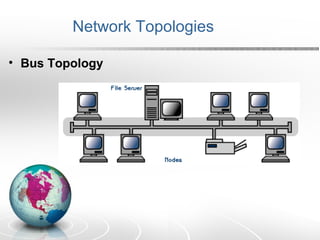
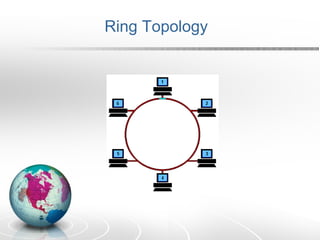
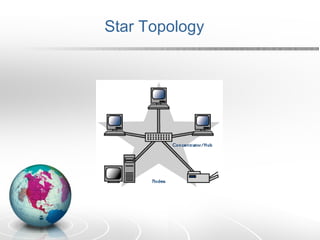
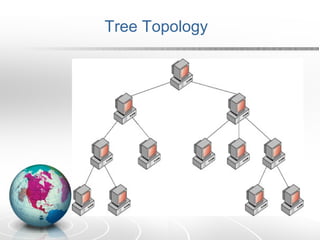
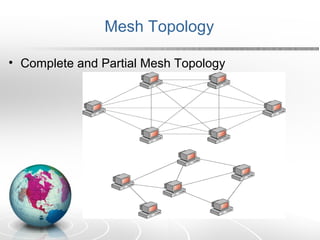
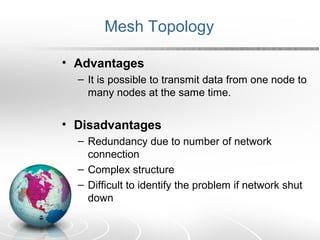
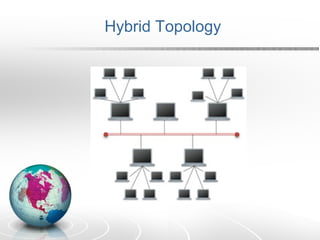
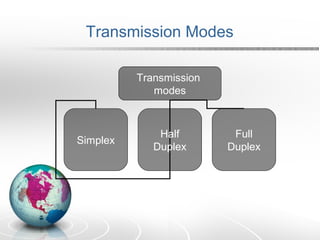
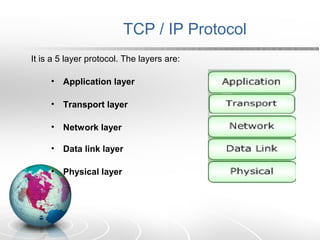
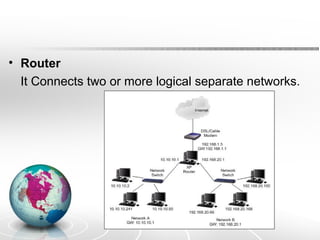
Networking allows two or more computers to exchange information when connected. There are different types of networks like LAN, WAN, and MAN. Network topologies include bus, star, ring, tree and mesh. TCP/IP is a 5 layer protocol model used to connect networks. Common internet protocols are HTTP, SMTP, POP3 and UDP. The World Wide Web is a system of hyperlinked documents accessed using a web browser.