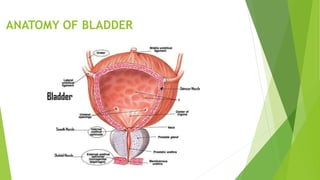
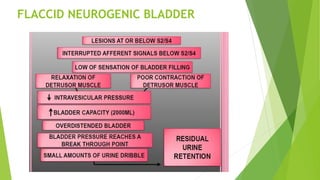
This document discusses neurogenic bladder, which refers to bladder dysfunction caused by diseases of the central or peripheral nervous system. There are two main types: a flaccid bladder that does not contract fully, causing urine to drip out continuously and potentially cause rashes, and a spastic bladder that has involuntary contractions causing frequent urges to urinate. Causes include conditions like stroke, Parkinson's, and spinal cord injuries. Symptoms are things like frequent urination, incontinence, and urine retention. Treatment options include medications to relax or stimulate the bladder, botulinum toxin injections, exercises, and sometimes surgery.