This document provides an introduction to computer networking. It discusses:
- The history and importance of computer networks, including the ARPANET.
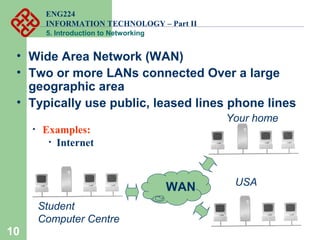
- Types of networks classified by size (LAN, WAN, MAN, CAN, PAN) and structure (peer-to-peer, client-server).
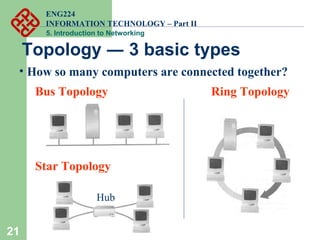
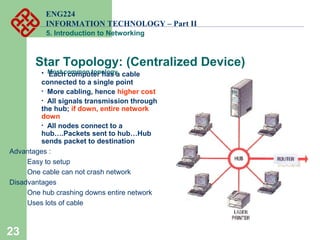
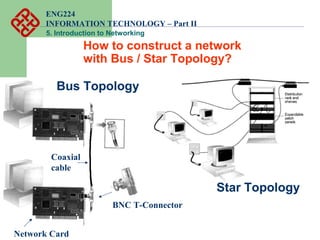
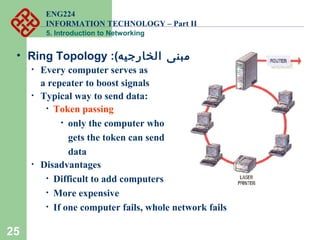
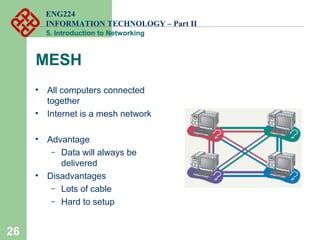
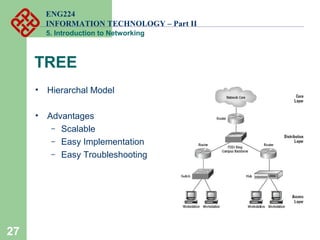
- Common network topologies like bus, star, ring, mesh, and tree.
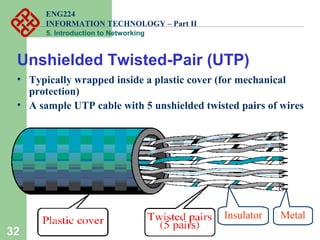
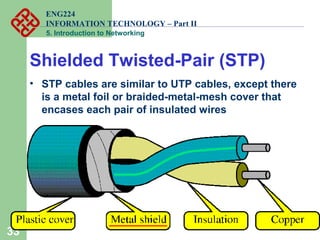
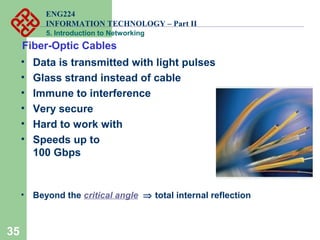
- Popular transmission media including twisted pair, coaxial, and fiber optic cables.
- Network vendors and considerations around guided vs. unguided transmission media.