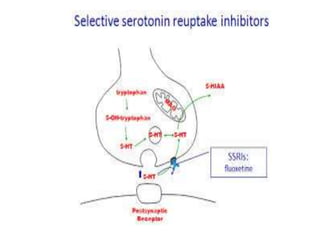
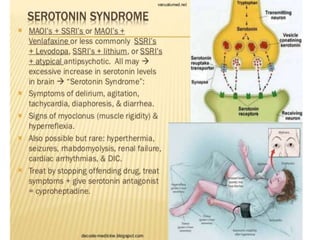
Serotonin is a monoamine neurotransmitter synthesized from tryptophan. It is found primarily in enterochromaffin cells in the GI tract, platelets, and the central nervous system. Serotonin acts through multiple receptor subtypes and has diverse physiological effects including regulation of mood, appetite, sleep, cognition, cardiovascular function, platelet aggregation, and intestinal motility. Imbalances in the serotonin system have been implicated in psychiatric conditions like depression and anxiety. Drugs that affect serotonin synthesis, reuptake, and receptor activity are used to treat mood disorders, migraine, nausea/vomiting, and other clinical conditions.
















![TERMINATION
• Serotonergic action is terminated primarily via
uptake of 5-HT from the synapse.
• This is accomplished through the specific
monoamine transporter for 5-HT, SERT, on the
presynaptic neuron.
• Another monoamine transporter known as Plasma
membrane monoamine transporter [PMAT] has been
regarded to be important in the clearance of
Serotonin.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/serotoninmbbs-190704054526/85/Serotonin-17-320.jpg)