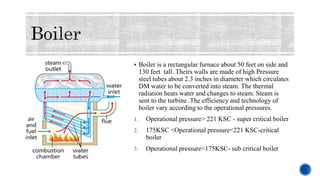
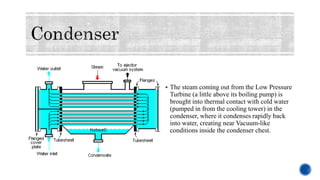
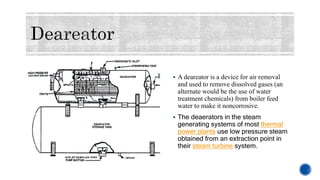
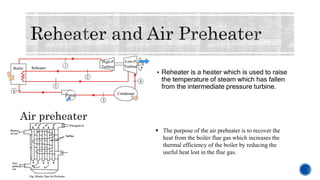
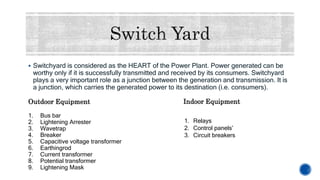
The document provides details about Rahul Raj's summer internship at NTPC Barh Super Thermal Power Station. It summarizes that NTPC is India's largest power generation company operating 55 power stations. NTPC Barh has a generation capacity of 3,300 MW and uses coal from nearby mines to power steam turbines that drive electric generators. The document describes the various components of the power generation process including boilers, turbines, condensers, and switchyards that transmit power to the electricity grid.