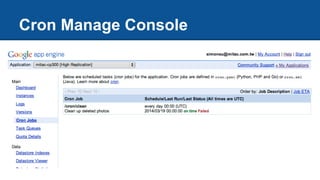
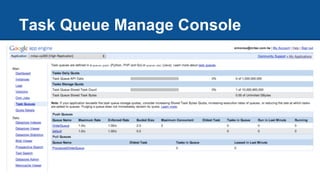
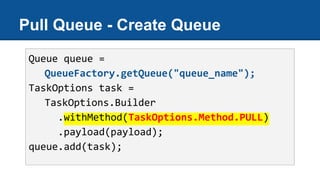
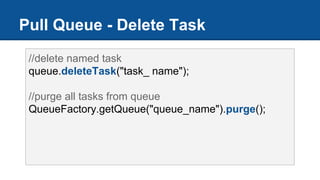
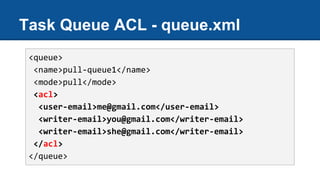
The document discusses Google App Engine task queues and cron jobs. It provides examples of creating and using default and named push queues, as well as pull queues. It explains how to add tasks, lease tasks from pull queues, and delete tasks. It also covers using task queues within transactions. Additionally, it demonstrates configuring and using cron jobs to schedule recurring tasks.





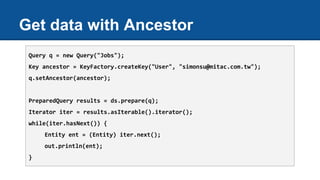


![Memcache - operation
MemcacheService cache = MemcacheServiceFactory.getMemcacheService();
cache.setErrorHandler(
ErrorHandlers.getConsistentLogAndContinue(Level.INFO));
// read from cache
value = (byte[]) cache.get(key);
// save to cache
if (value == null) {
// ........
cache.put(key, value);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gaedeveloper-day3-140323124938-phpapp02/85/Google-App-Engine-Developer-Day3-10-320.jpg)
![Async memcache - get
// Using the asynchronous cache
AsyncMemcacheService asyncCache =
MemcacheServiceFactory.getAsyncMemcacheService();
asyncCache.setErrorHandler(
ErrorHandlers.getConsistentLogAndContinue(Level.INFO));
// read from cache
Future<Object> futureValue = asyncCache.get(key);
// ... do other work in parallel to cache retrieval
value = (byte[]) futureValue.get();](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gaedeveloper-day3-140323124938-phpapp02/85/Google-App-Engine-Developer-Day3-11-320.jpg)


![Using jcache - get & put
String key; // ...
byte[] value; // ...
// Put the value into the cache.
cache.put(key, value);
// Get the value from the cache.
value = (byte[]) cache.get(key);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gaedeveloper-day3-140323124938-phpapp02/85/Google-App-Engine-Developer-Day3-14-320.jpg)
![Testing with ab benchmark
ab -c 50 -n 50 http://[app-address]/[servlet_path]
or
ab -c 50 -t 50 http://[app-address]/[servlet_path]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gaedeveloper-day3-140323124938-phpapp02/85/Google-App-Engine-Developer-Day3-15-320.jpg)





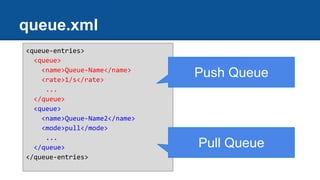

![Detail Configure
● Task queues use token bucket algorithm [ref]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gaedeveloper-day3-140323124938-phpapp02/85/Google-App-Engine-Developer-Day3-24-320.jpg)




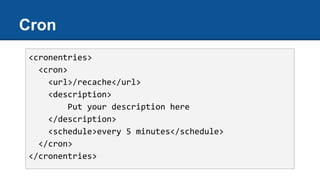
![● every 12 hours
● every 5 minutes from 10:00 to 14:00
● 2nd,third mon,wed,thu of march 17:00
● every monday 09:00
● 1st monday of sep,oct,nov 17:00
● every day 00:00
● every N (hours|mins|minutes) ["from" (time) "to" (time)]
● every 2 hours synchronized
Cron Schedule Format](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gaedeveloper-day3-140323124938-phpapp02/85/Google-App-Engine-Developer-Day3-33-320.jpg)