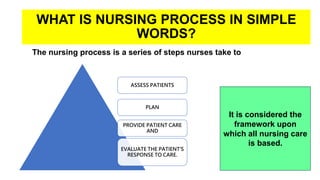
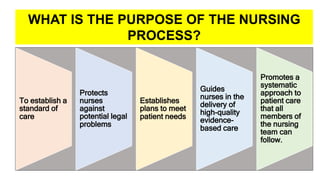
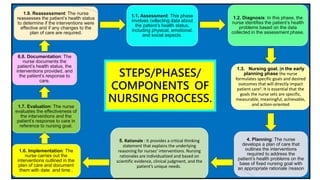
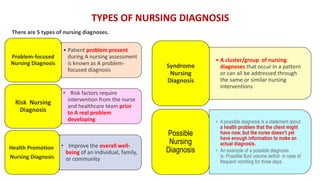
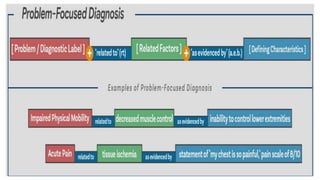
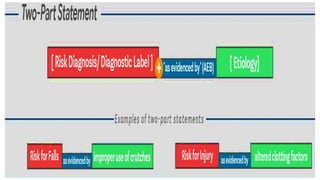
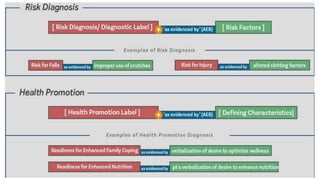
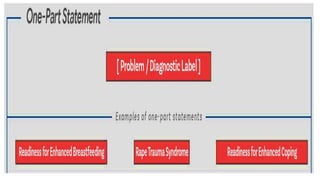
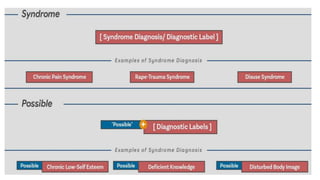
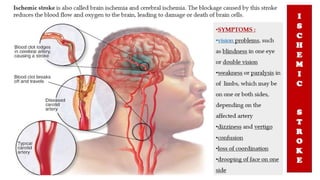
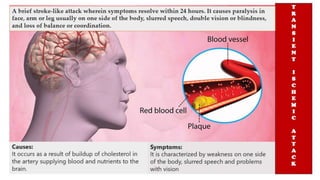
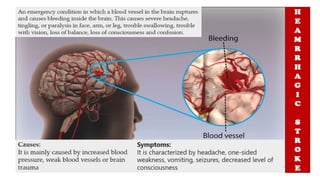
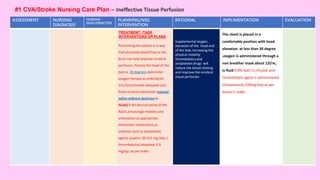
The document discusses the nursing process applied in stroke management, outlining its definition, development, and key components such as assessment, diagnosis, planning, implementation, and evaluation. It emphasizes the importance of evidence-based practice and critical thinking in patient care, alongside describing common nursing diagnoses associated with stroke patients. Additionally, it presents a case scenario illustrating the nursing process in action for a stroke patient.