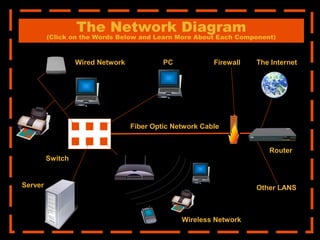
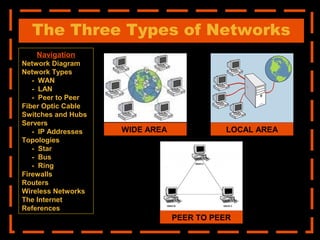
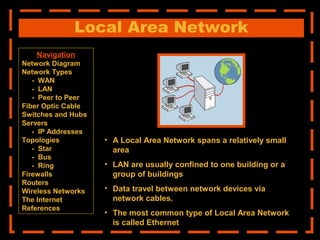
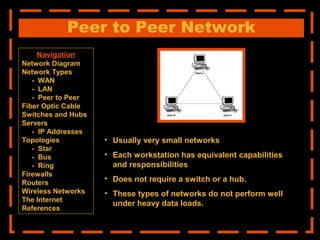
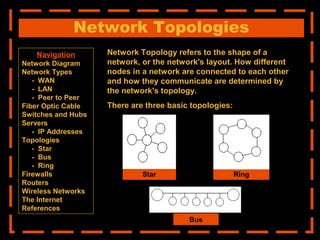
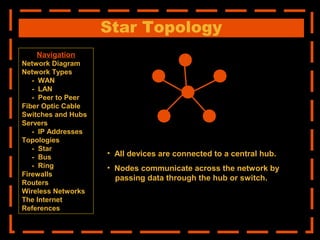
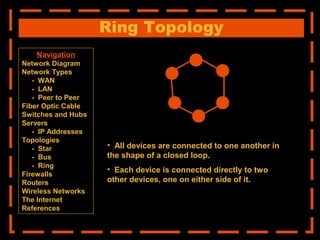
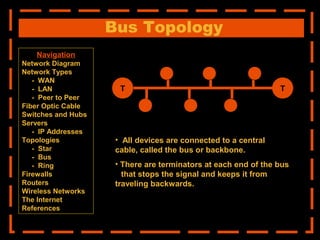
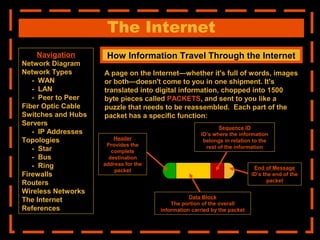
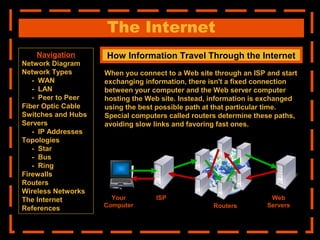
The document provides an overview of computer networking systems through a presentation at East Africa University's Faculty of Economics. It begins by explaining how computer networks have revolutionized communication over the past 20 years. It then defines what a computer network is and provides navigation links to sections that will describe various network components in more detail, including network diagrams, different network types, fiber optic cables, switches and hubs, servers, IP addresses, network topologies, firewalls, routers, wireless networks, and the Internet.


![The Computer Network
What is a Computer Network
net·work: [net-wurk] – noun, a system containing any
combination of computers, computer terminals, printers,
audio or visual display devices, or telephones
interconnected by telecommunication equipment or
cables: used to transmit or receive information.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thebasicsofcomputernetworking-141227000231-conversion-gate01/85/The-basics-of-computer-networking-3-320.jpg)