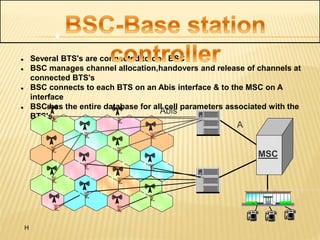
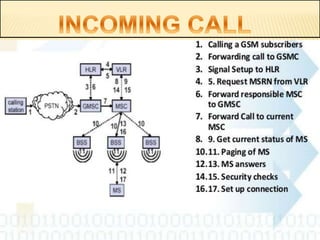
Aircel, India's fourth largest GSM mobile service provider, operates in several states with a focus on optimizing network performance and efficiency. The document outlines the GSM standard for mobile communication, detailing the network components, such as base transceiver stations (BTS) and mobile switching centers (MSC), and addresses health concerns related to electromagnetic radiation from mobile phones and base stations. It also presents calculations for effective isotropic radiated power (EIRP) and debunks myths regarding mobile phone radiation and its effects on health.