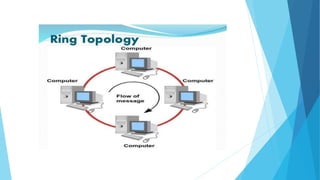
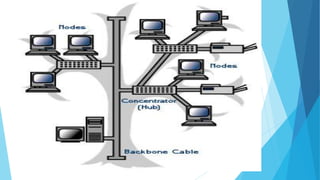
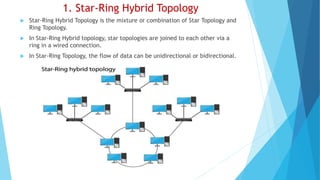
The document provides an overview of various network topologies, including bus, ring, star, mesh, tree, and hybrid topologies, detailing their configurations, advantages, and disadvantages. Each topology presents unique characteristics and use cases, impacting network performance, reliability, and scalability. Additionally, hybrid topologies combine features of multiple topologies, offering flexibility and adaptability for complex networking needs.