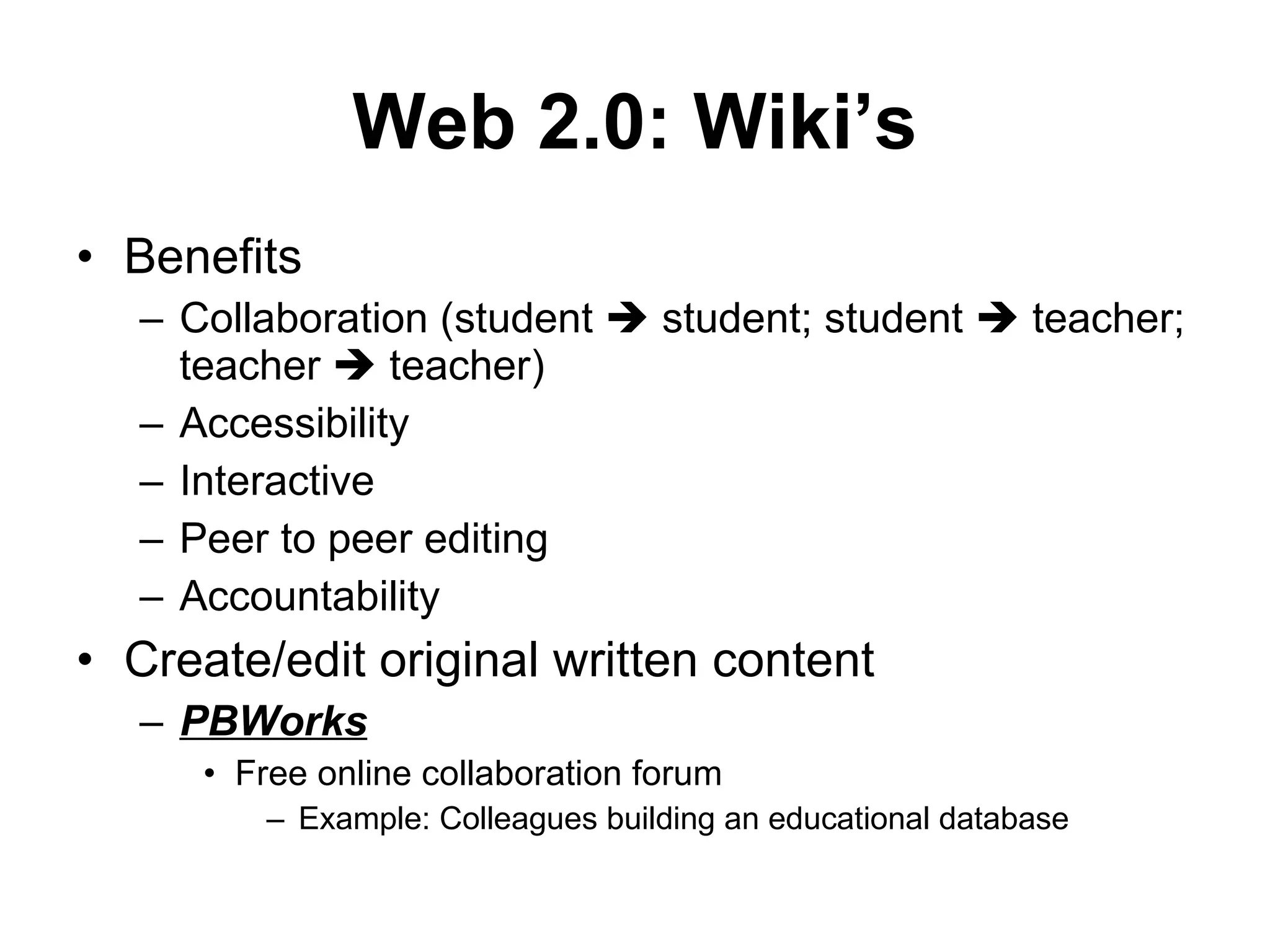
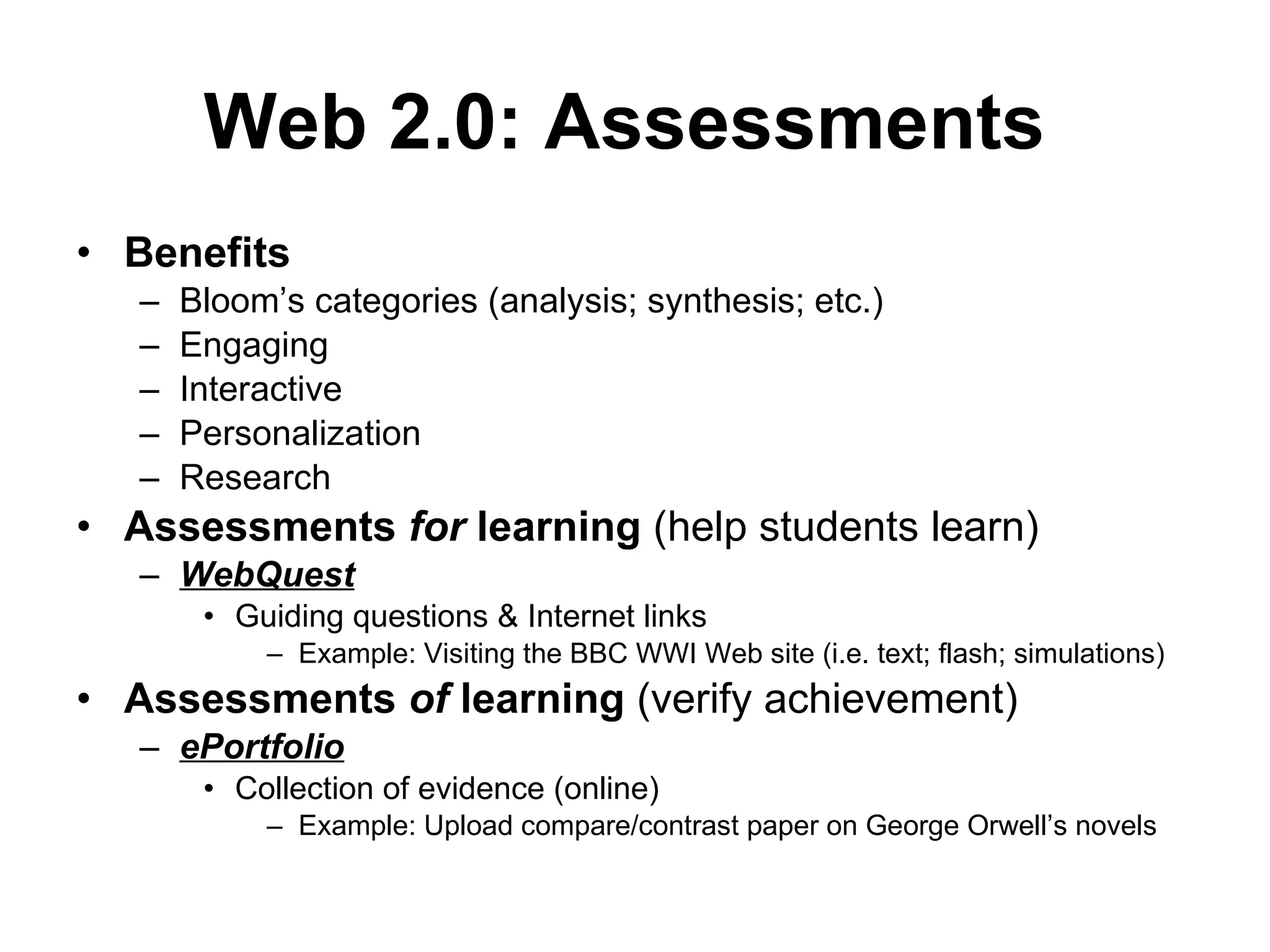
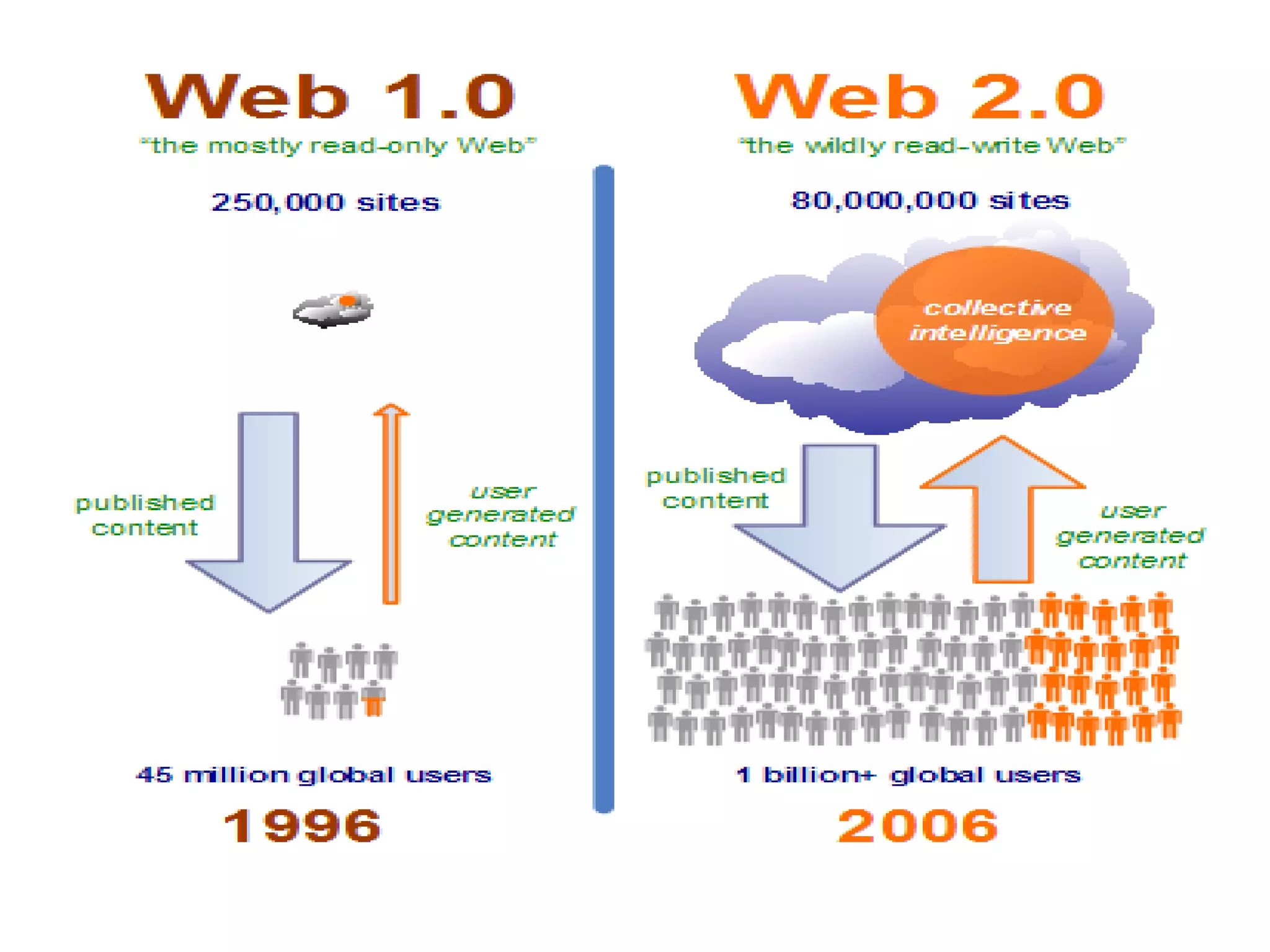
This document discusses how Web 2.0 technologies can transform passive learners into active learners by encouraging collaboration, accessibility, and student engagement. It provides examples of how tools like wikis, podcasts, and online assessments can be used to improve learning outcomes by making content more interactive and personalized for students. The document also acknowledges some potential drawbacks of technology in education, but argues that when used properly Web 2.0 has mostly positive impacts on learning.


![“ Today's [digital learners] brains are shaped by various information streams… constantly popping and sparking and competing for attention” ( Susan Blackmore, Ph.D in Psychology, Oxford University ) “ Young people (ages 8-18) mainline electronic media for more than six hours a day, on average” ( Henry J. Kaiser Family Foundation ) “ Students attitudes towards learning and their own self-concept improved consistently when computers were being used” ( Jay Sivin-Kachala research study 1998 ) “ [computer usage] Maximizes student reflection and encourages progressive thought, taking multiple perspectives, and independent thinking” ( Scardamalia & Bereiter’s CSILE studies 1996 ) Web 2.0: Studies Have Shown…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/web2point0-100319094511-phpapp01/75/Web-2point0-4-2048.jpg)