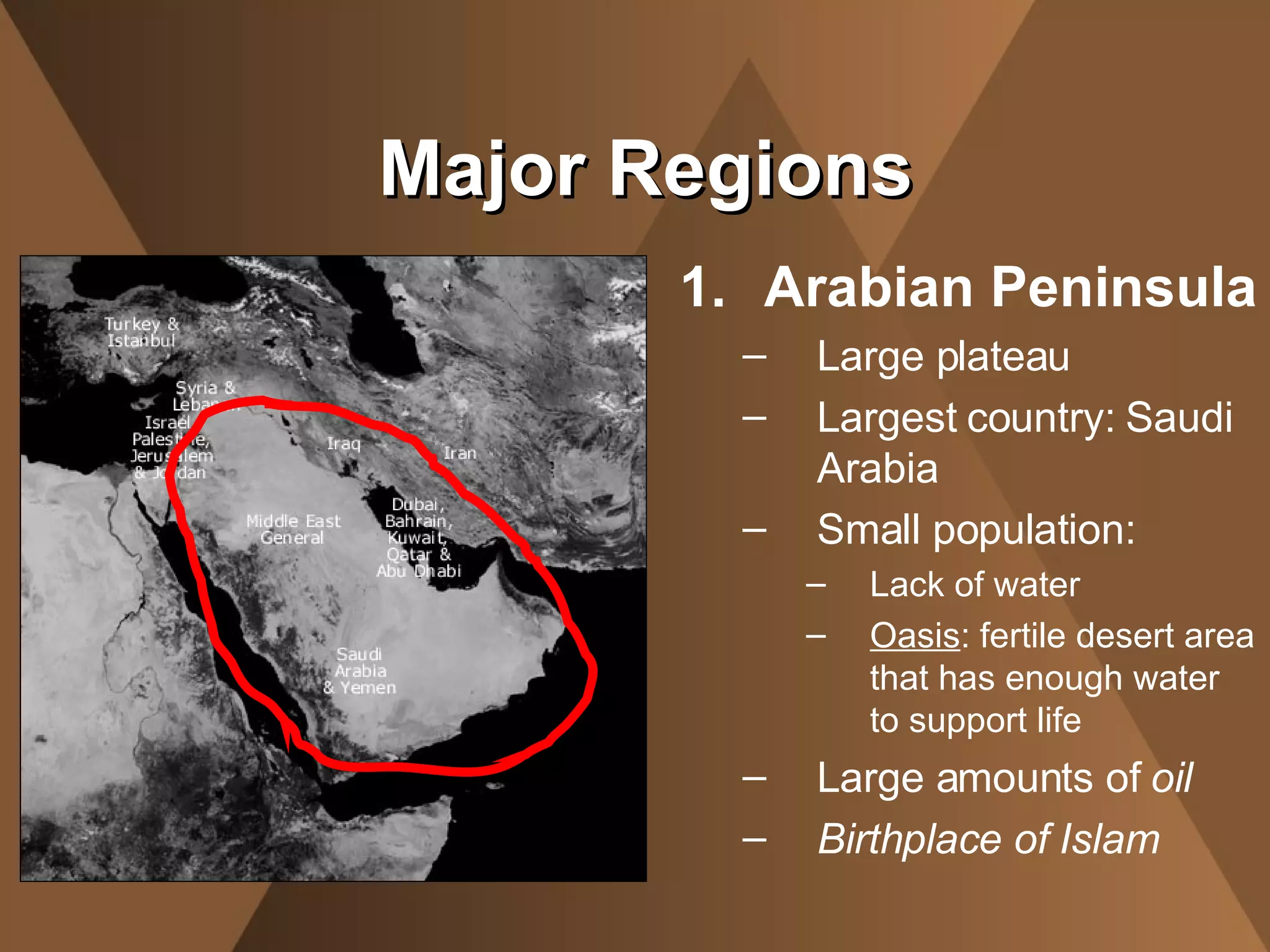
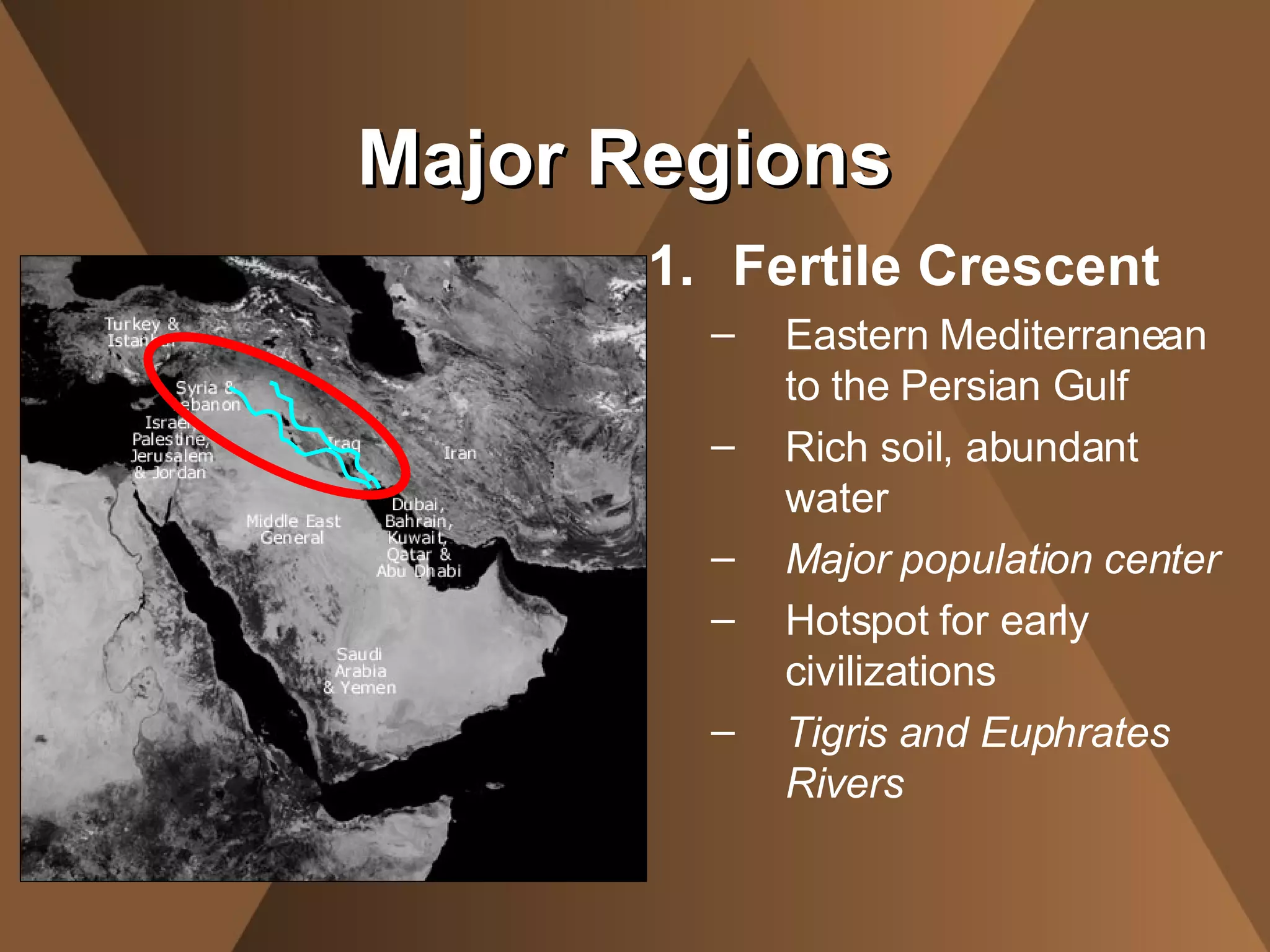
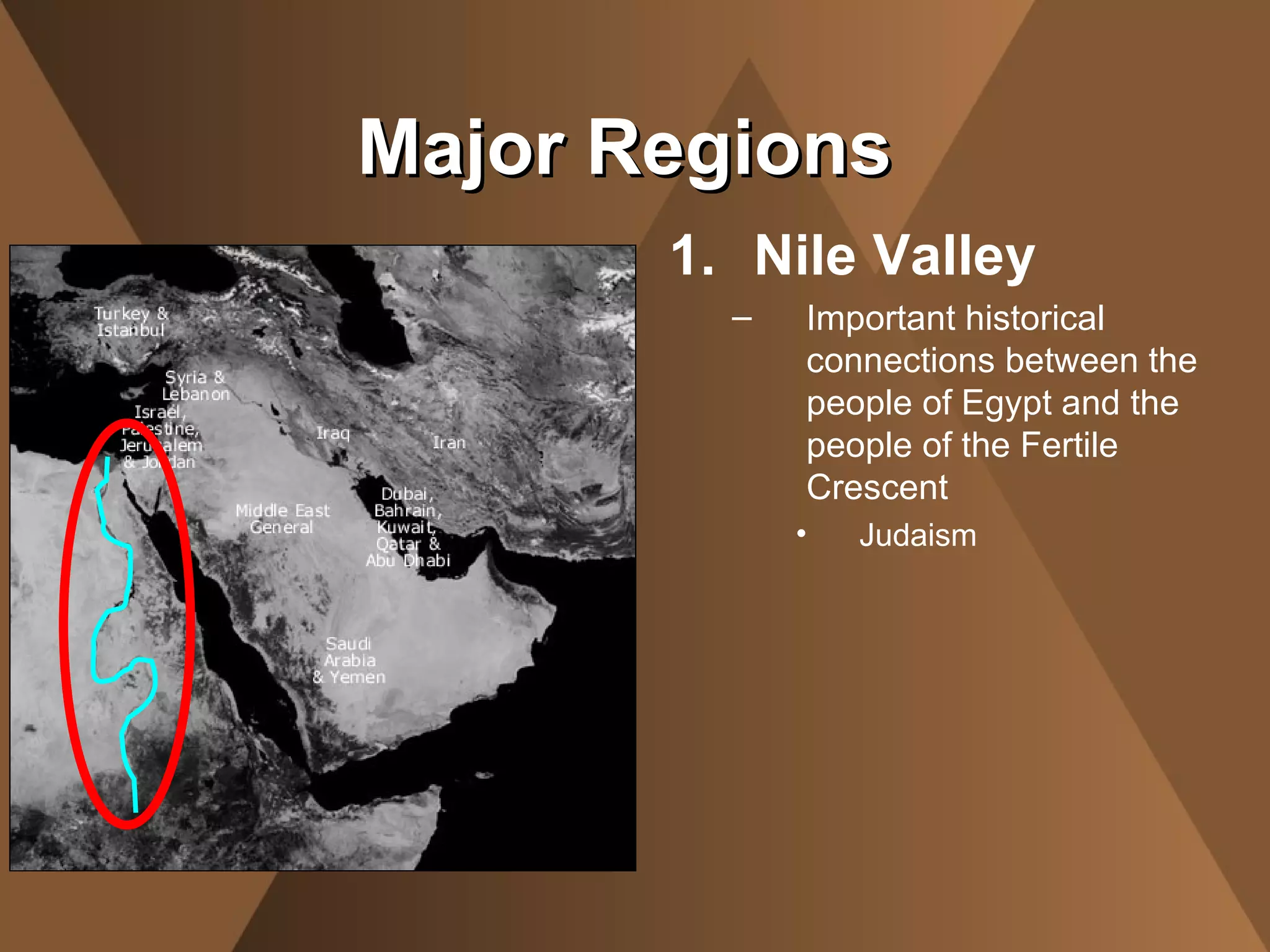
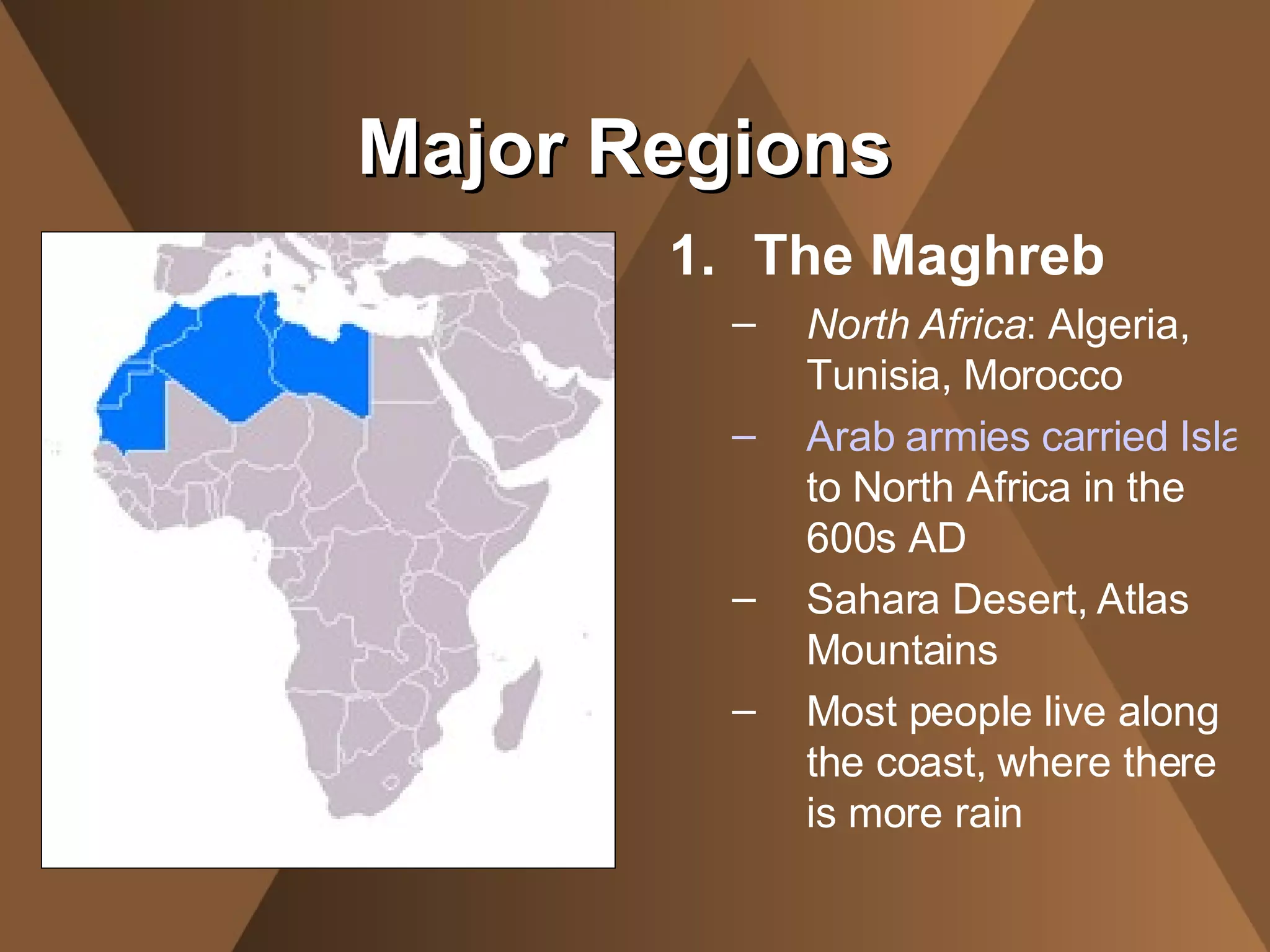
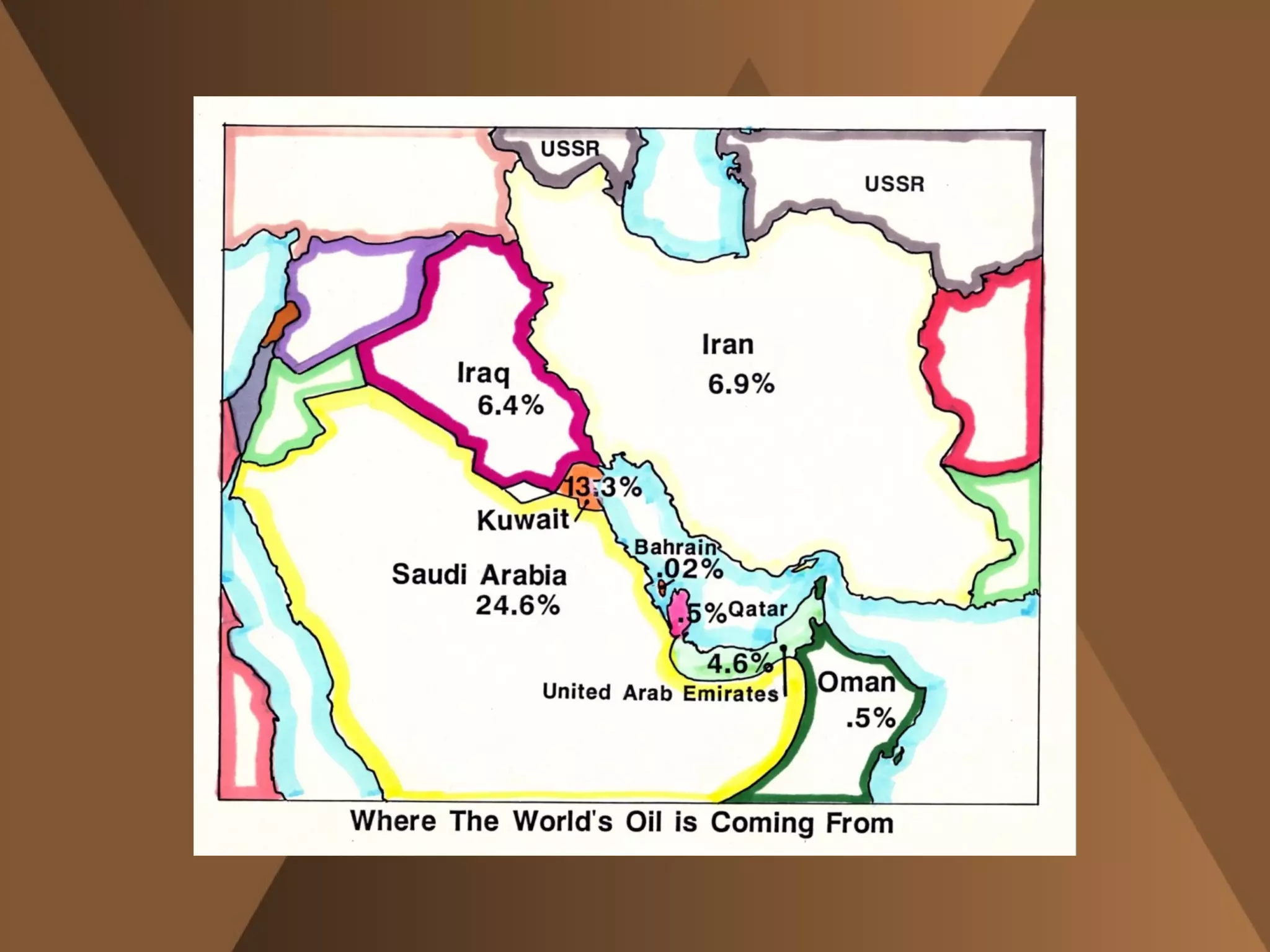
The document summarizes the physical landscape and people of the Middle East region. It describes the Middle East as a crossroads between Africa, Asia and Europe, where migrating people spread ideas and culture. It outlines five major regions - the Northern Tier, Arabian Peninsula, Fertile Crescent, Nile Valley and Maghreb. The climate is mostly desert with a lack of water, though civilizations developed around oasis and rivers. The people are ethnically and religiously diverse, with Arabs and Islam being the majority populations.