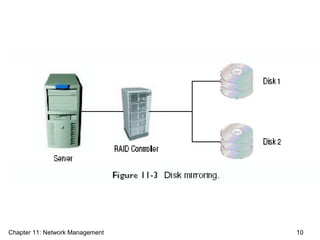
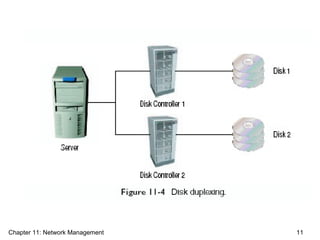
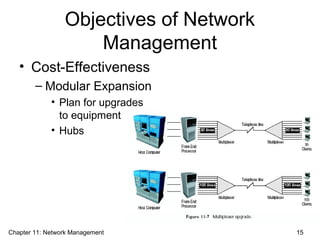
This document discusses network management. It describes the five levels of network management defined by the ISO, including performance, fault, configuration, accounting, and security management. The objectives of network management are to ensure user satisfaction through metrics like response time, availability, and reliability, as well as cost-effectiveness through prior planning. Network managers must oversee both voice and data networks as well as e-commerce. Various network monitoring tools and protocols are discussed.