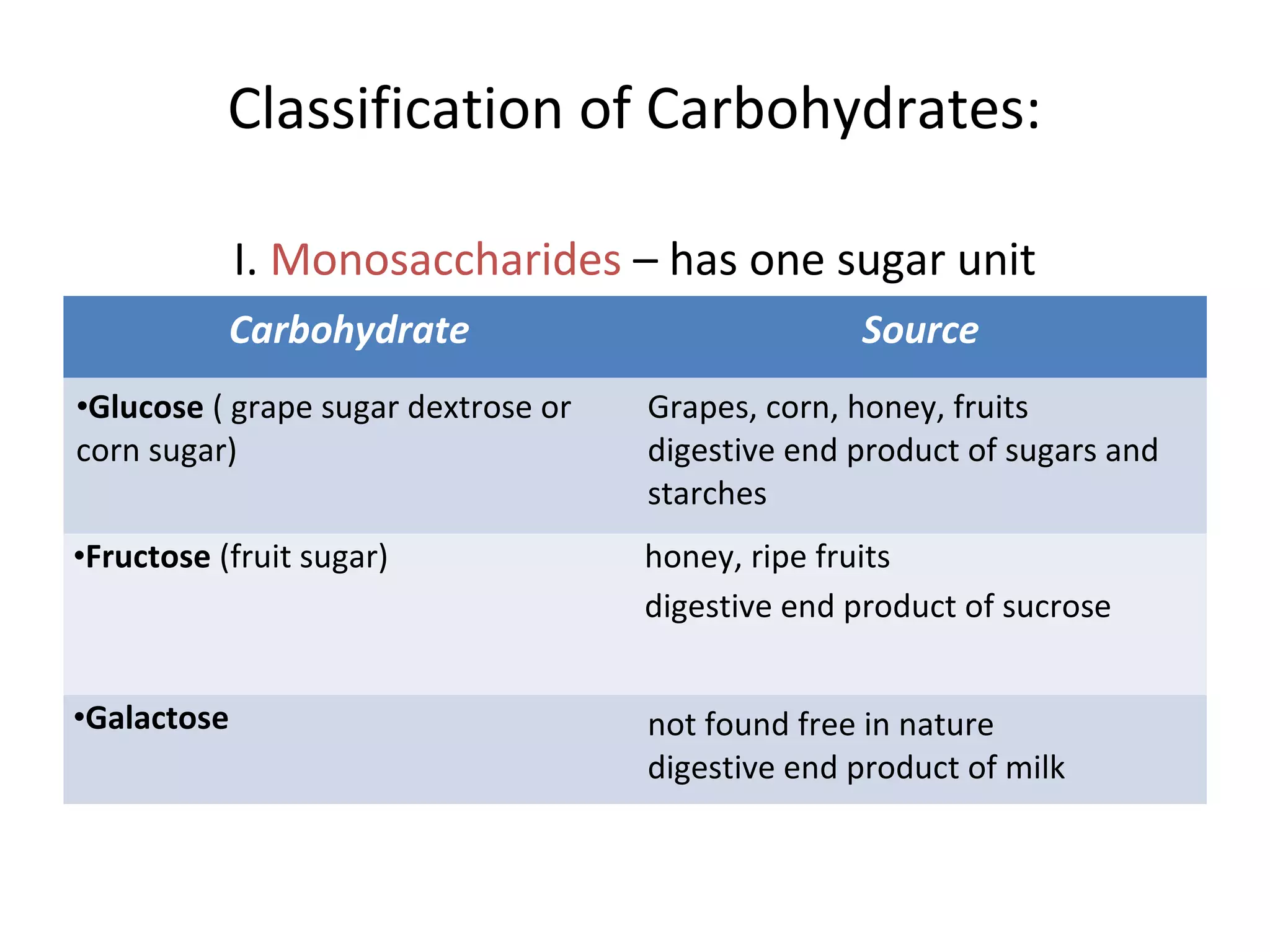
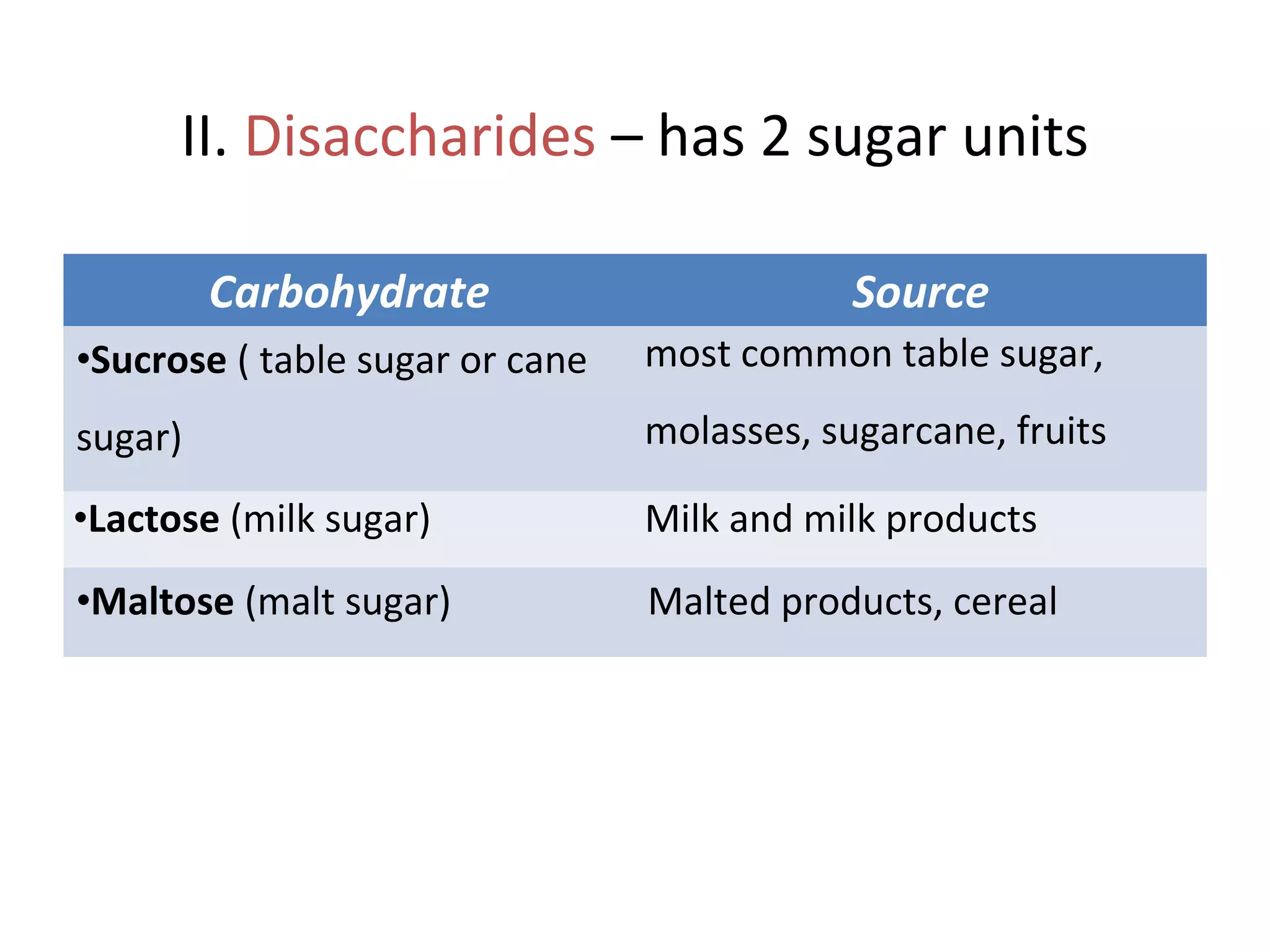
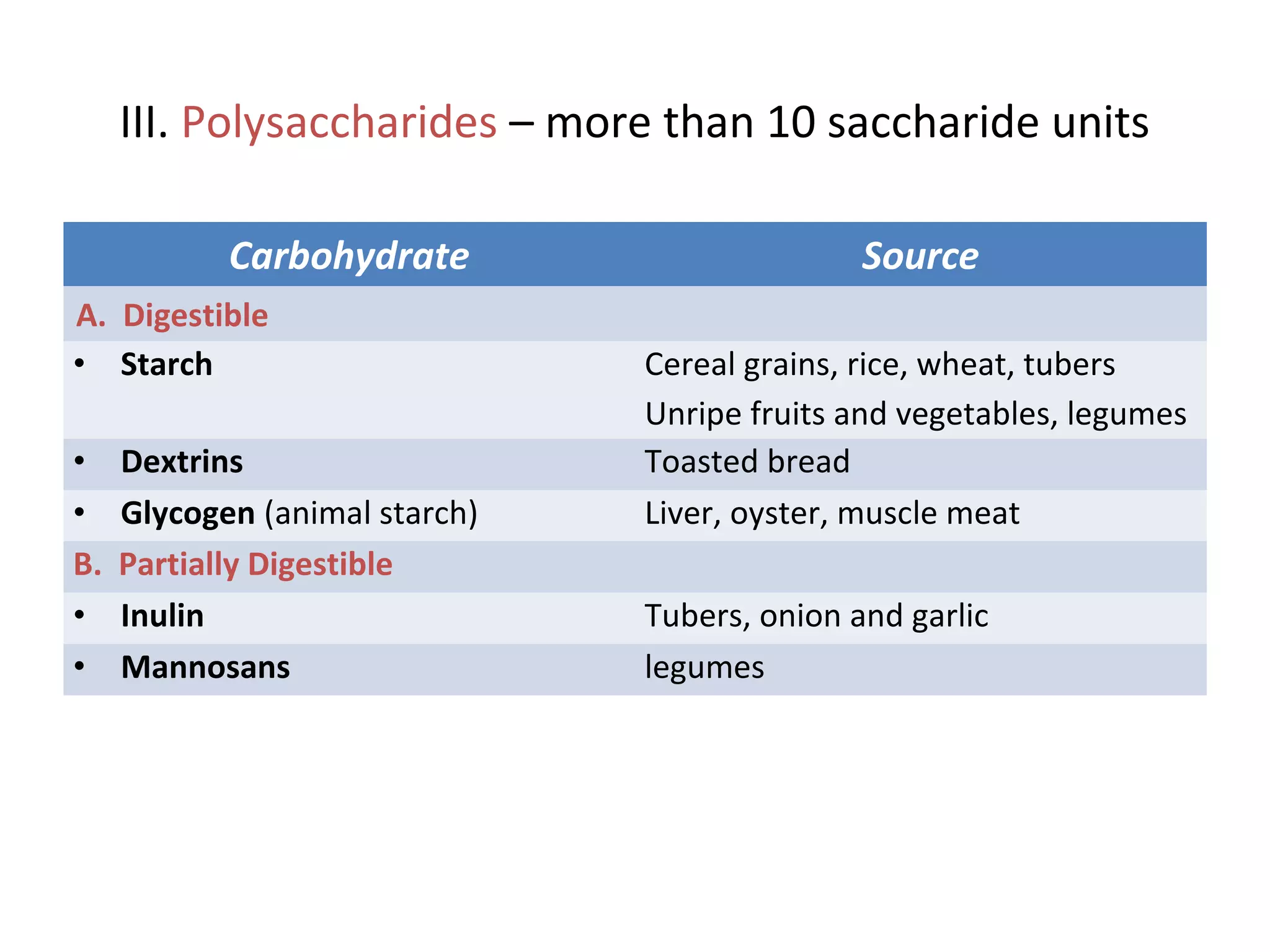
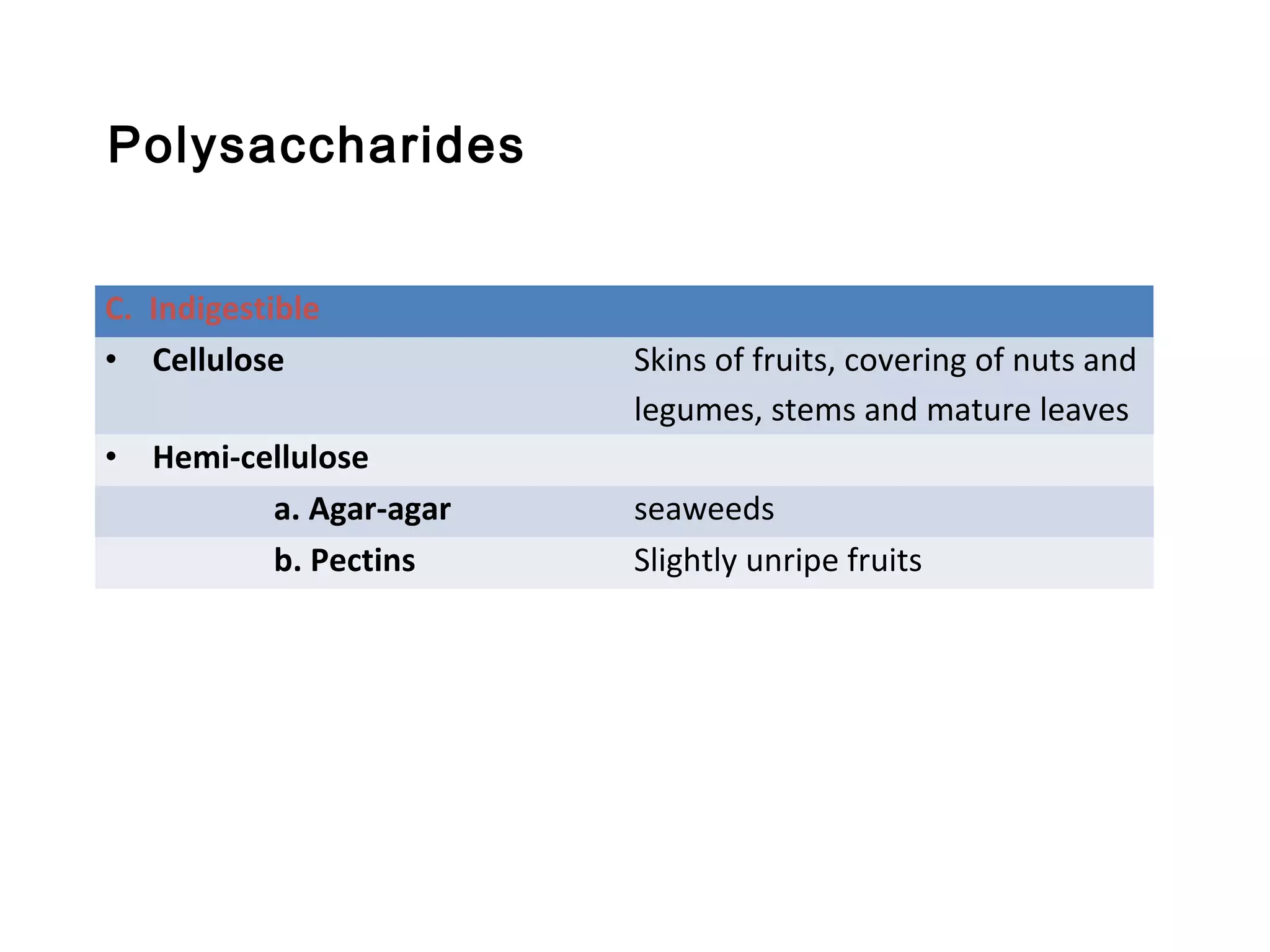
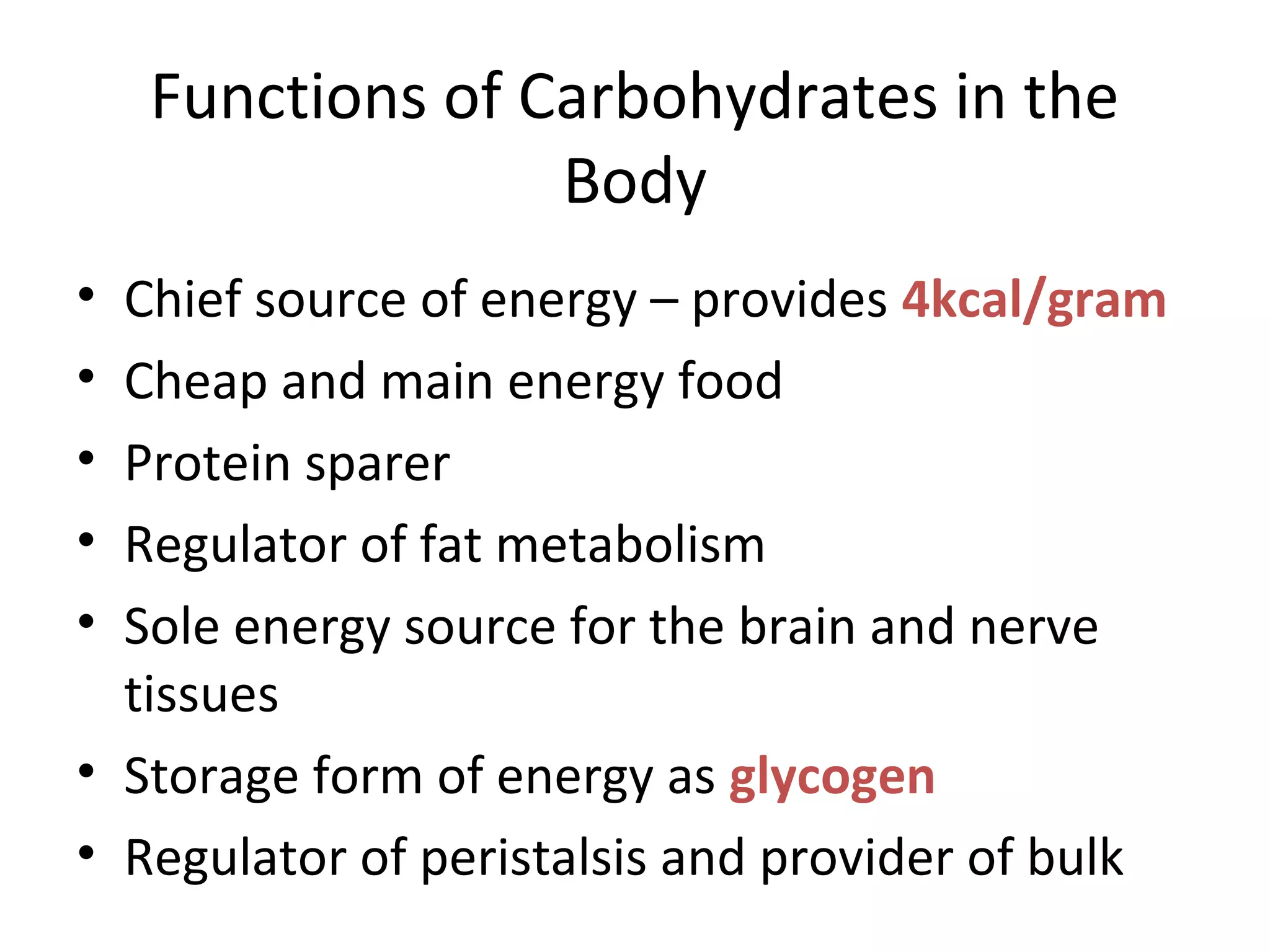
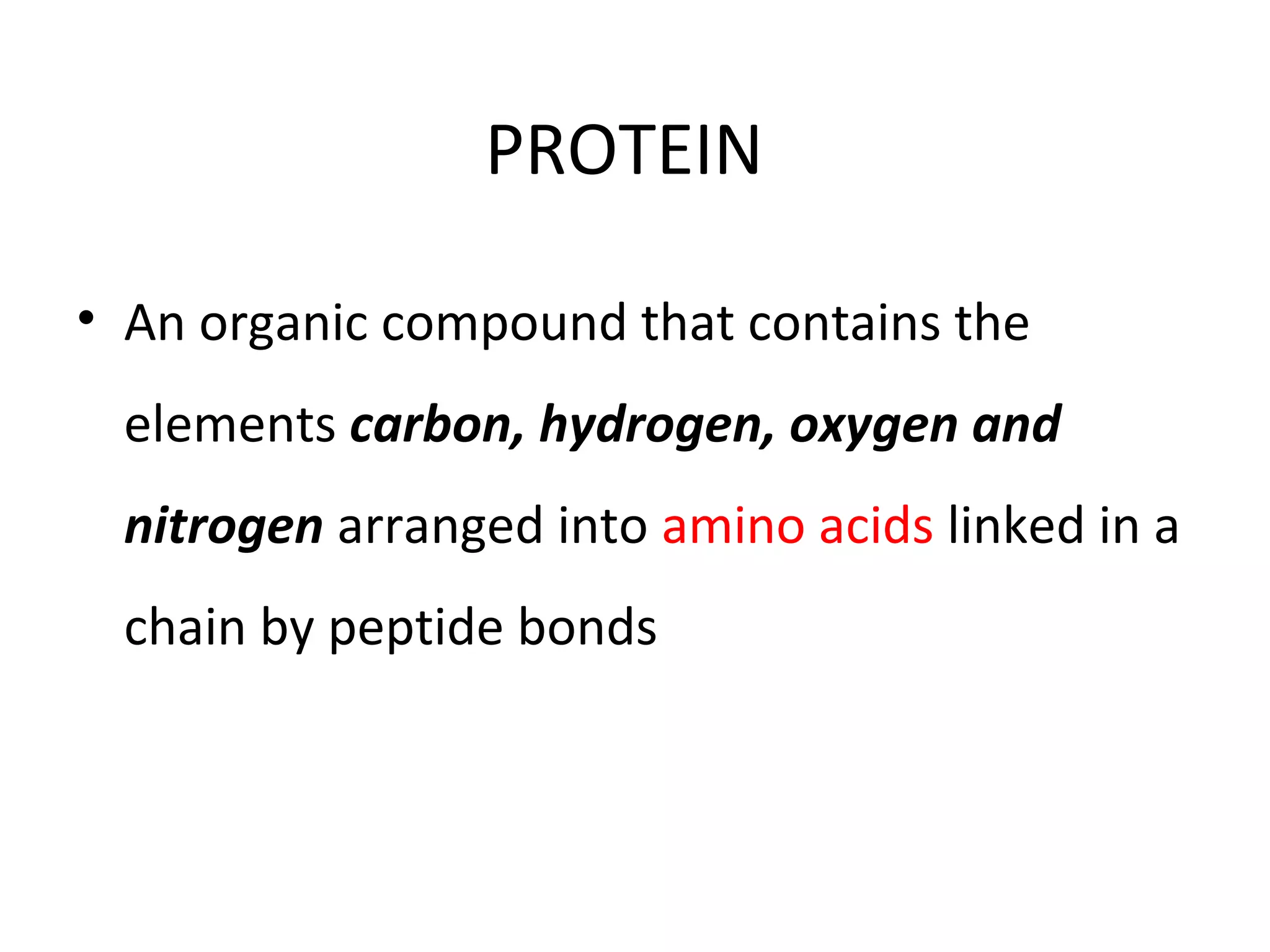
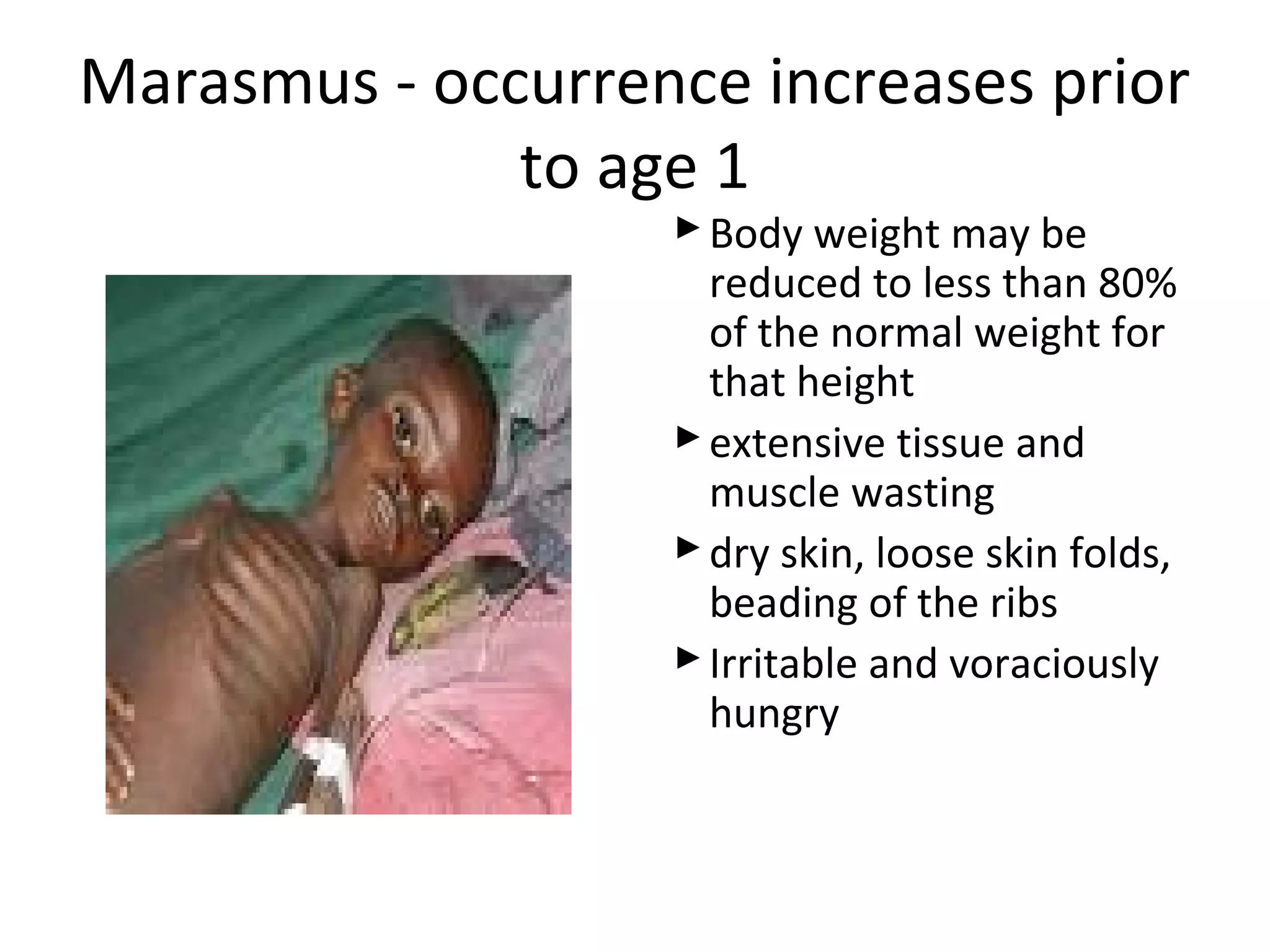
This document discusses the nutrients carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids. It defines each nutrient and classifies them into different types. Carbohydrates are classified into monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides. Proteins are made of amino acids and are classified as complete, incomplete, or essential/nonessential. Lipids contain fatty acids and are classified by degree of saturation. The document also describes the functions of each nutrient in the body.