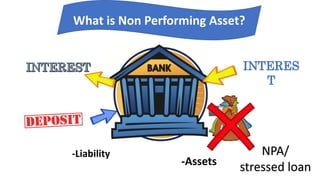
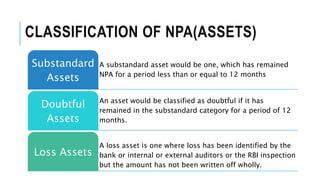
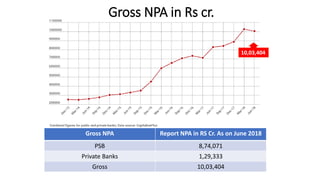
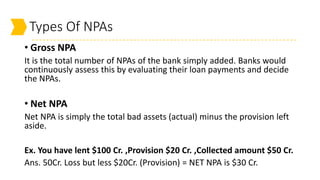
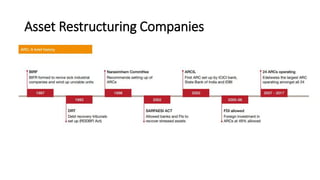
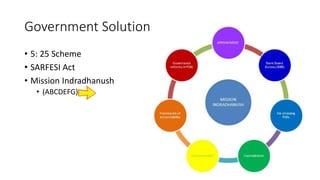
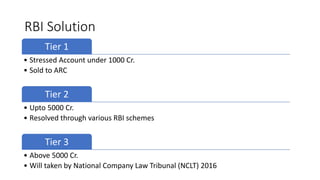
Non-performing assets (NPAs) are loans classified by banks as sub-standard, doubtful, or loss assets due to borrower defaults. Factors contributing to NPAs include economic conditions, poor risk management, and mismanagement of funds. Strategies for managing NPAs encompass preventive measures, such as credit assessments, and curative actions like corporate debt restructuring and recovery through legal channels.