The document discusses Linux network drivers and provides information about:
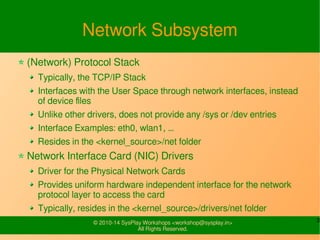
- The Linux network subsystem and protocol stack, typically using TCP/IP.
- Network interface card (NIC) drivers which provide a uniform interface for the network layer to access physical network cards.
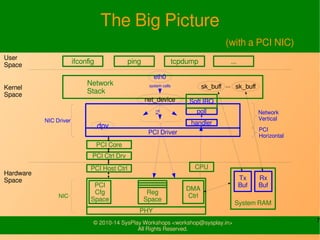
- Key data structures like struct sk_buff and struct net_device that network drivers interact with for packet handling and device operations.
- Functions for network device registration, open/close, interrupt handling, and flow control.
- Examples of simple network drivers and how to write one for a Realtek NIC.