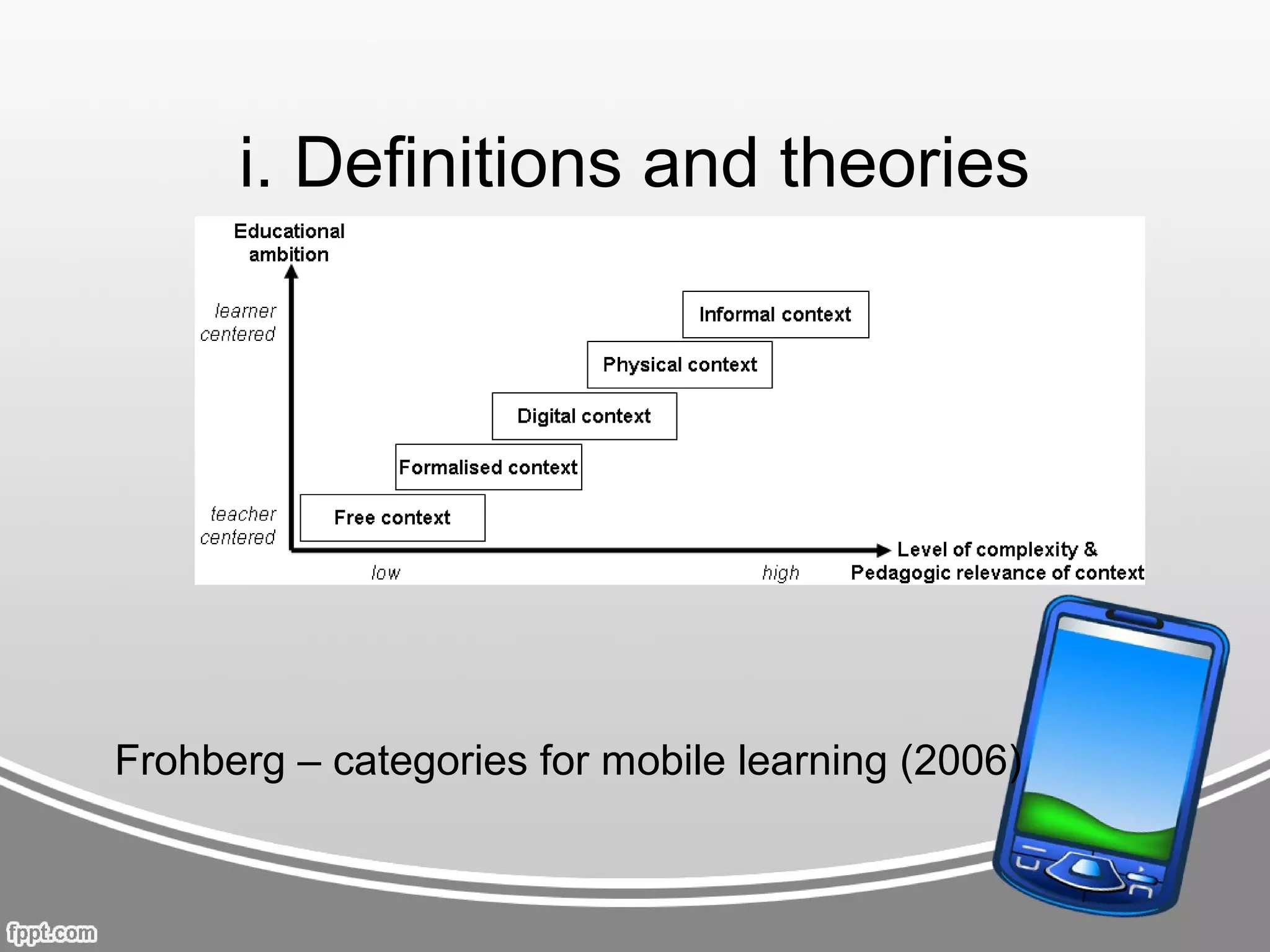
This document provides an overview of mobile learning theory and practice presented by Neil Davie in a webinar. It begins with definitions of mobile learning from various scholars and theoretical models for categorizing mobile learning. It then discusses results from student surveys on technology use and interest in mobile learning. Finally, it explores practical applications of mobile learning considering opportunities and challenges, and outlines Neil Davie's plans and recommendations for implementing mobile learning on a limited budget.