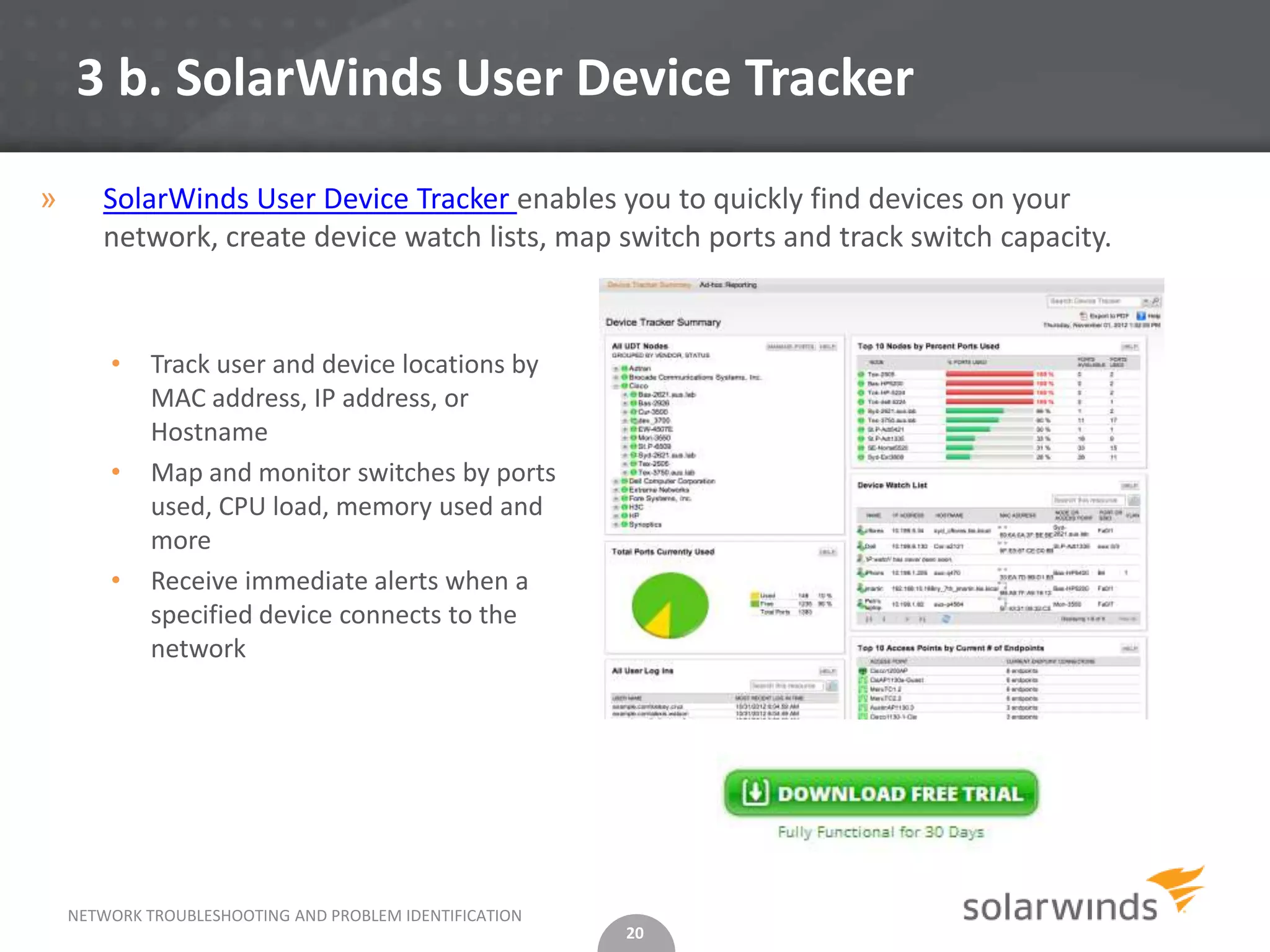
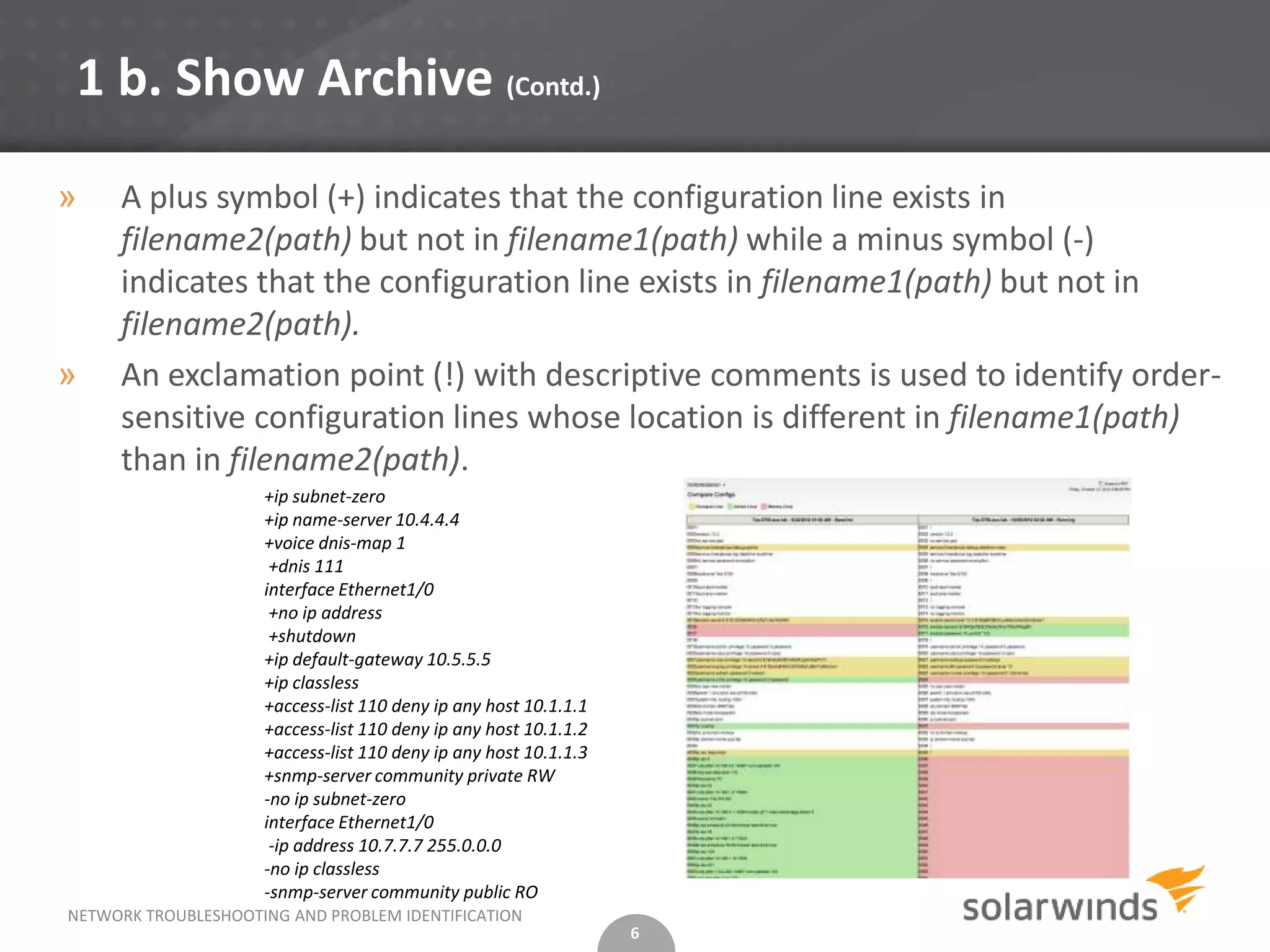
This document discusses network troubleshooting, focusing on configuration issues and IP address conflicts, which are common causes of network problems. It outlines steps for troubleshooting both issues, including archiving configurations, identifying duplicate IP addresses, and using tools like SolarWinds for network management. Additionally, it provides preventative measures and emphasizes the importance of using automated tools for monitoring and alerting on IP infrastructure.

![1 b. Show Archive
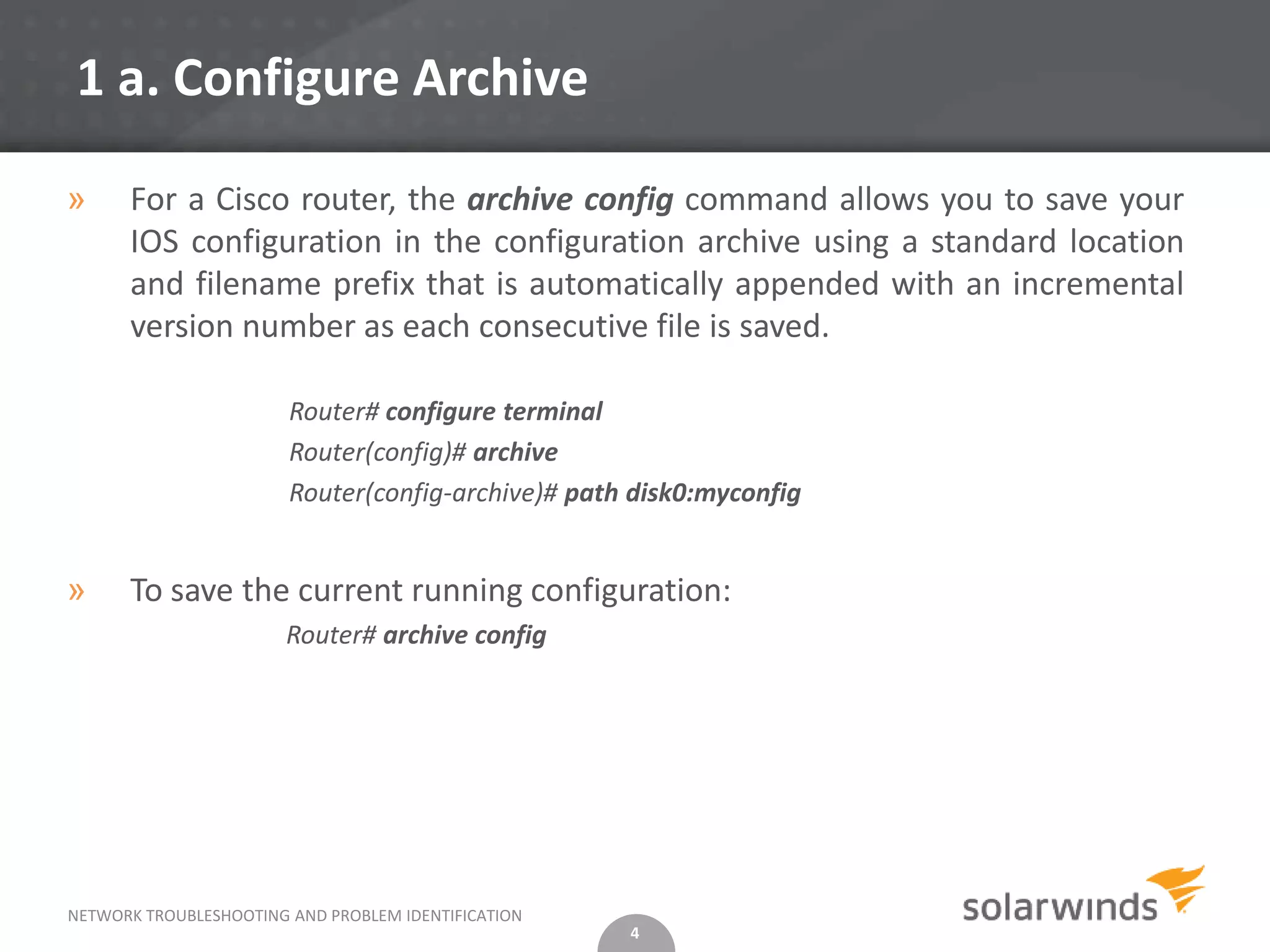
» The show archive command displays information on the files saved in the
configuration archive as shown in the following sample output:
Router# show archive
There are currently 1 archive configurations saved.
The next archive file will be named disk0:myconfig-2
Archive # Name
0
1 disk0:myconfig-1 <- Most Recent
2
» Assuming that you have a config archive, you can perform a line-by-line comparison of
any two configuration files and generate a list of the differences between them using
the show archive config differences command.
show archive config differences[filename1(path)[filename2(path)][ignorecase]]
NETWORK TROUBLESHOOTING AND PROBLEM IDENTIFICATION
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/npmnetworktroubleshootingpart2final-121213143034-phpapp02/75/Network-Troubleshooting-Part-2-5-2048.jpg)
![1 b. Show Archive (Contd.)
» Once you determine that a config has changed, its easy to replace the current
running config with any saved config file using the configure replace command.
Router# configure replace disk0:myconfig
This will apply all necessary additions and deletions
to replace the current running configuration with the
contents of the specified configuration file, which is
assumed to be a complete configuration, not a partial
configuration.
Enter Y if you are sure you want to proceed. ? [no]: Y
Total number of passes: 1
Rollback Done
NETWORK TROUBLESHOOTING AND PROBLEM IDENTIFICATION
7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/npmnetworktroubleshootingpart2final-121213143034-phpapp02/75/Network-Troubleshooting-Part-2-7-2048.jpg)