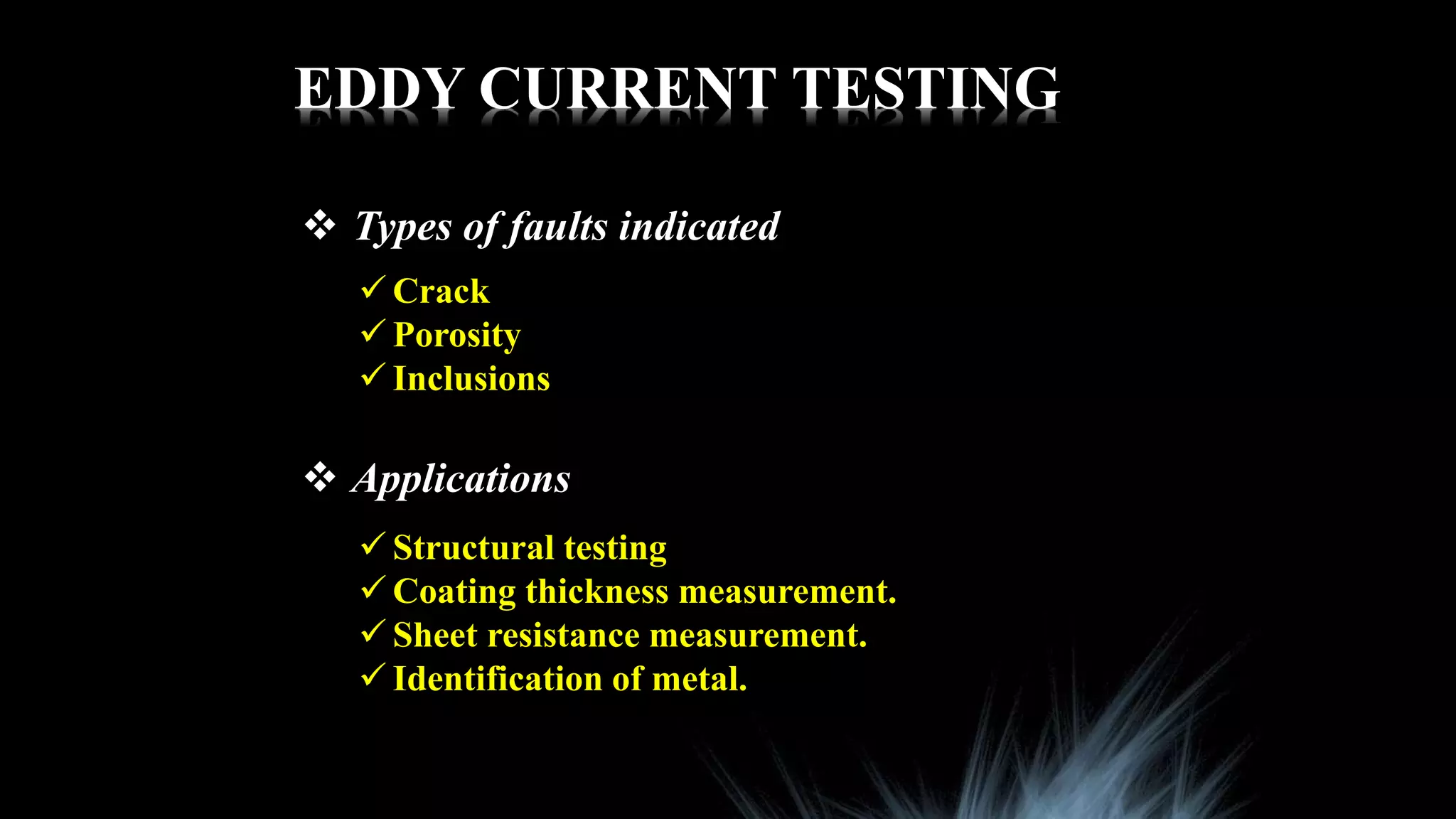
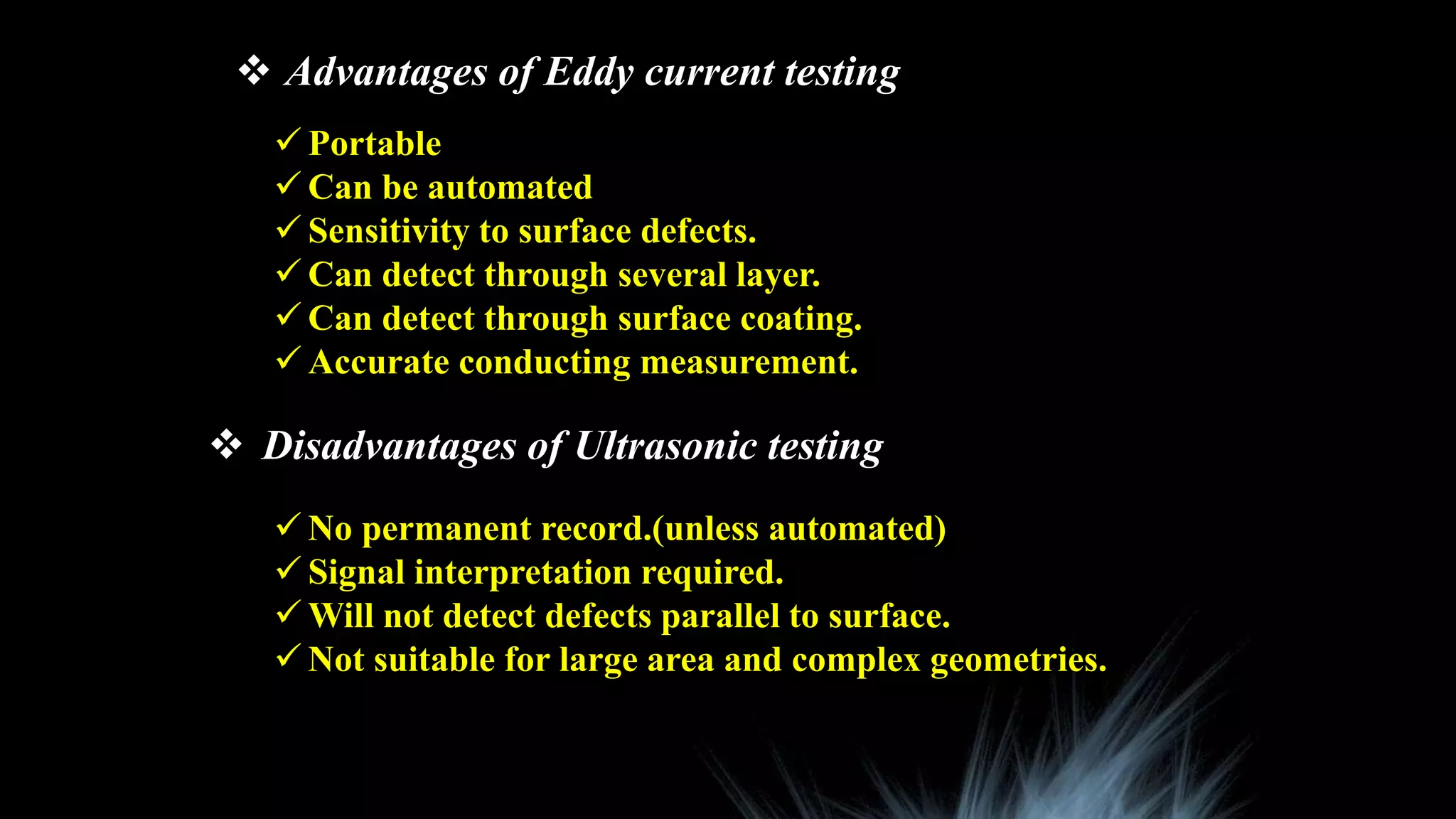
This document summarizes various non-destructive testing techniques presented by Sonam Paljor, including ultrasonic testing, magnetic particle testing, eddy current testing, radiography testing, and liquid penetrant testing. It provides details on the types of faults each method can indicate, their applications, advantages, and disadvantages. The final section compares destructive and non-destructive testing, noting that non-destructive techniques allow inspection without damaging the material but require indirect measurements, while destructive testing directly measures material properties but requires loading that damages the sample.