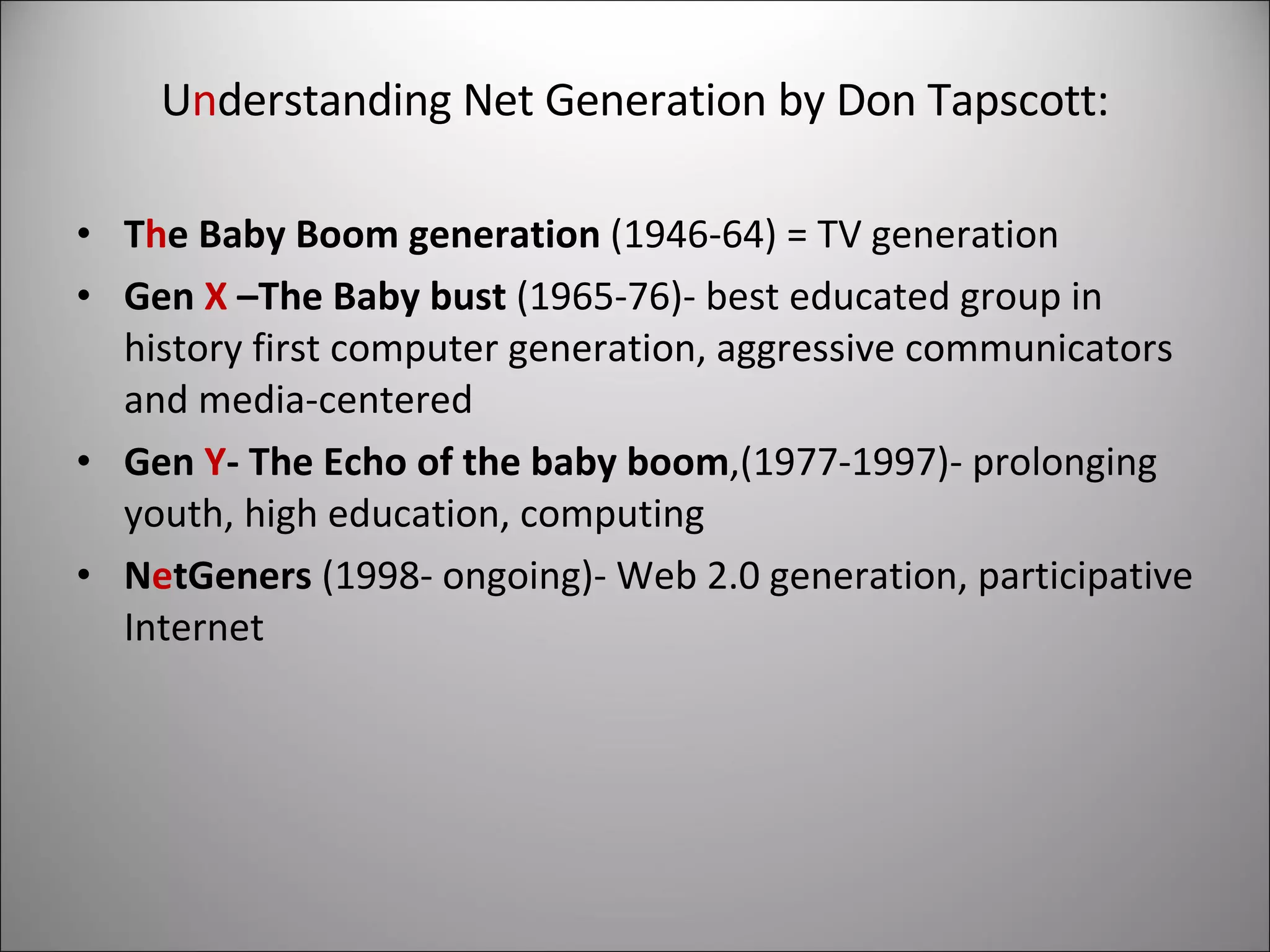
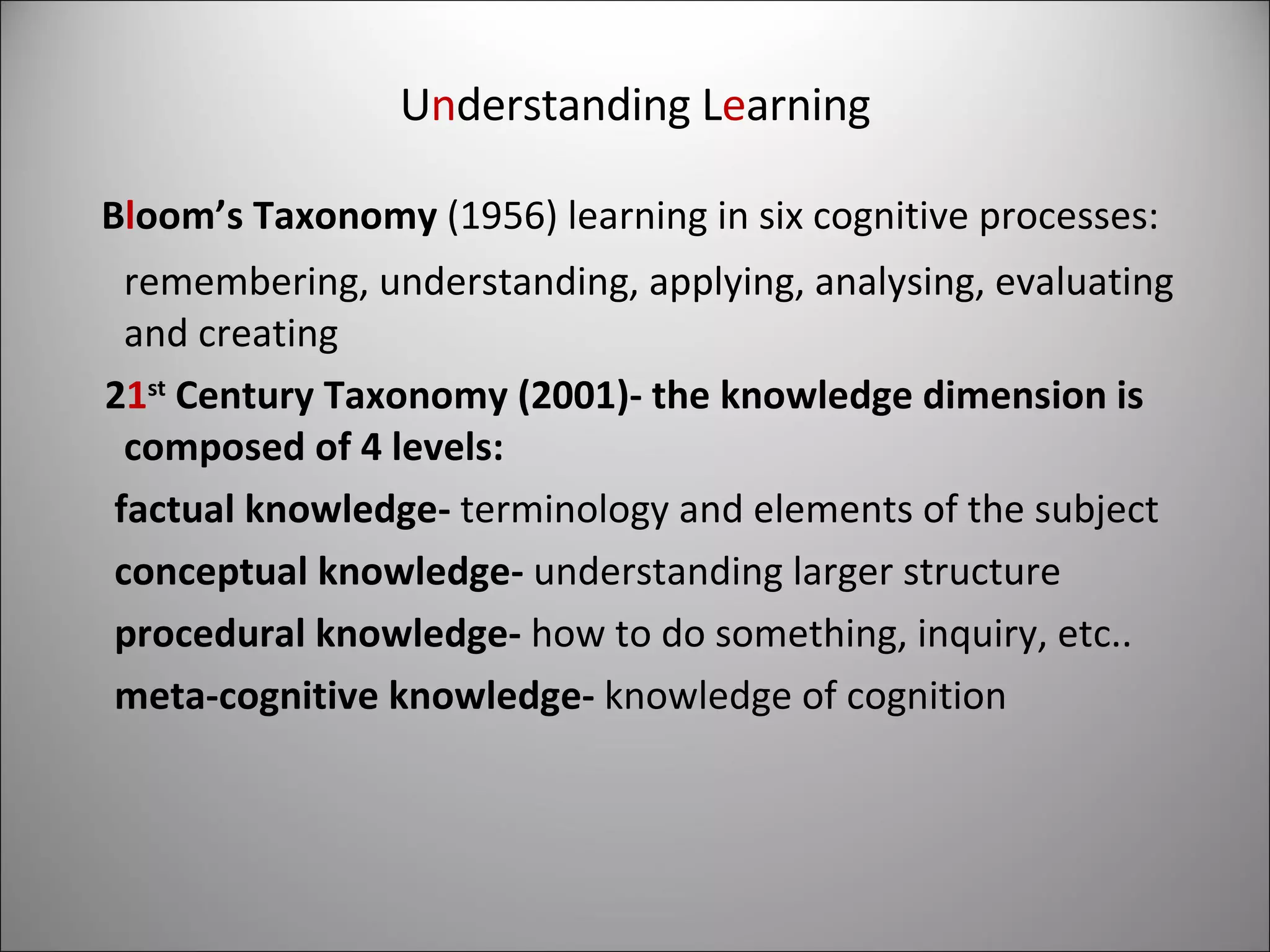
The document discusses the evolution of the web from the initial vision of Tim Berners-Lee to create a collaborative medium, to the graphical web of the 1990s requiring HTML knowledge, to today's easy-to-use Web 2.0 tools. It outlines key aspects of the new web like being location-free and user-focused, leveraging collective intelligence. 21st century skills like collaboration, communication and problem solving are increasingly important. New technologies and ways of working are flattening the world. Learning should bridge the gap between how students live and learn by using Web 2.0 tools for more than just play.

















![H o pe you enjoyed it [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/newtoolsnewschools-090510110632-phpapp01/75/New-Tools-New-Schools-20-2048.jpg)