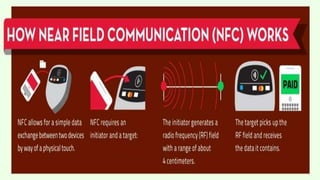
NFC, or Near Field Communication, allows short-range wireless communication between electronic devices when they are 10 cm or closer. It works by generating magnetic fields to transmit data at rates up to 424 kbps. NFC has several modes and applications, including payments, information sharing, tickets, and secure access. While security risks exist from signal interception, solutions include encrypting data transmission and requiring close physical proximity for interactions. Overall, NFC offers convenient contactless connectivity and its security compares similarly to other wireless technologies when proper protections are implemented.