The document discusses various aspects of file systems, including:
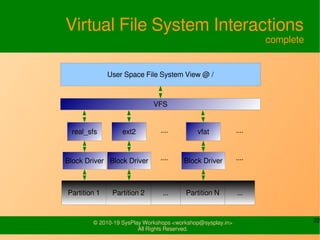
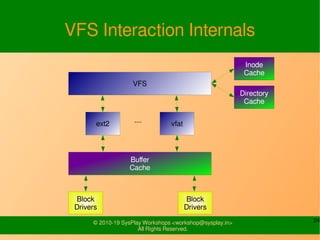
- It defines file systems as having three levels - the physical storage organization, kernel-level drivers, and the user-level view.
- It describes the three types of file systems - hardware/storage, kernel-level, and user-level file systems. It also discusses how they relate and the role of the mount function.
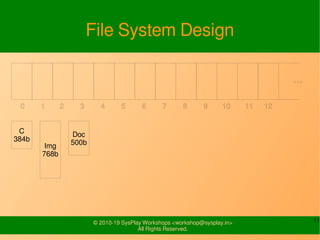
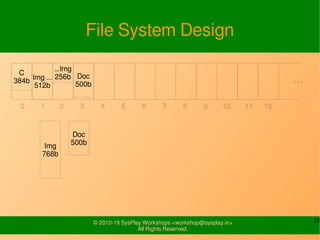
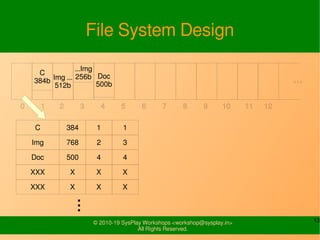
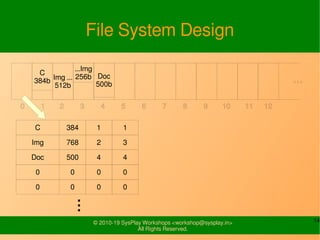
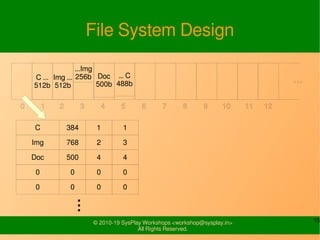
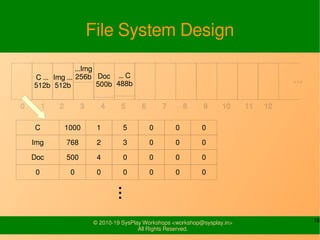
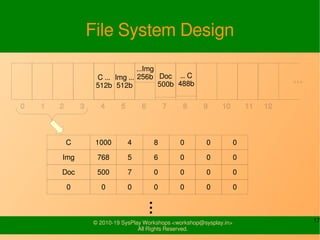
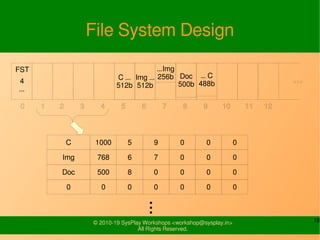
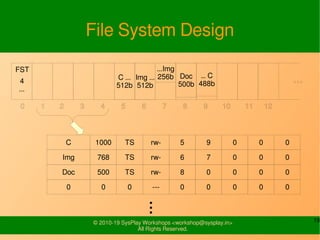
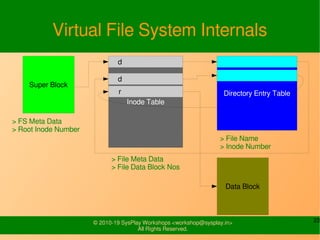
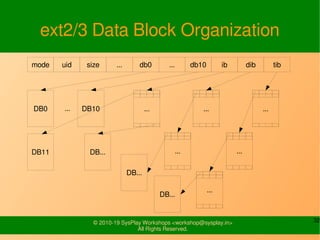
- It provides examples of designing a simple file system layout and implementing it using data structures like inodes and block pointers.



















![© 2010-19 SysPlay Workshops <workshop@sysplay.in>
All Rights Reserved.
File System Pieces – Set 1
Hardware Space
File System Design (Logic) – real_sfs_ds.h
File System Creator (Application) – format_real_sfs.c /
mkfs.sfs.c
Kernel Space
File System Decoder (Driver) – real_sfs_ops.[hc]
File System Translator (Driver) – real_sfs.c
File System Show-er (VFS)
User Space
File System Connector (mount)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/filesystemmodules-191226145828/85/File-System-Modules-34-320.jpg)
![© 2010-19 SysPlay Workshops <workshop@sysplay.in>
All Rights Reserved.
File System Pieces – Set 2
Hardware Space
File System Design (Logic) – ddk_fs_ds.h
File System Creator (Application) – mkfs.ddkfs.c
Kernel Space
File System Decoder (Driver) – ddk_fs_ops.[hc]
File System Translator (Driver) – ddk_fs.c
File System Show-er (VFS)
User Space
File System Connector (mount)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/filesystemmodules-191226145828/85/File-System-Modules-35-320.jpg)

