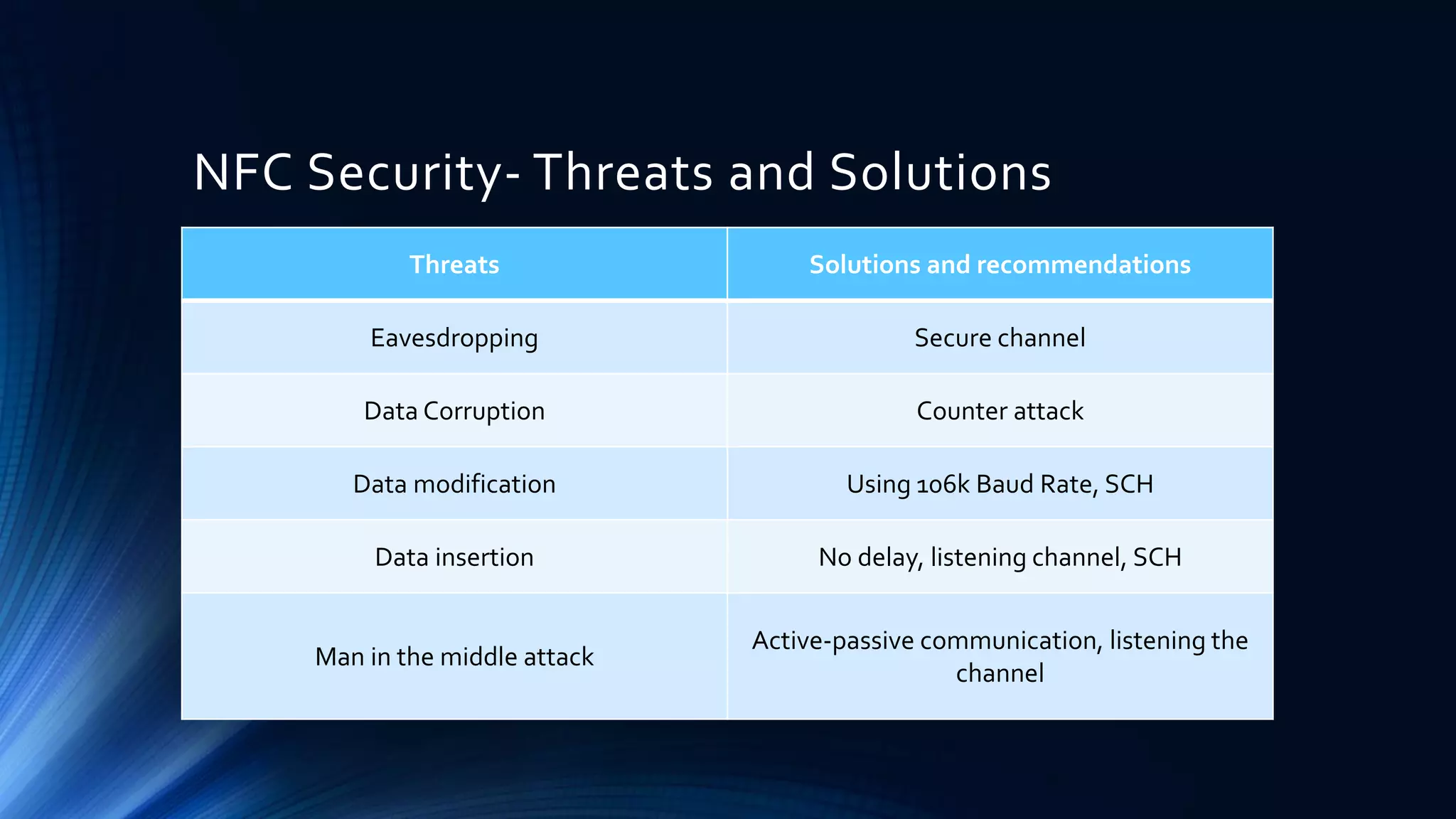
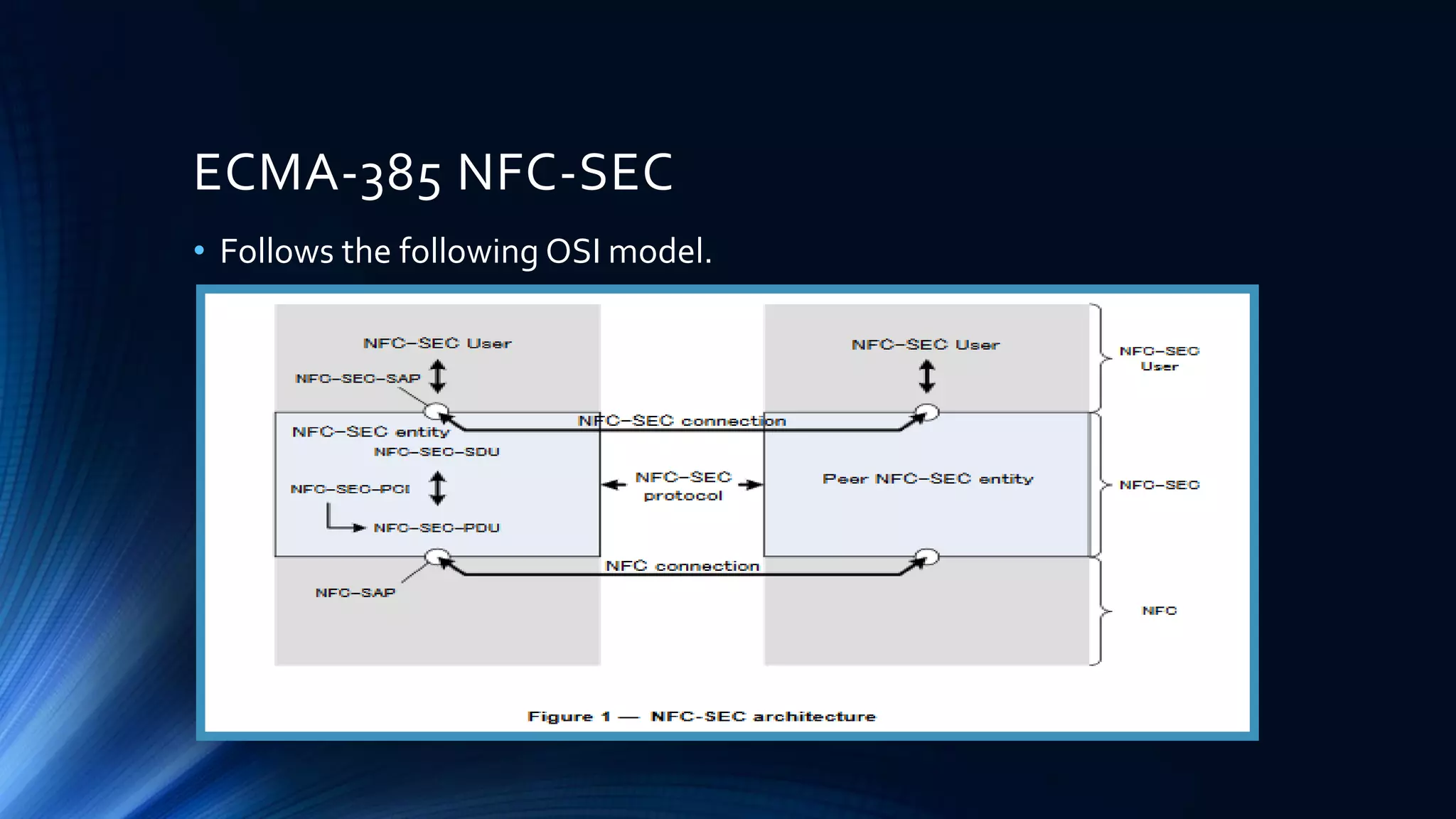
The document discusses the NFC (Near Field Communication) standards and security measures, focusing on the NFC work principles, communication modes, and protocols like NFCIP-1 and NFCIP-2. It highlights various security threats such as eavesdropping and man-in-the-middle attacks, along with recommended solutions, including secure channels and shared secret services defined in NFC-SEC standards. Additionally, it discusses cryptographic methods and concludes that NFC alone does not provide protection against data security issues without implementing a secure channel.