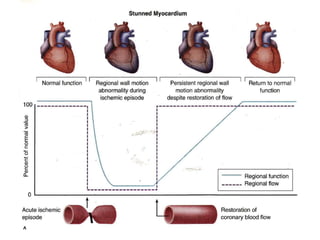
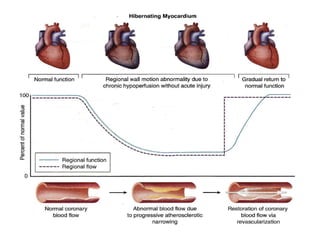
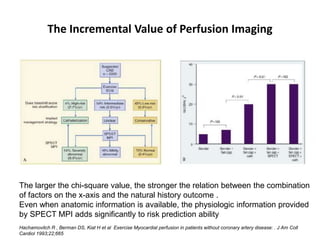
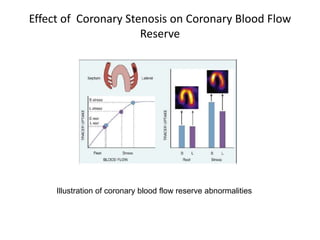
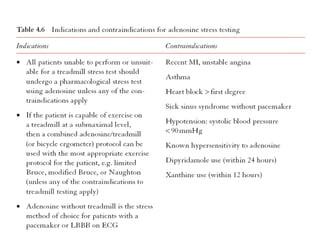
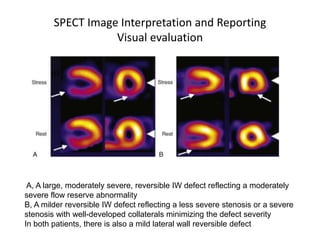
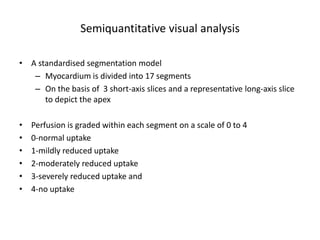
This document provides an overview of nuclear cardiology techniques used in the assessment of coronary artery disease (CAD). It discusses the history and development of nuclear medicine imaging including planar imaging and SPECT/PET. Key aspects summarized are:
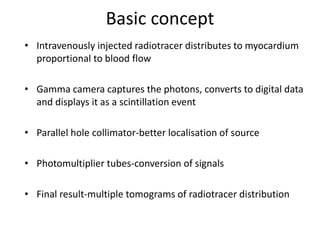
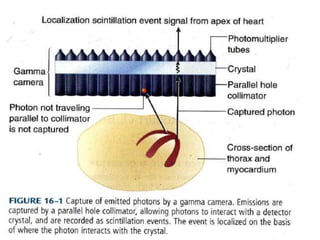
1. SPECT imaging involves injection of radiotracers like thallium-201 or technetium-99m which distribute to the myocardium proportional to blood flow. Gamma photons are detected and reconstructed to provide 3D images of radiotracer distribution.
2. PET imaging uses positron-emitting radiotracers like rubidium-82 or ammonia-13 for perfusion and fluorodeoxyglucose for metabolism. It provides higher resolution functional imaging

















































![Limitations
• Requirement of an on-site cyclotron for [13N]ammonia
• High cost of monthly generator replacement for 82Rb
• Relatively short half-lives of both 82Rb and [13N]ammonia limit the utility
of PET to patients undergoing pharmacologic stress only](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nuclearcardiology-181123083411/85/Nuclear-cardiology-66-320.jpg)