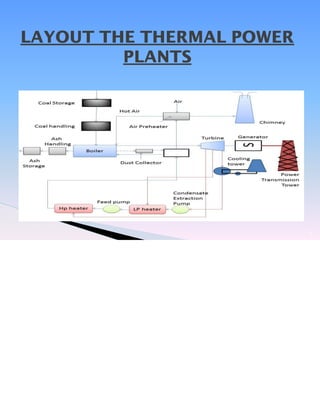
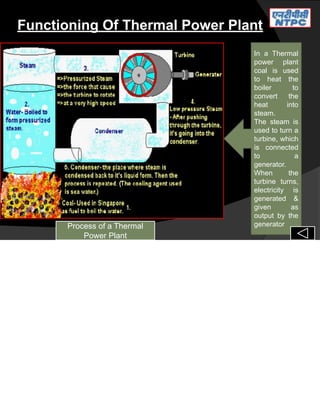
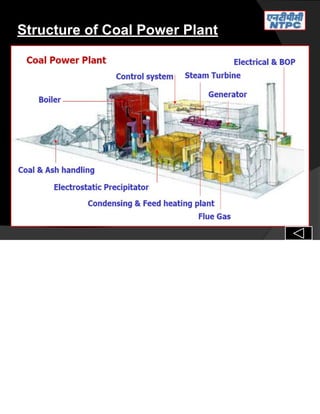
Shivam Dubey, a mechanical engineer, presented on thermal power plants for vocational training at NTPC Vindhyachal in Singrauli, Madhya Pradesh. The presentation covered the key components and processes within a thermal power plant, including the coal handling plant, main plant (boiler, steam turbine, cooling tower, generator), ash handling plant, and safety procedures. It discussed the flow of coal from source to combustion in the furnace, generation of steam to power the turbine and generator, and production of electricity, highlighting each major component along the process.