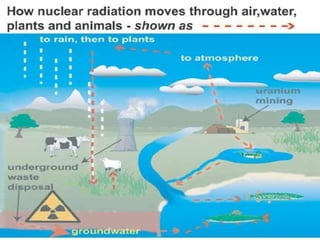
Radiation pollution is caused by radioactive substances released into the environment through human activities like nuclear power plants, nuclear weapons, uranium mining, and medical procedures. There are two types of radiation - ionizing radiation which can damage DNA and cause cancer, and non-ionizing radiation which is generally less dangerous. Exposure to radiation can cause health effects ranging from skin irritation to death depending on the dose received and parts of the body exposed. Proper disposal of nuclear waste and safety measures around nuclear materials and accidents can help prevent radiation pollution.