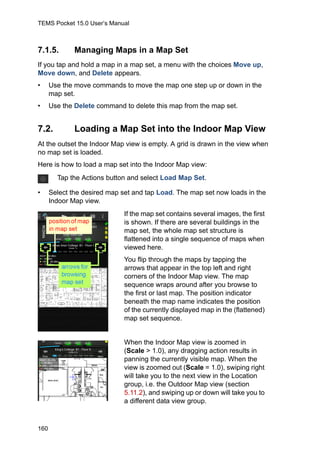
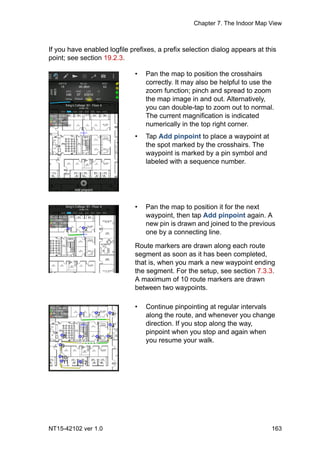
This document section describes the indoor map view feature of the TEMS Pocket software. It allows importing floor plans and positioning measurements on them. Route pinpointing can be done manually or according to a pre-planned route. Value elements like signal strength can be plotted along the route for visualization. Map sets containing multiple floor plans can be created and layers like the legend and transmitters can be shown or hidden in the indoor map view.










![TEMS Pocket 15.0 User’s Manual
168
Cells listed in the transmitter file for the map (floor) currently displayed in the
Indoor Map view are also presented in other places in TEMS Pocket:
• The cells are included in the results of cell searches performed as an aid
to target selection for the RAT, band, and cell lock functions; see various
subsections of chapter 13.
7.7. Presentation of iBwave Zones
iBwave indoor map sets (*.ibwc) may define a collection of zones for each
map it contains. Each zone consists of a closed polygon covering some part
of the map.
If you do not want the zones shown, deselect the Zones map layer as
described in section 7.5.
7.8. Unloading a Map Set
To unload the currently loaded map set:
• Cell names appear in the data view header
and in cell list data views, just like cell
names from TEMS-specific cell files. These
names are enclosed within square brackets
[ ], which are meant to symbolize the walls
of a building.
These zones are by default displayed in TEMS
Pocket if present, colored and labeled
according to their definitions. Zones are drawn
on top of the map image itself but beneath
everything else (waypoints, value element
markers, events, transmitters).
Tap the Actions button and select Unload Map Set.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/7d3bde87-84bf-47b9-8cb8-731053657b9a-150807085330-lva1-app6891/85/Extract-1-from-TEMS-Pocket-15-0-User-s-Manual-13-320.jpg)