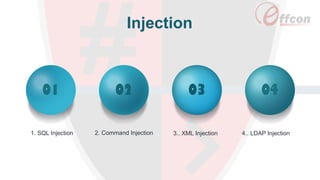
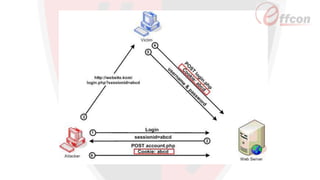
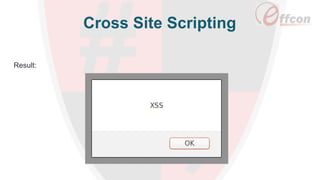
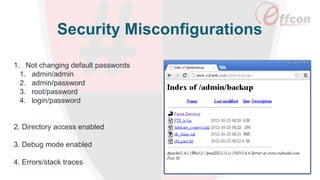
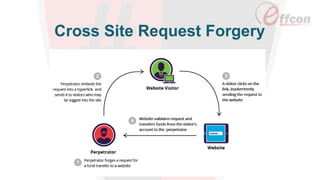
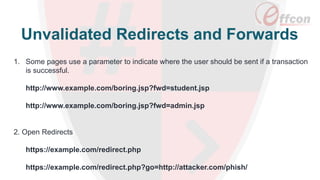
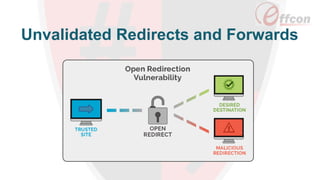
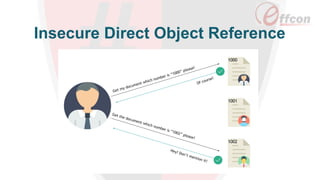
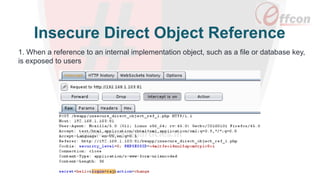
This document discusses the importance of web security and outlines the top 8 web security threats. It notes that there is a hack attack every 39 seconds and cybersecurity spending is expected to reach $6 trillion globally by 2021. The top threats discussed are injection, broken authentication, sensitive data exposure, cross-site scripting, security misconfigurations, cross-site request forgery, unvalidated redirects and forwards, and insecure direct object references. Throughout, it emphasizes the importance of security and provides examples of each threat.