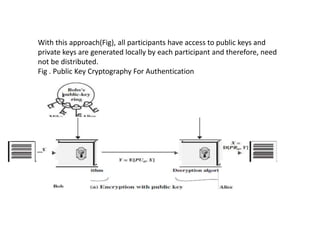
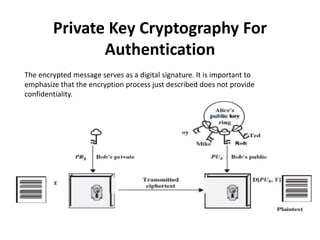
1. Public key cryptography uses asymmetric key encryption where each user has a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption.
2. The RSA algorithm is an example of public key encryption that uses modular exponentiation with large prime numbers to encrypt plaintext and decrypt ciphertext.
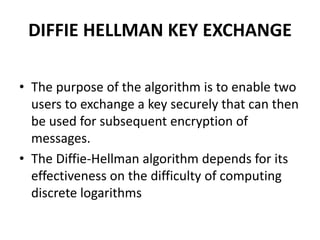
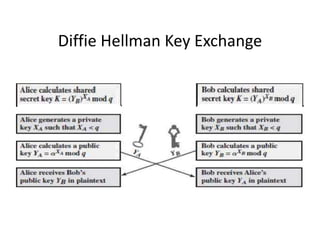
3. Diffie-Hellman key exchange allows two users to securely exchange a secret key over an insecure channel without any prior secrets.


![• Let the plaintext be X=[X1, X2. X3, . .,X ] where m
is the number of letters in some finite alphabets.
Suppose A wishes to send a message to B.
• B generates a pair of keys: a public key KUb and a
private key KRb KRb is known only to B, whereas
KUb is publicly available and therefore accessible
by A.
• With the message X and encryption key KUb as
input, A forms the cipher text Y=[Y1, Y2, Y3› ,Y n]
i.e., Y=EKUb(X)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cns3rdunitppt-231104042120-e6a85a67/85/CNS-3RD-UNIT-PPT-pptx-4-320.jpg)
![Applications for Public-Key
Cryptosystems
We can classify the use of public-key cryptosystems into three categories
• 1. Encryption /decryption: The sender encrypts a message with the recipient‘s public key.
• 2. Digital signature: The sender ―signs" a message with its private key. Signing is achieved by a cryptographic
algorithm applied to the message or to a small block of data that is a function of the message.
• 3. Key exchange: Two sides cooperate to exchange a session key. Several different approaches are possible,
involving the private key(s) of one or both parties.
Requirements for public key cryptography
• It is computationally easy for a party B to generate a pair [KUb ,KRb]
• It is computationally easy for a sender A, knowing the public key and the message to be encrypted M, to generate
the corresponding ciphertext: C=EKUb(M).
• It is computationally easy for the receiver B to decrypt the resulting ciphertext using the private key to recover the
original message:
M = DKRb (C) = DKRb [E KUb (M)]
• It is computationally infeasible for an opponent, knowing the public key KUb, to determine the](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cns3rdunitppt-231104042120-e6a85a67/85/CNS-3RD-UNIT-PPT-pptx-6-320.jpg)