This document provides an introduction to the network simulator NS-2 and its scripting language OTcl. It discusses basics of OTcl like classes, objects, and methods. It provides examples of creating classes and objects in OTcl. It also explains the structure of an NS-2 simulation including creating the event scheduler, topology, sending data using UDP/TCP, and tracing outputs. Suggested readings on OTcl and NS-2 tutorials are provided at the end.



![Basics of OTcl - II
• Object initialization:
– set ctr [ new Counter ]
• ctr is an object of class Counter
• It calls the constructor to initialize the instance
variables.
• Method invocation:
– $ctr increment
• invokes the method increment of class Counter
– puts [ $ctr getValue ]
• invokes the method getValue of class Counter and
prints the value returned from the member function
NS-2/AN/Intro/ 5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ns2otcllab2-170531091214/85/Ns2-OTCL-PArt-II-5-320.jpg)

![Example – Class-Object (II)
NS-2/AN/Intro/ 7
# Create a mom and a kid object & set age for each
set mom [new Mom]
$mom set age 45
set kid [new Kid]
$kid set age 15
# Calling member function "greet" of each object
$mom greet
$kid greet
Output:
45 year old mom say:
How are you doing?
15 year old kid say:
what’s up dude?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ns2otcllab2-170531091214/85/Ns2-OTCL-PArt-II-7-320.jpg)

![Task I contd.
Class Integer -superclass Real
Integer instproc divide {x} {
... FILL IN ...
}
set realA [new Real 12.3]
set realB [new Real 0.5]
$realA multiply $realB
$realA divide $realB
set integerA [new Integer 12]
set integerB [new Integer 5]
$integerA multiply $integerB
$integerA divide $integerB
NS-2/AN/Intro/ 9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ns2otcllab2-170531091214/85/Ns2-OTCL-PArt-II-9-320.jpg)

![Creating the event scheduler
• Create event scheduler
– set ns [new Simulator]
• Schedule an event
– syntax: $ns at <time> <event>
– $ns at 5.0 “finish”
• Start Scheduler
– $ns run
NS-2/AN/Intro/ 11
proc finish {} {
global ns nf
close $nf
exec nam out.nam &
exit 0
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ns2otcllab2-170531091214/85/Ns2-OTCL-PArt-II-11-320.jpg)
![Tracing (outputs)
• Packet/Event Trace
– $ns trace-all[open out.tr w]
• NAM Trace (Network Animator)
– set nf [open out.nam w]
– $ns namtrace-all $nf
NS-2/AN/Intro/ 12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ns2otcllab2-170531091214/85/Ns2-OTCL-PArt-II-12-320.jpg)
![Creating topology
(Two nodes connected by a link)
• Creating nodes
– set n0 [$ns node]
– set n1 [$ns node]
• Creating link between
nodes
– syntax: $ns <link_type> <node1> <node2>
<bandwidth> <delay> <queueType>
– $ns duplexlink $n0 $n1 1Mb 10ms DropTail
NS-2/AN/Intro/ 13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ns2otcllab2-170531091214/85/Ns2-OTCL-PArt-II-13-320.jpg)
![Program for two node network
1. Create a file named
twoNode.tcl and add the
following contents in it.
set ns [new Simulator]
set nf [open twoNode.nam w]
$ns namtrace-all $nf
set n0 [$ns node]
set n1 [$ns node]
$ns duplex-link $n0 $n2
100Mb 5ms DropTail
$ns run
NS-2/AN/Intro/ 14
2. Save and exit from the editor,
Now execute the program with
following command in command
line
ns twoNode.tcl
3. This will generate
twoNode.nam. To see the
visualization, issue the following
command in command line
nam twoNode.nam &](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ns2otcllab2-170531091214/85/Ns2-OTCL-PArt-II-14-320.jpg)


![Sending data (UDP)
• Create UDP source agent (transport
connection)
– set udp [new Agent/UDP]
– $ns attach-agent $n0 $udp
• Create UDP sink agent
– set null [new Agent/Null]
– $ns attach-agent $n1 $null
• Connect two transport (source-sink) agents
– $ns connect $udp $null
NS-2/AN/Intro/ 17](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ns2otcllab2-170531091214/85/Ns2-OTCL-PArt-II-17-320.jpg)
![Sending data contd.
• Create CBR traffic source on the top of UDP
agent (Application)
– set cbr [new Application/Traffic/CBR]
– $cbr attach-agent $udp
• Start and stop of data transmission
– $ns at 0.5 “$cbr start”
– $ns at 4.5 “$cbr stop”
NS-2/AN/Intro/ 18](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ns2otcllab2-170531091214/85/Ns2-OTCL-PArt-II-18-320.jpg)
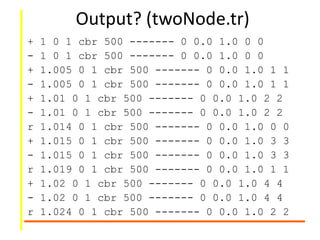
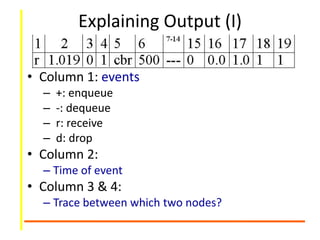
![Complete Program
set ns [new Simulator]
set n0 [$ns node]
set n1 [$ns node]
$ns trace-all [open
twoNode.tr w]
set nf [open twoNode.nam w]
$ns namtrace-all $nf
$ns duplex-link $n0 $n1
100Kb 10ms DropTail
set udp [new Agent/UDP]
$ns attach-agent $n0 $udp
set null [new Agent/Null]
$ns attach-agent $n1 $null
$ns connect $udp $null
NS-2/AN/Intro/ 19
set cbr [new
Application/Traffic/CBR]
$cbr attach-agent $udp
$ns at 0.1 “$cbr start”
$ns at 2.35 “$cbr stop”
$ns at 2.4 “finish”
proc finish {} {
global nf ; close $nf
exec nam twoNode.nam &
exit 0
}
$ns run](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ns2otcllab2-170531091214/85/Ns2-OTCL-PArt-II-19-320.jpg)
![Sending data (TCP)
• Create TCP agent and attach it to the node
– set tcp0 [new Agent/TCP]
– $ns attach-agent $n0 $tcp0
• Create a Null Agent and attach it to the node
– set null0 [new Agent/TCPSink]
– $ns attach-agent $n1 $null0
• Connect the agents
– $ns connect $tcp0 $null0
• Trafic on the top of TCP (FTP or Telnet)
– set ftp [new Application/FTP]
– $ftp attach-agent $tcp0 OR
– set telnet [new Application/Telnet]
– $telnet attach-agent $tcp0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ns2otcllab2-170531091214/85/Ns2-OTCL-PArt-II-20-320.jpg)