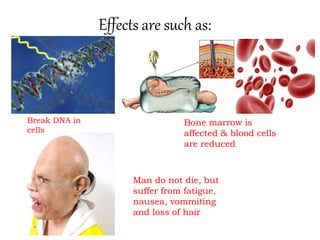
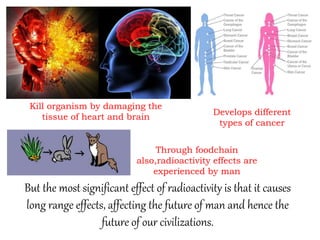
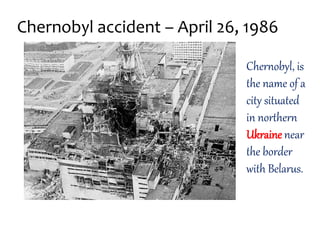
This document presents information on nuclear hazards from a group presentation. It discusses radioactive pollution and its sources from natural occurrences like cosmic rays and radioactive materials in the earth's crust, as well as man-made sources such as nuclear power plants, nuclear weapons, and mining. Nuclear accidents can cause meltdowns when temperatures rise too high in nuclear reactors. The effects of nuclear hazards include cancer, reduced lifespan, and genetic mutations in organisms and future generations. Examples of major nuclear accidents provided are at Three Mile Island, Goiania, Chernobyl, and Fukushima. Preventing nuclear hazards involves containment, isolation of wastes, and dilution of wastes.