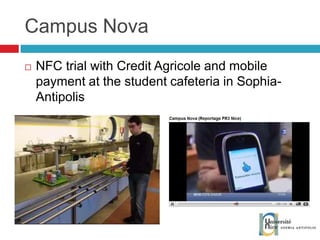
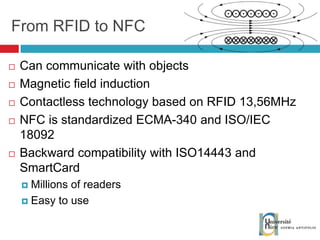
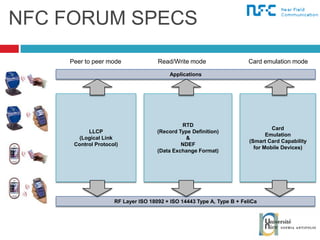
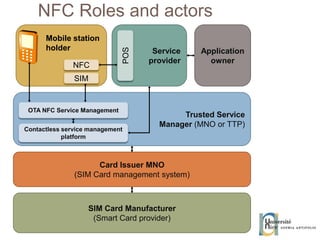
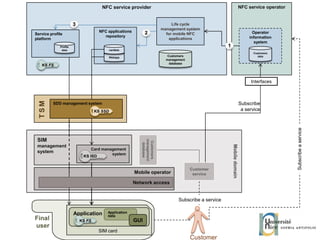
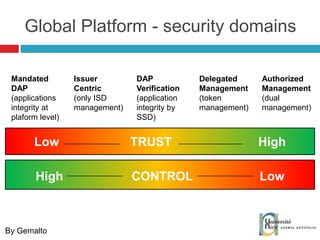
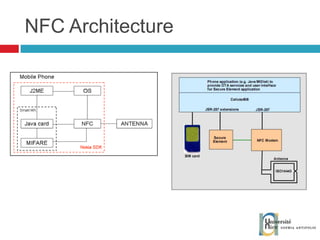
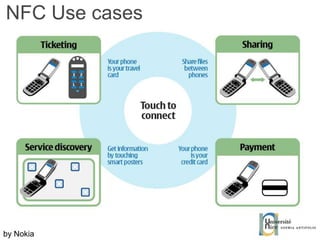
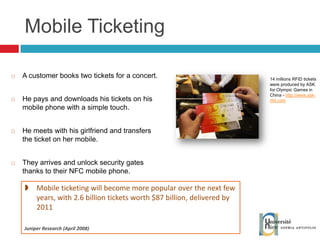
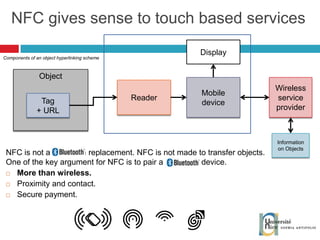
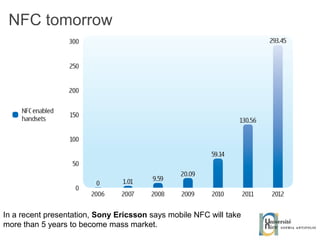
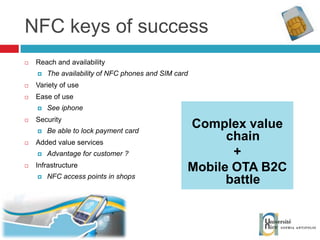
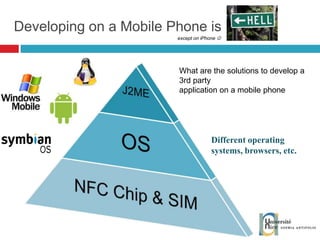
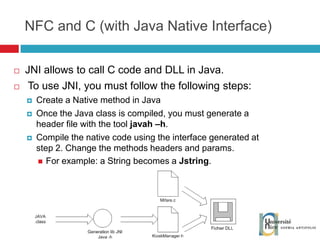
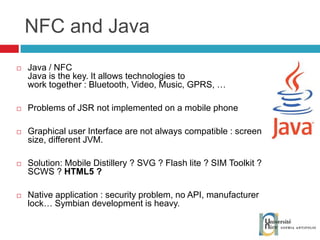
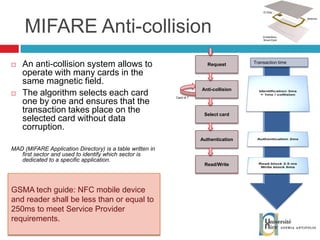
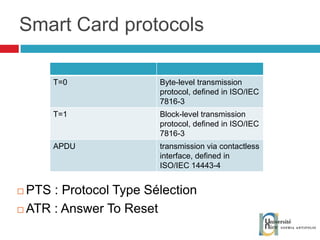
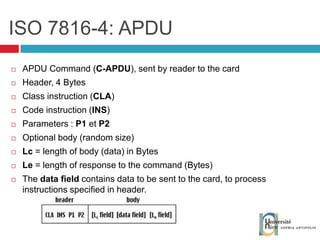
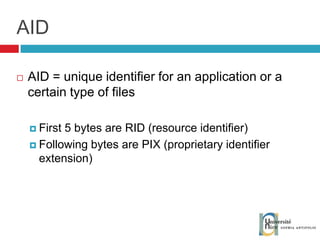
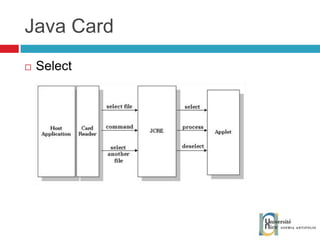
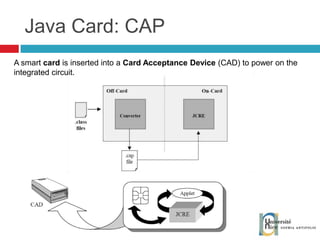
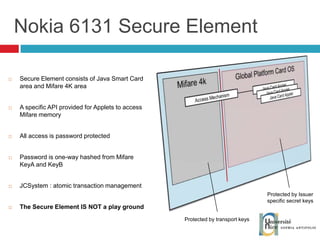
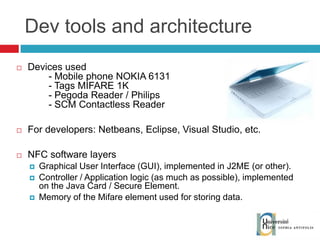
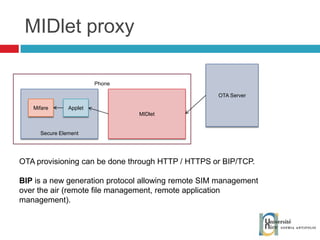
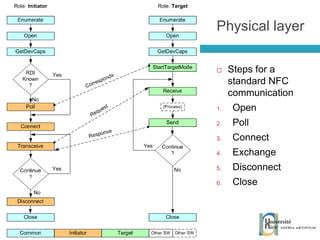
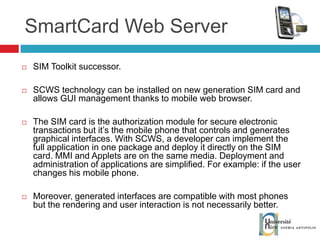
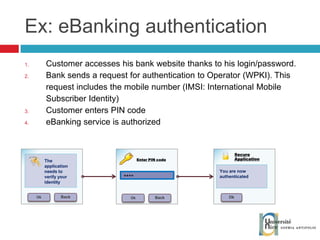
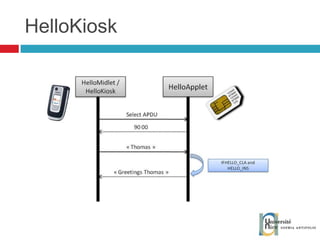
The document discusses the architecture and development of NFC applications, focusing on Java development, mobile money transfer, and various NFC services. It explores the ecosystem of NFC technology, including its uses, roles of different actors, and standardization bodies, while highlighting its secure payment capabilities and potential future applications. Additionally, it examines the current state of NFC trials and implementations in different locations, emphasizing the need for developer resources to create compatible applications.


































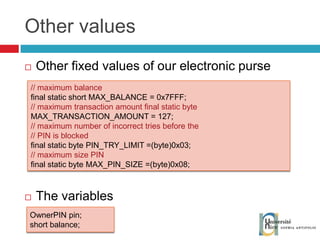
![JCOP Tools String uri = System.getProperty("internal.se.url"); ISO14443Connection iseConn = (ISO14443Connection) Connector.open(uri); Applet extends javacard.framework.Applet MIDlet JCOP tools need activation key: [email_address] compatible PC/SC reader Configure SE keyset to 42 ENC, MAC and KEY are all "404142434445464748494A4B4C4D4E4F” public void process(APDU apdu){ byte[] buf = apdu.getBuffer(); // Ignore Select instruction. if (buf[ISO7816.OFFSET_CLA] == 0x00 && buf[ISO7816.OFFSET_INS] == (byte)0xA4) { return; }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thomasdelazzariarchitectureanddevelopmentofnfcapplicationssmart-university092009-090920081125-phpapp01/85/Architecture-and-Development-of-NFC-Applications-66-320.jpg)




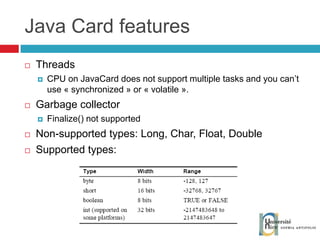






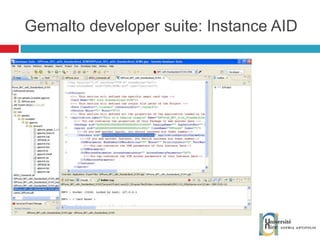
![Send and receive APDUs setIncomingAndReceive(); setOutgoingAndSend() Transfer mode Expected length for the answer Send bytes in response byte[] apduBuffer = apdu.getBuffer(); apduBuffer[0] = byte1; apduBuffer[1] = byte2; apduBuffer[2] = byte3; //0-offset, 3-number of bytes to send apdu.setOutgoingAndSend(0, 3); byte[] buffer = apdu.getBuffer(); short bytes_left = (short) buffer[ISO.OFFSET_LC]; short readCount = apdu.setIncomingAndReceive(); while (bytes_left > 0) { //{process received data in buffer} … bytes_left -= readCount; //get more data readCount = apdu.receiveBytes (ISO.OFFSET_CDDATA); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thomasdelazzariarchitectureanddevelopmentofnfcapplicationssmart-university092009-090920081125-phpapp01/85/Architecture-and-Development-of-NFC-Applications-95-320.jpg)













![Contact me Master MBDS , University of Nice Sophia-Antipolis [email_address] http://www.mbds-fr.org http://tdelazzari.blogspot.com http://twitter.com/tdelazzari](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thomasdelazzariarchitectureanddevelopmentofnfcapplicationssmart-university092009-090920081125-phpapp01/85/Architecture-and-Development-of-NFC-Applications-122-320.jpg)