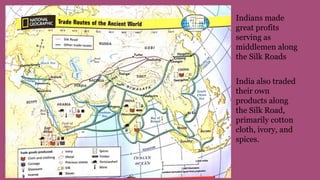
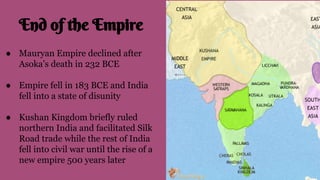
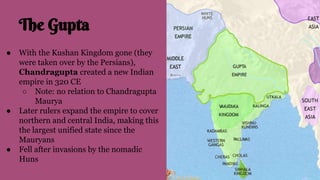
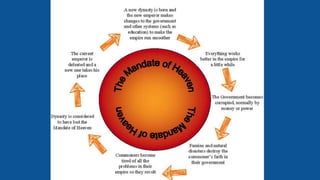
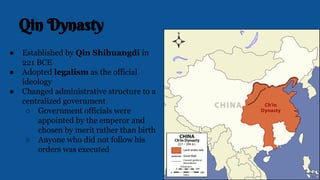
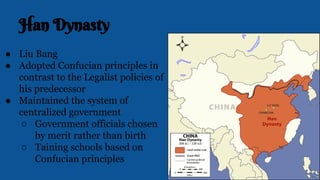
The document summarizes the key influences, empires, and philosophies that shaped classical India and China. In India, the Aryans established cultural traditions like Hinduism while the Persians and Greeks influenced government structures. The Mauryan Empire unified much of India under Chandragupta Maurya and the Buddhist emperor Ashoka, who built infrastructure and spread Buddhism. In China, the Zhou Dynasty gave way to warring states before the Qin unified China through legalism and centralized rule. The long-lasting Han Dynasty adopted Confucian principles and saw peace and prosperity, though problems with land ownership would later undermine their rule.