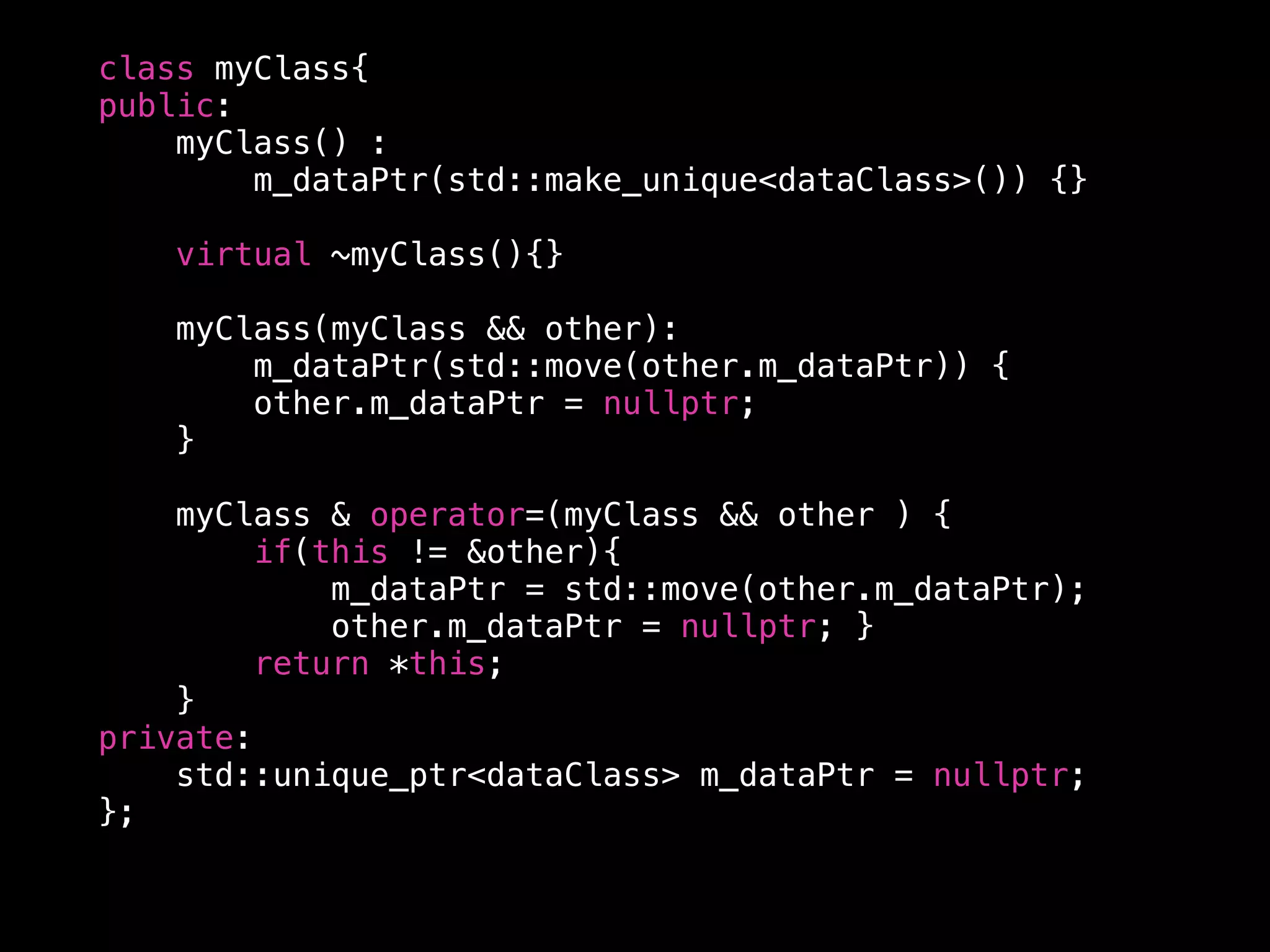
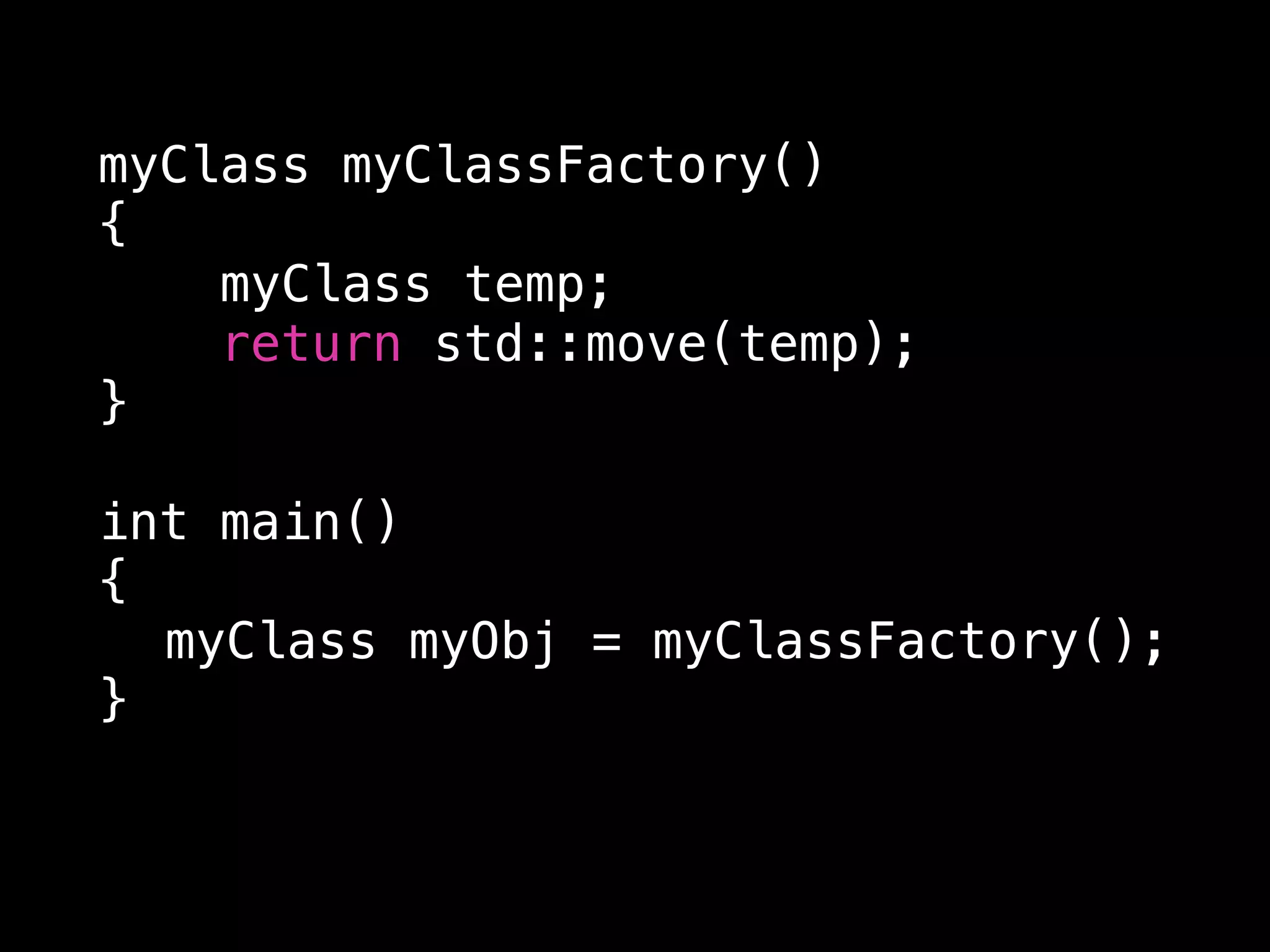
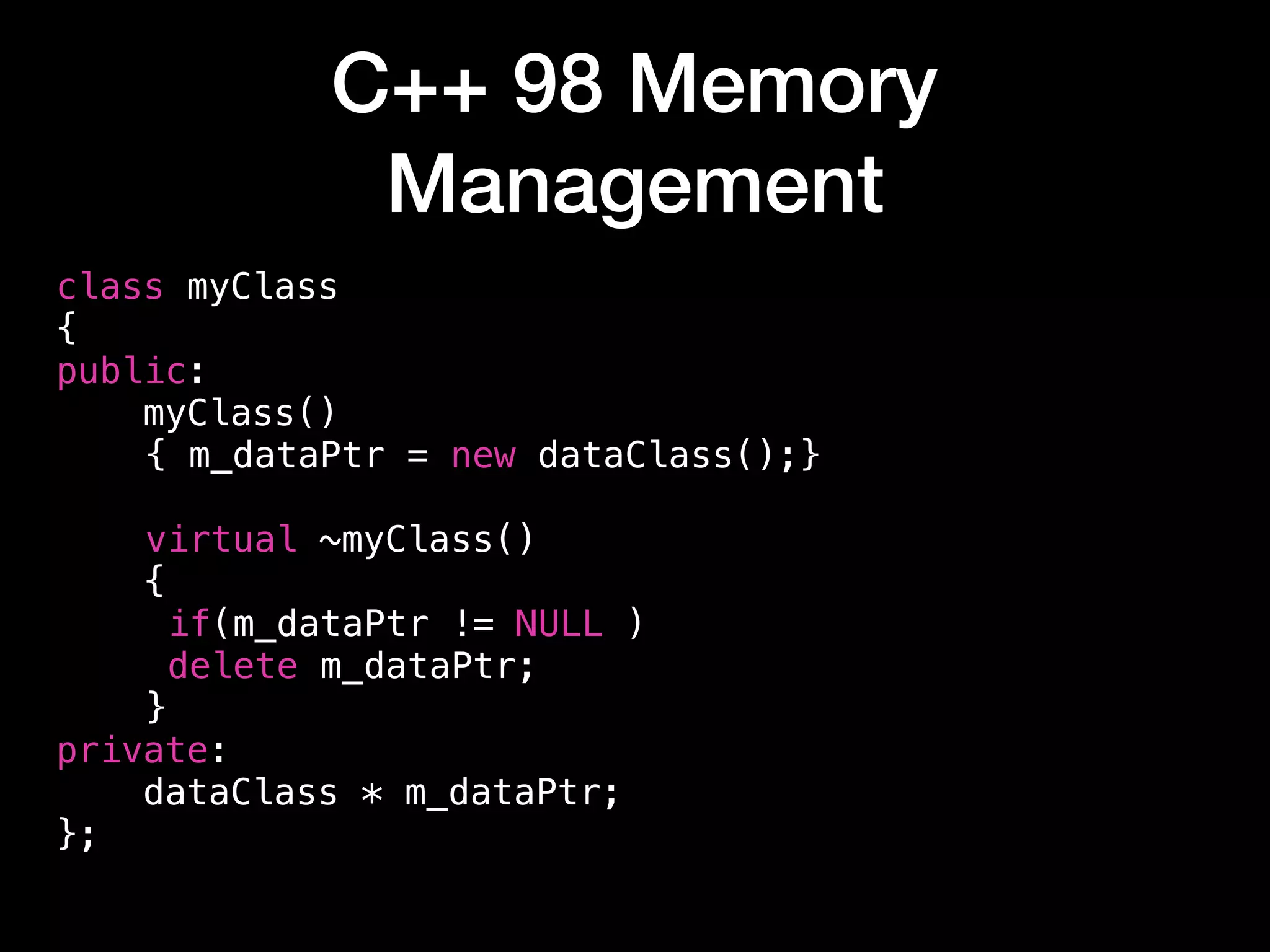
The document discusses modern C++ memory management techniques as presented by Alan Uthoff, a game developer and founder of Swordpoint Studio. It highlights improvements in memory management from C++98 to C++17, emphasizing the use of smart pointers like std::unique_ptr and std::shared_ptr, as well as features such as move semantics and copy elision. Additionally, the document provides examples of factory functions and working with legacy code while introducing std::any and std::optional for more flexible type handling.


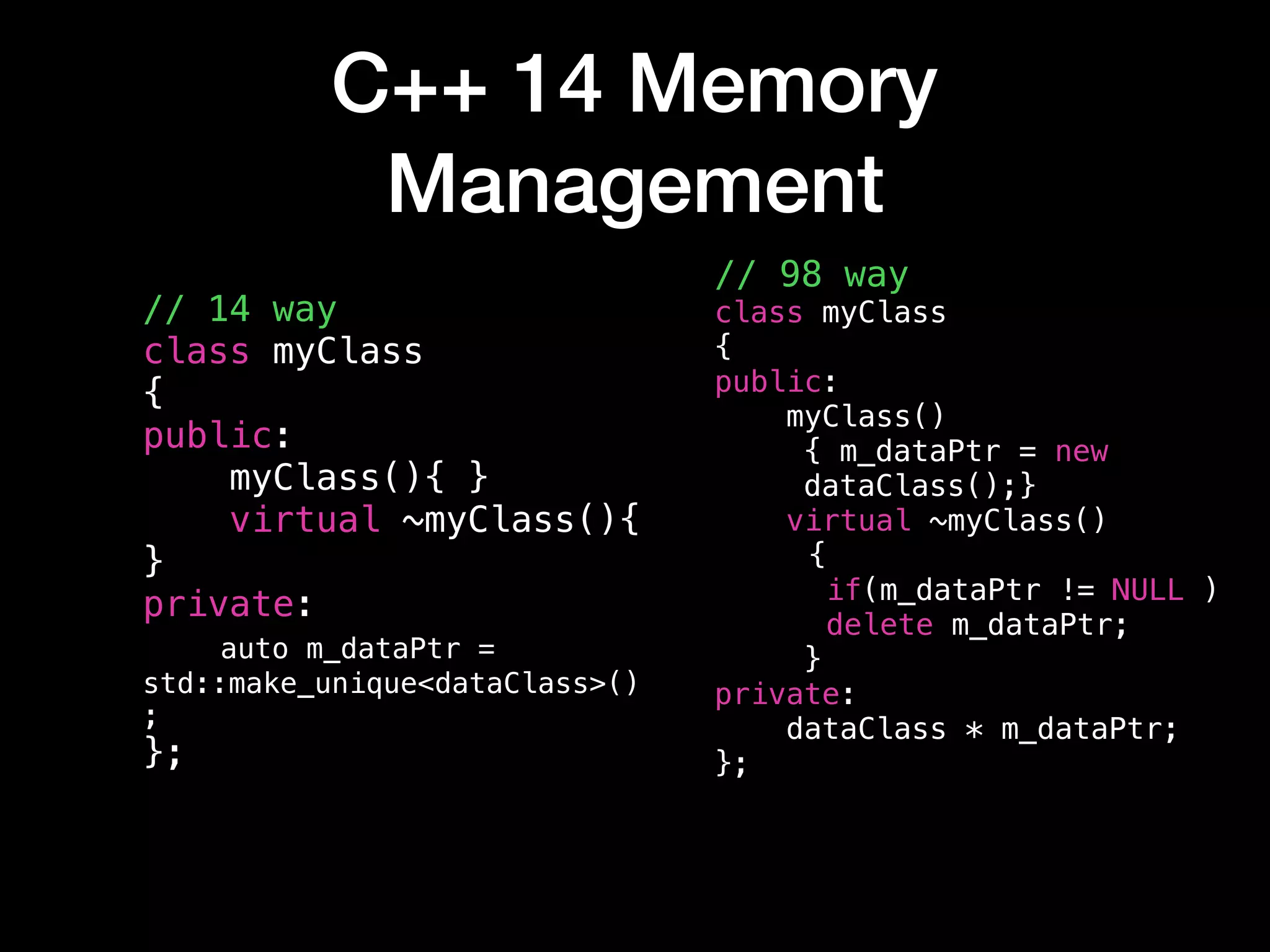

![std::unique_ptr
• std::unique_ptr
• operator bool
• operator=
• operator->
• operator*
• operator[]
• get
• release](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/moderncmemorymanagement-171103205216/75/Modern-c-Memory-Management-7-2048.jpg)