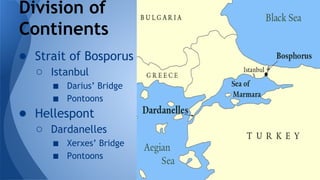
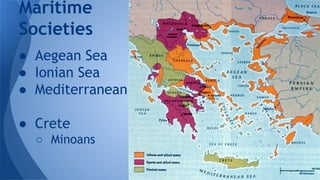
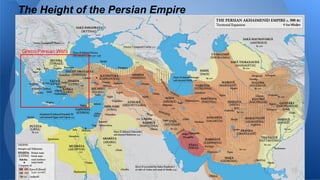
This document provides an overview of classical Greece, including its geography, early civilizations like Minoans and Mycenaeans, and the development of city-states like Athens and Sparta. It discusses the Persian Wars between Greece and Persia in the 5th century BCE and the rise of Athenian power through the Delian League. It then covers the Peloponnesian Wars between Athens and Sparta and the subsequent conquest of Greece by Philip II and Alexander the Great, establishing Hellenistic rule across Western Asia and Egypt.