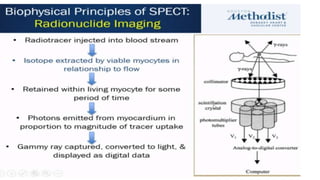
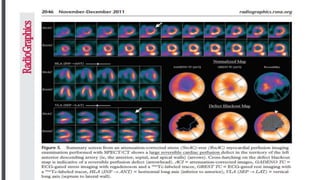
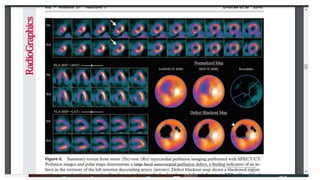
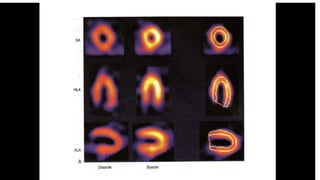
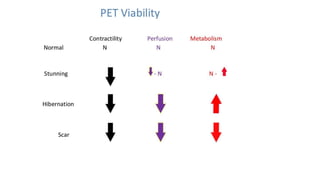
Nuclear imaging techniques like SPECT and PET scans use radioactive tracers to evaluate myocardial perfusion and function. SPECT involves injecting radioactive materials like thallium or technetium intravenously, which accumulate in heart muscle cells and are detected by a gamma camera. Images are obtained at rest and after stress to identify any reduced radiotracer uptake indicating ischemia. PET scans use tracers like rubidium or ammonia to assess perfusion, or FDG to evaluate glucose metabolism in the heart muscle. These nuclear imaging modalities can detect coronary artery disease, evaluate viability after interventions, and predict future cardiac risks.